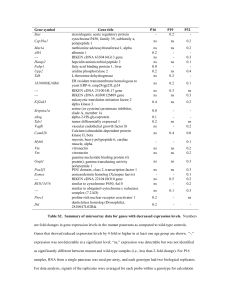
Table S2. Summary of microarray data for genes with decreased
... are fold changes in gene expression levels in the mutant pancreata as compared to wild-type controls. Genes that showed reduced expression levels by 4 fold or higher in at least one age group are shown. “-,” expression was not detectable at a significant level; “ns,” expression was detectable but wa ...
... are fold changes in gene expression levels in the mutant pancreata as compared to wild-type controls. Genes that showed reduced expression levels by 4 fold or higher in at least one age group are shown. “-,” expression was not detectable at a significant level; “ns,” expression was detectable but wa ...
Gene to protein
... • Made of proteins and RNA • Part of SPLICEOSOME (complex that edits pre-mRNA cuts out the introns and reattaches the remaining mRNA ALTERNATIVE RNA SPLICINGcan produce different proteins by editing mRNA in different ways EX: Immunoglobulins (antibodies) that match new antigens RIBOZYMES = RNA molec ...
... • Made of proteins and RNA • Part of SPLICEOSOME (complex that edits pre-mRNA cuts out the introns and reattaches the remaining mRNA ALTERNATIVE RNA SPLICINGcan produce different proteins by editing mRNA in different ways EX: Immunoglobulins (antibodies) that match new antigens RIBOZYMES = RNA molec ...
Ch 1617 Study Guide - Dublin City Schools
... • Made of proteins and RNA • Part of SPLICEOSOME (complex that edits pre-mRNA cuts out the introns and reattaches the remaining mRNA ALTERNATIVE RNA SPLICINGcan produce different proteins by editing mRNA in different ways EX: Immunoglobulins (antibodies) that match new antigens RIBOZYMES = RNA molec ...
... • Made of proteins and RNA • Part of SPLICEOSOME (complex that edits pre-mRNA cuts out the introns and reattaches the remaining mRNA ALTERNATIVE RNA SPLICINGcan produce different proteins by editing mRNA in different ways EX: Immunoglobulins (antibodies) that match new antigens RIBOZYMES = RNA molec ...
Lesson18_Cultivation of microorganism
... A suffix that means “the agent inhibits growth.” A fungistatic agent inhibits the growth of fungi, but doesn’t necessarily kill it. ...
... A suffix that means “the agent inhibits growth.” A fungistatic agent inhibits the growth of fungi, but doesn’t necessarily kill it. ...
Transcript
... a. Surface receptors can be involved in taking up molecules through endocytosis. LDL receptors bind LDL and take it into cell- basic endocytosis. b. Some are basic enzymes like kinases, which is a protein which adds a phosphate to something. A phosphatase is something that dephosphorylates a molecul ...
... a. Surface receptors can be involved in taking up molecules through endocytosis. LDL receptors bind LDL and take it into cell- basic endocytosis. b. Some are basic enzymes like kinases, which is a protein which adds a phosphate to something. A phosphatase is something that dephosphorylates a molecul ...
MBMB451A Section1 Fall 2008 KEY These questions may have
... sure to highlight the features of the DNA as well as the protein that are important in this intermolecular interaction. (7points) Keywords – DNA sequence recognition ( donor and acceptor sites in neucleotide base and proteins), alpha helix used to bind inside of the major groove and minor groove rec ...
... sure to highlight the features of the DNA as well as the protein that are important in this intermolecular interaction. (7points) Keywords – DNA sequence recognition ( donor and acceptor sites in neucleotide base and proteins), alpha helix used to bind inside of the major groove and minor groove rec ...
1 Confusion from last week: Purines and Pyrimidines
... their corresponding amino acids. One end has an anti-codon which binds to the mRNA. The tRNA codon sequence is the same as the gene sequence – mRNA is inverse of DNA, tRNA is inverse of mRNA – RNA, so U instead of T ...
... their corresponding amino acids. One end has an anti-codon which binds to the mRNA. The tRNA codon sequence is the same as the gene sequence – mRNA is inverse of DNA, tRNA is inverse of mRNA – RNA, so U instead of T ...
Gene Section BCL2L12 (BCL2-like 12 (proline-rich)) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... and encodes the full-length protein. The second splice variant lacks exon 3, which consists of 143 bp, thus resulting in no ORF. The third splice variant lacks 3 bp at the beginning of exon 3 and encodes a protein having one amino acid residue less than the full-lengh protein. ...
... and encodes the full-length protein. The second splice variant lacks exon 3, which consists of 143 bp, thus resulting in no ORF. The third splice variant lacks 3 bp at the beginning of exon 3 and encodes a protein having one amino acid residue less than the full-lengh protein. ...
Protein Structure - Laboratory of Molecular Modelling
... similar to those found in individual amino acids and small peptides (2) peptide bond – should be planer (3) overlaps – not permitted, pairs of atoms no closer than sum of their covalent radii (4) stabilization – have sterics that permit hydrogen bonding ...
... similar to those found in individual amino acids and small peptides (2) peptide bond – should be planer (3) overlaps – not permitted, pairs of atoms no closer than sum of their covalent radii (4) stabilization – have sterics that permit hydrogen bonding ...
Protein Structure
... similar to those found in individual amino acids and small peptides (2) peptide bond – should be planer (3) overlaps – not permitted, pairs of atoms no closer than sum of their covalent radii (4) stabilization – have sterics that permit hydrogen bonding ...
... similar to those found in individual amino acids and small peptides (2) peptide bond – should be planer (3) overlaps – not permitted, pairs of atoms no closer than sum of their covalent radii (4) stabilization – have sterics that permit hydrogen bonding ...
Pancreatin Select
... enzymatic output by the exocrine pancreas, an organ which is strained by modern diets high in processed foods and low in enzyme-rich raw and fermented foods. Diets high in sugars and starches similarly overstress the endocrine pancreas, which must constantly produce hormones needed to balance blood ...
... enzymatic output by the exocrine pancreas, an organ which is strained by modern diets high in processed foods and low in enzyme-rich raw and fermented foods. Diets high in sugars and starches similarly overstress the endocrine pancreas, which must constantly produce hormones needed to balance blood ...
Use only these to make sequential assignments
... 1. Identify resonances for each amino acid 2. Put amino acids in order ...
... 1. Identify resonances for each amino acid 2. Put amino acids in order ...
a Disulfide Bridge DataBase for the predictive analysis of cysteine
... experiments [2] showed that disulfide bridges can increase the thermodynamic stability of the native structure of proteins by reducing the number of unfolded conformations. Therefore, an exact prediction of disulfide connectivity can strongly reduce the conformational search space and increase the a ...
... experiments [2] showed that disulfide bridges can increase the thermodynamic stability of the native structure of proteins by reducing the number of unfolded conformations. Therefore, an exact prediction of disulfide connectivity can strongly reduce the conformational search space and increase the a ...
Leukaemia Section t(5;11)(q33;p13) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... Schrader JW. Distinct structural features of caprin-1 mediate its interaction with G3BP-1 and its induction of phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2alpha, entry to cytoplasmic stress granules, and selective interaction with a subset of mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Mar;27(6):232 ...
... Schrader JW. Distinct structural features of caprin-1 mediate its interaction with G3BP-1 and its induction of phosphorylation of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2alpha, entry to cytoplasmic stress granules, and selective interaction with a subset of mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 2007 Mar;27(6):232 ...
testing for organic macromolecules
... without double bonds. Unsaturated fatty acids contain double bonds within the carbon chain, which results in a bend of the chain. 3. Proteins Proteins are complex, specialized molecules composed of carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen and sometimes sulfur. The building blocks of proteins are amino aci ...
... without double bonds. Unsaturated fatty acids contain double bonds within the carbon chain, which results in a bend of the chain. 3. Proteins Proteins are complex, specialized molecules composed of carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen and sometimes sulfur. The building blocks of proteins are amino aci ...
Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins Dr AN Boa Section 1
... B = (Ala, 2×Lys, Phe, Pro, Ser, Tyr) C = (Arg, Gly, Met, Ser, Val) (v) ...
... B = (Ala, 2×Lys, Phe, Pro, Ser, Tyr) C = (Arg, Gly, Met, Ser, Val) (v) ...
Respiratory Substrates
... • Animals store glucose as glycogen, and plants as starch • Theoretical maximum energy yield for one mole of glucose is 2870 kJ • It takes 30.6 kJ to produce 1 mol ATP • Respiration of 1 mol glucose should produce nearly 94 mol ATP, but the actual yield is more like 30, as it has an efficiency of 32 ...
... • Animals store glucose as glycogen, and plants as starch • Theoretical maximum energy yield for one mole of glucose is 2870 kJ • It takes 30.6 kJ to produce 1 mol ATP • Respiration of 1 mol glucose should produce nearly 94 mol ATP, but the actual yield is more like 30, as it has an efficiency of 32 ...
The following equations and constants may be useful:
... a) the residual energy present in the reactants at equilibrium. b) the residual energy present in the products at equilibrium. c) the difference in the residual energy of reactants and products at equilibrium. d) The energy required to convert one mole of reactants to one mole of products. 5. Disulf ...
... a) the residual energy present in the reactants at equilibrium. b) the residual energy present in the products at equilibrium. c) the difference in the residual energy of reactants and products at equilibrium. d) The energy required to convert one mole of reactants to one mole of products. 5. Disulf ...
Amino Acids Worksheet and Problem Set
... fully protonated structure to a fully unprotonated structure. Chapter 3.4: Use Aspartic Acid and Leucine and form a peptide bond between them: Using the structure above show how the peptide bond can have resonance: Chapter 3.5: N/A Do not need to read ...
... fully protonated structure to a fully unprotonated structure. Chapter 3.4: Use Aspartic Acid and Leucine and form a peptide bond between them: Using the structure above show how the peptide bond can have resonance: Chapter 3.5: N/A Do not need to read ...
mid-term-exam-versio..
... Some of the vesicles produced by the Golgi are lysosomes, which are small spherical organelles that contains the cell’s digestive enzymes. ...
... Some of the vesicles produced by the Golgi are lysosomes, which are small spherical organelles that contains the cell’s digestive enzymes. ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.