Biochemistry – Problem Set 2 Problem Set 2
... Biochemistry – Problem Set 2 Problem Set 2 solution key ...
... Biochemistry – Problem Set 2 Problem Set 2 solution key ...
Information Extraction in Biology
... Anandamide induces vasodilation by activating vanilloid receptors. the activation of Rap1 by C3G the GTPase-activating protein rhoGAP the stress-activated group of MAP kinases ...
... Anandamide induces vasodilation by activating vanilloid receptors. the activation of Rap1 by C3G the GTPase-activating protein rhoGAP the stress-activated group of MAP kinases ...
Product Insert Sheet
... proteins, such as bone morphogenetic protein-4 (BMP4). By diffusing through extracellular matrices more efficiently than members of the TGF-beta superfamily, noggin may have a principal role in creating morphogenic gradients. Noggin appears to have pleiotropic effect, both early in development as we ...
... proteins, such as bone morphogenetic protein-4 (BMP4). By diffusing through extracellular matrices more efficiently than members of the TGF-beta superfamily, noggin may have a principal role in creating morphogenic gradients. Noggin appears to have pleiotropic effect, both early in development as we ...
Single-stranded DNA-binding Proteins
... The combination of electrostatic, hydrogen-bonding and stacking interactions from proteins to ssDNA forms the basis for ssDNA binding and specificity. Unfortunately, dsDNA, dsRNA and single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) share many of these properties. How does an ssDNA-binding protein exclude these competing ...
... The combination of electrostatic, hydrogen-bonding and stacking interactions from proteins to ssDNA forms the basis for ssDNA binding and specificity. Unfortunately, dsDNA, dsRNA and single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) share many of these properties. How does an ssDNA-binding protein exclude these competing ...
Bioenergetics
... Metabolic pathways are chains of reactions facilitated by enzymes in which the product of one reaction becomes the substrate for the next o Rate limiting enzymes are generally present at the start of a metabolic pathway and control the rate at which reactions occur In the case of ATP production, l ...
... Metabolic pathways are chains of reactions facilitated by enzymes in which the product of one reaction becomes the substrate for the next o Rate limiting enzymes are generally present at the start of a metabolic pathway and control the rate at which reactions occur In the case of ATP production, l ...
ANSWERS TO PROBLEMS
... tension of water at that point and the water film moves away. The area of the surface from which the water film moves away depends on how oily the finger is. 11. Wetting is a phenomenon which depends to a large extent on the difference between the adhesive force between a liquid and the surface in c ...
... tension of water at that point and the water film moves away. The area of the surface from which the water film moves away depends on how oily the finger is. 11. Wetting is a phenomenon which depends to a large extent on the difference between the adhesive force between a liquid and the surface in c ...
S1 Text Section A Annotation by structural analysis In case of aldose
... would probably remain conserved even if reactions from other pathways are included within the iAS142 network as they represent a tightly balanced subset which satisfies ATP and redox balance within different compartments and thereby maximizes the biomass. Reactions that form a part of this subnetwor ...
... would probably remain conserved even if reactions from other pathways are included within the iAS142 network as they represent a tightly balanced subset which satisfies ATP and redox balance within different compartments and thereby maximizes the biomass. Reactions that form a part of this subnetwor ...
... B15 (13 pts) The HIV reverse transcriptase (HIV-RT) is also a drug target for AIDS drugs. As with the HIV protease, mutations arise in this enzyme, generating HIV viruses that are resistant to existing drugs. Pharmaceutical companies would like to characterize these altered reverse transcriptases to ...
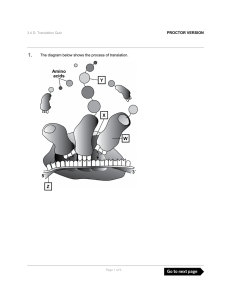
The diagram below shows the process of translation. PROCTOR
... (D) Structure Z is a growing polypeptide chain that is being synthesized by tRNA and rRNA, and that will be folded and moved to its final location in or out of the cell. Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that polypeptides are synthesized based on the interaction o ...
... (D) Structure Z is a growing polypeptide chain that is being synthesized by tRNA and rRNA, and that will be folded and moved to its final location in or out of the cell. Distractor Rationale: This answer suggests the student may understand that polypeptides are synthesized based on the interaction o ...
Tissue-Specific Protein Expression in Plant Mitochondria
... 1989). Although these studies reveal that isolated mitochondria from different tissues or genotypes vary in the complement of proteins they synthesize, no conclusions can be drawn concerning the possible physiological or biochemical roles these unidentified proteins may play. The alternative oxidase ...
... 1989). Although these studies reveal that isolated mitochondria from different tissues or genotypes vary in the complement of proteins they synthesize, no conclusions can be drawn concerning the possible physiological or biochemical roles these unidentified proteins may play. The alternative oxidase ...
Dietary protein for athletes - Inside Outside Wellness Center
... lower than that seen with lower-quality proteins. In addition, the intensity of the exercise performed by the subjects in studies in which protein requirements were elevated (Friedman and Lemon 1989; Lemon et al. 1992; Meredith et al. 1989; Tarnopolsky et al. 1988, 1992) was greater than that in stu ...
... lower than that seen with lower-quality proteins. In addition, the intensity of the exercise performed by the subjects in studies in which protein requirements were elevated (Friedman and Lemon 1989; Lemon et al. 1992; Meredith et al. 1989; Tarnopolsky et al. 1988, 1992) was greater than that in stu ...
Egg Components Dong Ahn Animal Science Department Iowa State University
... A ganglioside is a ceramide with a polar head group that is a complex oligosaccharide, including the acidic sugar derivative sialic acid. Cerebrosides and gangliosides, collectively called glycosphingolipids, are commonly found in the outer leaflet of the plasma membrane bilayer, with their sugar ch ...
... A ganglioside is a ceramide with a polar head group that is a complex oligosaccharide, including the acidic sugar derivative sialic acid. Cerebrosides and gangliosides, collectively called glycosphingolipids, are commonly found in the outer leaflet of the plasma membrane bilayer, with their sugar ch ...
ATPase - cloudfront.net
... to fold up into its particular shape Synthesis: accomplished through a process called translation. After DNA is transcribed into a messenger RNA molecule during transcription, the mRNA must be translated to produce a protein. http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/0/0f/Peptide_syn.png Eve ...
... to fold up into its particular shape Synthesis: accomplished through a process called translation. After DNA is transcribed into a messenger RNA molecule during transcription, the mRNA must be translated to produce a protein. http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/0/0f/Peptide_syn.png Eve ...
BIOANALYTICAL/CLINICAL ANALYSIS
... SOMOGI METHOD:STARCH + AMYLASE REDUCING SUGAR ADD FEHLINGS SOLUTION BLUE COLOR ...
... SOMOGI METHOD:STARCH + AMYLASE REDUCING SUGAR ADD FEHLINGS SOLUTION BLUE COLOR ...
Proteins and enzymes - Delivery guide
... clotting process. Students will have the opportunity to make molecular representations of key biochemicals to demonstrate their understanding of the basic structure of amino acids and polypeptides, to include levels of protein structure. They will also be expected to undertake practical work in aspe ...
... clotting process. Students will have the opportunity to make molecular representations of key biochemicals to demonstrate their understanding of the basic structure of amino acids and polypeptides, to include levels of protein structure. They will also be expected to undertake practical work in aspe ...
LIPIDS
... phosphate yields sphingomyelin while the addition of sugars yields cerebrosides and globosides. Those glycolipids that contain sialic acid are known as gangliosides. ...
... phosphate yields sphingomyelin while the addition of sugars yields cerebrosides and globosides. Those glycolipids that contain sialic acid are known as gangliosides. ...
Test 2
... specific acid or base catalysis, covalent catalysis, or metal ion catalysis. While this mechanism does not include any binding interactions, discuss how binding interactions also could be used by this enzyme to enhance the reaction rate. Lys 345 acts as a gneral base Glu 211 acts as a general acid 2 ...
... specific acid or base catalysis, covalent catalysis, or metal ion catalysis. While this mechanism does not include any binding interactions, discuss how binding interactions also could be used by this enzyme to enhance the reaction rate. Lys 345 acts as a gneral base Glu 211 acts as a general acid 2 ...
The potato tuber mitochondrial proteome
... Evaluation of the mitochondria proteome by transient fluorescence assay in tobacco epidermal cell ...
... Evaluation of the mitochondria proteome by transient fluorescence assay in tobacco epidermal cell ...
Catabolism
... • Metabolism may be divided into two major parts: catabolism and anabolism. • Catabolism: larger and more complex molecules are broken down into smaller, simpler molecules with the release of energy. • Anabolism: the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler ones with the input of energy. ...
... • Metabolism may be divided into two major parts: catabolism and anabolism. • Catabolism: larger and more complex molecules are broken down into smaller, simpler molecules with the release of energy. • Anabolism: the synthesis of complex molecules from simpler ones with the input of energy. ...
Proteins - The Open University
... Defence Antibodies (immunoglobulins) are proteins that recognise specific targets (usually proteins themselves). This facility is critical for an immune response. Transport Proteins are key molecules in the transport of substances both within a cell and to and from the cell. Storage A number of prot ...
... Defence Antibodies (immunoglobulins) are proteins that recognise specific targets (usually proteins themselves). This facility is critical for an immune response. Transport Proteins are key molecules in the transport of substances both within a cell and to and from the cell. Storage A number of prot ...
Akashi_Gojobori.PNAS02
... in the synthesis of the protein would render the substitution neutral in the broader sense of the organism’s integrated functioning. The substituted amino acid must be present within the cell in equivalent quantity compared with the original amino acid and, indeed, its synthesis or derivation from o ...
... in the synthesis of the protein would render the substitution neutral in the broader sense of the organism’s integrated functioning. The substituted amino acid must be present within the cell in equivalent quantity compared with the original amino acid and, indeed, its synthesis or derivation from o ...
File
... Dairy products such as milk contain a sugar called lactose. Lactose is a disaccharide (meaning “two sugars”) that is composed of the two simple sugars Glucose and Galactose. Some people are “lactose intolerant,” meaning that their digestive system cannot break down the Lactose sugar into these simpl ...
... Dairy products such as milk contain a sugar called lactose. Lactose is a disaccharide (meaning “two sugars”) that is composed of the two simple sugars Glucose and Galactose. Some people are “lactose intolerant,” meaning that their digestive system cannot break down the Lactose sugar into these simpl ...
Proteolysis
Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion. Low pH or high temperatures can also cause proteolysis non-enzymatically.Proteolysis in organisms serves many purposes; for example, digestive enzymes break down proteins in food to provide amino acids for the organism, while proteolytic processing of a polypeptide chain after its synthesis may be necessary for the production of an active protein. It is also important in the regulation of some physiological and cellular processes, as well as preventing the accumulation of unwanted or abnormal proteins in cells. Consequently, dis-regulation of proteolysis can cause diseases, and is used in some venoms to damage their prey.Proteolysis is important as an analytical tool for studying proteins in the laboratory, as well as industrially, for example in food processing and stain removal.