chapt 3 The Molecules of Cells
... 3.12 A protein’s specific shape determines its function A polypeptide chain contains hundreds or thousands of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. The amino acid sequence causes the polypeptide to assume a particular shape. ...
... 3.12 A protein’s specific shape determines its function A polypeptide chain contains hundreds or thousands of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. The amino acid sequence causes the polypeptide to assume a particular shape. ...
Predicting Secondary Structures of Proteins
... substances are present, and then releases it, the protein immediately folds back to the same 3-D structure it had before. This folding process takes less than a second. Therefore, it seems that all the information necessary for the protein to achieve its “native structure” is contained in its amino ...
... substances are present, and then releases it, the protein immediately folds back to the same 3-D structure it had before. This folding process takes less than a second. Therefore, it seems that all the information necessary for the protein to achieve its “native structure” is contained in its amino ...
WATER SOLUBLE VITA
... NAD and NADP – coenzymes of many оxidoreductases (about 100) Take part in: -glycolisis -gluconeogenesis -PPC -FA synthesis and oxidation -AA deamination -Krebs cycle (3 enzymes) -ETC -nucleic acids formation NADP takes part in: -FA synthesis -cholesterol synthesis ...
... NAD and NADP – coenzymes of many оxidoreductases (about 100) Take part in: -glycolisis -gluconeogenesis -PPC -FA synthesis and oxidation -AA deamination -Krebs cycle (3 enzymes) -ETC -nucleic acids formation NADP takes part in: -FA synthesis -cholesterol synthesis ...
The relationship between amino acid sequences and protein folds.
... site and and intracellular recognition site for a GTP-binding protein. •! Single-transmembrane (1-TMS) catalytic receptors- contain a single transmembrane segment, an extracellular ligand domain and intracellular catalytic domain (tyrosine kinase or guanylyl cyclase) •! Oligomeric ion channels- cont ...
... site and and intracellular recognition site for a GTP-binding protein. •! Single-transmembrane (1-TMS) catalytic receptors- contain a single transmembrane segment, an extracellular ligand domain and intracellular catalytic domain (tyrosine kinase or guanylyl cyclase) •! Oligomeric ion channels- cont ...
Document
... • However, the immunomodulatory properties of biopeptides are seemed to be not appreciated. • This is perhaps due to the many challenges occurred during the practical application, due to the complexity of chemical reaction and mechanism effect resulting by the end of primary and secondary metabolite ...
... • However, the immunomodulatory properties of biopeptides are seemed to be not appreciated. • This is perhaps due to the many challenges occurred during the practical application, due to the complexity of chemical reaction and mechanism effect resulting by the end of primary and secondary metabolite ...
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
... Eukaryotes have only one release factor eRF which requires GTP termination of protein synthesis. It recognizes all the three stop codons. In eukaryotes the mRNA is synthesized in the nucleus, then processed, modified and passed on into the cytoplasm through nucleopores. The protein synthesis takes p ...
... Eukaryotes have only one release factor eRF which requires GTP termination of protein synthesis. It recognizes all the three stop codons. In eukaryotes the mRNA is synthesized in the nucleus, then processed, modified and passed on into the cytoplasm through nucleopores. The protein synthesis takes p ...
The world of proteases Diversity and function
... Different proteases result in different hydrolysis products Very specific protease ...
... Different proteases result in different hydrolysis products Very specific protease ...
Ch7 Enzymes II: Coenzymes, Regulation, Abzymes, and Ribozymes
... • Zymogen: – inactive precursor – Is cleaved at one or a few specific peptide bonds to produce the active form of the enzyme. ...
... • Zymogen: – inactive precursor – Is cleaved at one or a few specific peptide bonds to produce the active form of the enzyme. ...
Transcript - University of Idaho
... acids. The genetic code is said to be universal since it applies to ALL organisms. Note that most amino acids are encoded by more than one codon. However, every codon always encodes for only one amino acid; thus the genetic code is unambiguous. The first two letters for the codons of a particular am ...
... acids. The genetic code is said to be universal since it applies to ALL organisms. Note that most amino acids are encoded by more than one codon. However, every codon always encodes for only one amino acid; thus the genetic code is unambiguous. The first two letters for the codons of a particular am ...
Do Legume Storage Proteins Play a Role in
... effects seen with resistant seeds (Macedo et al., 1993). This finding prompted us to investigate why vicilins isolated from TVu 2027 seeds conferred resistance to infestation by C. maculatus. We found that neither the C. maculatus-resistant seeds or vicilins isolated from them had any effect on the ...
... effects seen with resistant seeds (Macedo et al., 1993). This finding prompted us to investigate why vicilins isolated from TVu 2027 seeds conferred resistance to infestation by C. maculatus. We found that neither the C. maculatus-resistant seeds or vicilins isolated from them had any effect on the ...
MPB IPG - E
... B) It states that all organisms are composed of cells. C) It states that all cells come from preexisting cells. D) It states that bacteria and other small organisms can arise spontaneously. E) It is accepted today by biologists as applying to virtually all forms of life. Which is NOT a reason for th ...
... B) It states that all organisms are composed of cells. C) It states that all cells come from preexisting cells. D) It states that bacteria and other small organisms can arise spontaneously. E) It is accepted today by biologists as applying to virtually all forms of life. Which is NOT a reason for th ...
REVIEW CHAPTER 4 and 5
... digest this Cellulose is made up of glucose rings in the ß (beta) form so every other glucose is upside down the respect to its neighbors; joined with 1,4 linkages; straight-never ...
... digest this Cellulose is made up of glucose rings in the ß (beta) form so every other glucose is upside down the respect to its neighbors; joined with 1,4 linkages; straight-never ...
The Body`s Fundamental Building Blocks
... important functions in the body including the regulation of muscle and hormone activity and the formation and maintenance of every tissue in the body (i.e., bone, ligaments, tendons, muscle). They play a major role in nearly every chemical process that affects both physical and mental function. Elev ...
... important functions in the body including the regulation of muscle and hormone activity and the formation and maintenance of every tissue in the body (i.e., bone, ligaments, tendons, muscle). They play a major role in nearly every chemical process that affects both physical and mental function. Elev ...
Transcription Translation
... Explain the process of transcription How eukaryotic cells modify RNA after transcription The steps of translation How point mutations change the amino acid ...
... Explain the process of transcription How eukaryotic cells modify RNA after transcription The steps of translation How point mutations change the amino acid ...
Caulobacter Export™ Manual
... Because RsaA is the protein that forms the S-layer it must be produced inside the cell and exported to the cell surface. Export is mediated by a secretion mechanism categorized as a Type I transporter. It is a bacterial secretion system that uses ATP to generate the energy needed for protein export ...
... Because RsaA is the protein that forms the S-layer it must be produced inside the cell and exported to the cell surface. Export is mediated by a secretion mechanism categorized as a Type I transporter. It is a bacterial secretion system that uses ATP to generate the energy needed for protein export ...
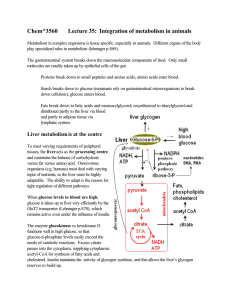
Chem*3560 Lecture 35: Integration of metabolism in animals
... input of nutrients, so the liver must be highly adaptable. The ability to adapt is the reason for tight regulation of different pathways. When glucose levels in blood are high, glucose is taken up in liver very efficiently by the GluT2 transporter (Lehninger p.870), which remains active even under t ...
... input of nutrients, so the liver must be highly adaptable. The ability to adapt is the reason for tight regulation of different pathways. When glucose levels in blood are high, glucose is taken up in liver very efficiently by the GluT2 transporter (Lehninger p.870), which remains active even under t ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.