Macromolecule Review (PP)
... Function: Provide structure for tissues and organs, allow muscles to contract, transport oxygen, and make up enzymes which carry out chemical reactions. ...
... Function: Provide structure for tissues and organs, allow muscles to contract, transport oxygen, and make up enzymes which carry out chemical reactions. ...
Unit 1: The Chemistry of Life
... 3. Explain what is meant by dehydration synthesis. What is the opposite process called? How are both important to most ...
... 3. Explain what is meant by dehydration synthesis. What is the opposite process called? How are both important to most ...
Science Vol 315 26 January 2007
... ingle nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are small genetic changes found in both coding and noncoding regions of the genome. The genetic code is degenerate in that most amino acids are represented by more than one triplet of nucleotide bases (a codon). Such codons are considered synonymous. Many SNPs a ...
... ingle nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) are small genetic changes found in both coding and noncoding regions of the genome. The genetic code is degenerate in that most amino acids are represented by more than one triplet of nucleotide bases (a codon). Such codons are considered synonymous. Many SNPs a ...
Solutions to 7.014 Quiz I
... Phospholipids are amphipathic, the hydrocarbon tails are hydrophobic and cluster together to exclude water. The phosphate heads are hydrophilic and associate with the aqueous environment. ...
... Phospholipids are amphipathic, the hydrocarbon tails are hydrophobic and cluster together to exclude water. The phosphate heads are hydrophilic and associate with the aqueous environment. ...
Protein Activity Control
... It is synthesized as a single-chain polypeptide of approx. 150 kDa, subsequently cleaved to form a di-chain molecules, in which a single disulfide bond links the light (50 kDa) and heavy chains (100 kDa) ...
... It is synthesized as a single-chain polypeptide of approx. 150 kDa, subsequently cleaved to form a di-chain molecules, in which a single disulfide bond links the light (50 kDa) and heavy chains (100 kDa) ...
DNA - California State University, Stanislaus
... Proteins can form so many functions because of the great diversity of structures that can form: • How many different chains of just 6 amino acids can be formed? ...
... Proteins can form so many functions because of the great diversity of structures that can form: • How many different chains of just 6 amino acids can be formed? ...
1 Glycosylation and Protein Folding I. Introduction. As a translocated
... I. Introduction. As a translocated polypeptide emerges into the lumen of the ER, it is generally processed in three ways: 1) its signal sequence is cleaved by signal peptidase; 2) it is glycosylated; and 3) it must be helped to fold into the correct conformation. II. Signal peptidase. Cleavage of th ...
... I. Introduction. As a translocated polypeptide emerges into the lumen of the ER, it is generally processed in three ways: 1) its signal sequence is cleaved by signal peptidase; 2) it is glycosylated; and 3) it must be helped to fold into the correct conformation. II. Signal peptidase. Cleavage of th ...
Study Guide
... a calcium-dependent photoprotein, which emits light (luminescence). Thus, the Y axis of Figures 2A, 2B, 2C, 3A, and 3B show the amount of luminescence detected, indicating the extent to which a particular stimulus was received. Homology modeling. Solving the 3-dimensional structure of a new protei ...
... a calcium-dependent photoprotein, which emits light (luminescence). Thus, the Y axis of Figures 2A, 2B, 2C, 3A, and 3B show the amount of luminescence detected, indicating the extent to which a particular stimulus was received. Homology modeling. Solving the 3-dimensional structure of a new protei ...
The cost of life is energy.
... price” of living by CATALYZING (or helping) reactions they need to stay alive. These reactions are called the METABOLISM. • Enzymes work to SYNTHESIZE molecules and break them apart. ...
... price” of living by CATALYZING (or helping) reactions they need to stay alive. These reactions are called the METABOLISM. • Enzymes work to SYNTHESIZE molecules and break them apart. ...
Metal chelate chrom
... Metal-Chelate Affinity Chromatography (MCAC), also known as Immobilized Metal Affinity Chromatography (IMAC), was first successfully demonstrated in 1975 by Porath and collaborators for human serum proteins. ...
... Metal-Chelate Affinity Chromatography (MCAC), also known as Immobilized Metal Affinity Chromatography (IMAC), was first successfully demonstrated in 1975 by Porath and collaborators for human serum proteins. ...
bonds form when water is removed to hold acids together.
... Color code the amino acid on this worksheet (carbon-black, hydrogen-yellow, nitrogen-blue, and oxygen-red). Basic Structure of Amino acid ...
... Color code the amino acid on this worksheet (carbon-black, hydrogen-yellow, nitrogen-blue, and oxygen-red). Basic Structure of Amino acid ...
Pulsatílla praténsis
... Amino acids are one of the physiologically important groups of compounds, taking part in synthesis of specific tissue proteins, enzymes, nucleic acids, fats, hormones and other compounds necessary for living organisms. They are capable of maintaining normal function of organs and systems at extreme ...
... Amino acids are one of the physiologically important groups of compounds, taking part in synthesis of specific tissue proteins, enzymes, nucleic acids, fats, hormones and other compounds necessary for living organisms. They are capable of maintaining normal function of organs and systems at extreme ...
Name: Cell Biology Test #1: 50 points
... hormone such as insulin can change cellular function? Name and describe a hormone that does not require amplification and how it functions in this regard. (20-40 words with diagrams if this helps) Some hormones are unable to enter the cytosol and otherwise unable to modify the intracellular function ...
... hormone such as insulin can change cellular function? Name and describe a hormone that does not require amplification and how it functions in this regard. (20-40 words with diagrams if this helps) Some hormones are unable to enter the cytosol and otherwise unable to modify the intracellular function ...
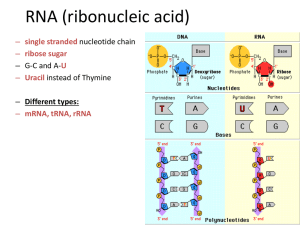
Central Dogma PPT
... Protein synthesis occurs in two major parts transcription and translation. 1. Transcription: Process in which DNA serves as a template to produce complementary mRNA 2. Translation: Process in which mRNA is used to link amino acids together to synthesize proteins. ...
... Protein synthesis occurs in two major parts transcription and translation. 1. Transcription: Process in which DNA serves as a template to produce complementary mRNA 2. Translation: Process in which mRNA is used to link amino acids together to synthesize proteins. ...
Chapter 4 Answers to Even Numbered Study Questions
... most archaea it is the protein layer, in which quaternary interactions among the individual protein molecules keep the layer intact. In other archaea, it is either the pseudomurein layer or the layer of polysaccharide. In bacteria and archaea that lack a defined cell envelope, it is the polysacchari ...
... most archaea it is the protein layer, in which quaternary interactions among the individual protein molecules keep the layer intact. In other archaea, it is either the pseudomurein layer or the layer of polysaccharide. In bacteria and archaea that lack a defined cell envelope, it is the polysacchari ...
HomologyModelingTutorial_Basic - APBioNet Training and Courses
... Proteins of biological interest with their orthologous proteins solved by X-ray crystallography or NMR can be modeled. Homology modeling is an important method used to predict the structures of membrane proteins, ion channels, transporters that are large and difficult to crystallize. ...
... Proteins of biological interest with their orthologous proteins solved by X-ray crystallography or NMR can be modeled. Homology modeling is an important method used to predict the structures of membrane proteins, ion channels, transporters that are large and difficult to crystallize. ...
Carbon Compounds
... 4. Amino Acid Structure - all 20 amino acids have same basic structure with one major difference, the R group ...
... 4. Amino Acid Structure - all 20 amino acids have same basic structure with one major difference, the R group ...
Nutrition & Metabolism
... Lipoprotein lipase in blood breaks down triglycerides: Fatty acids and glycerol can be taken up by ...
... Lipoprotein lipase in blood breaks down triglycerides: Fatty acids and glycerol can be taken up by ...
Protein structure prediction

Protein structure prediction is the prediction of the three-dimensional structure of a protein from its amino acid sequence — that is, the prediction of its folding and its secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure from its primary structure. Structure prediction is fundamentally different from the inverse problem of protein design. Protein structure prediction is one of the most important goals pursued by bioinformatics and theoretical chemistry; it is highly important in medicine (for example, in drug design) and biotechnology (for example, in the design of novel enzymes). Every two years, the performance of current methods is assessed in the CASP experiment (Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction). A continuous evaluation of protein structure prediction web servers is performed by the community project CAMEO3D.