Gene Section CLTCL1 (clathrin heavy polypeptide-like 1) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Other names: CLTCL; CLTD; CLH-22 Location: 22q11 Note: Must not be confused with CLTC (clathrin heavy chain gene), inasmuch as both are involved in translocations with ALK. ...
... Other names: CLTCL; CLTD; CLH-22 Location: 22q11 Note: Must not be confused with CLTC (clathrin heavy chain gene), inasmuch as both are involved in translocations with ALK. ...
NPN (Non-protein Nitrogen, Urea) Consumed by Horses
... Ruminant type animals such as cattle and sheep have microbial activity that takes place in the rumen of the animal before it reaches the stomach and small intestines. These animals are able to utilize ammonia from urea or other non-protein nitrogen sources to synthesize protein, provided that suffic ...
... Ruminant type animals such as cattle and sheep have microbial activity that takes place in the rumen of the animal before it reaches the stomach and small intestines. These animals are able to utilize ammonia from urea or other non-protein nitrogen sources to synthesize protein, provided that suffic ...
Document
... involved into formation of the whole organism body. •Motor proteins. These proteins can convert chemical energy into mechanical energy. actin and myosin are responsible for muscular motion. •Receptors These proteins are responsible for signal detection and translation into other type of signal. •Sig ...
... involved into formation of the whole organism body. •Motor proteins. These proteins can convert chemical energy into mechanical energy. actin and myosin are responsible for muscular motion. •Receptors These proteins are responsible for signal detection and translation into other type of signal. •Sig ...
Wheatgrass Chlorophyllcdmcoct022012
... anti-inflamatory, purification, and renewal. The anti inflammatory part of chlorophyll called Superoxide Dismutase plays a vital role in reducing inflammations throughout the body. The purification attributes stop the growth of bacteria in wounds, eliminates odors of the body, bad breath, and remove ...
... anti-inflamatory, purification, and renewal. The anti inflammatory part of chlorophyll called Superoxide Dismutase plays a vital role in reducing inflammations throughout the body. The purification attributes stop the growth of bacteria in wounds, eliminates odors of the body, bad breath, and remove ...
Protein Synthesis Notes - Hamilton Local Schools
... The “language” of mRNA instructions is called the ______________ _________. ...
... The “language” of mRNA instructions is called the ______________ _________. ...
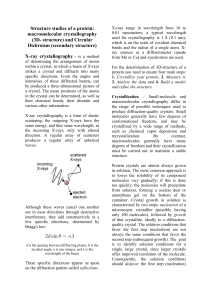
Structure studies of a protein: macromolecular crystallography (3D
... order of 100 nanoliters in volume. This means that 10-fold less protein is used perexperiment when compared to crystallization trials setup by hand. The growing crystals are generally held at a constant temperature and protected from shocks or vibrations that might disturb their crystallization. Con ...
... order of 100 nanoliters in volume. This means that 10-fold less protein is used perexperiment when compared to crystallization trials setup by hand. The growing crystals are generally held at a constant temperature and protected from shocks or vibrations that might disturb their crystallization. Con ...
Lecture 15, Feb 26
... A peptide bond between two amino acids consists of the four atoms shown at right. All 6 atoms shaded in grey (above) lie in the same rigid plane, with the double-bonded oxygen projecting in the opposite direction from the hydrogen atom that is bonded to the nitrogen atom. ...
... A peptide bond between two amino acids consists of the four atoms shown at right. All 6 atoms shaded in grey (above) lie in the same rigid plane, with the double-bonded oxygen projecting in the opposite direction from the hydrogen atom that is bonded to the nitrogen atom. ...
26.5 Cotobolism of smino ocids
... in the feces come mainly from indigestible materials. Children have a positive nitrogen balance-rhe excretion of lessnitrogen than is consumed.The nitrogen balance is positive becausechildren are growing and their cells are making new proteins and other nitrogen compounds. Several conditions result ...
... in the feces come mainly from indigestible materials. Children have a positive nitrogen balance-rhe excretion of lessnitrogen than is consumed.The nitrogen balance is positive becausechildren are growing and their cells are making new proteins and other nitrogen compounds. Several conditions result ...
File
... What a healthy diet must have: 1. Sufficient energy: If you don’t consume enough energy, you may end up using your body protein to stay alive as your fat and carbohydrate run out. 2. Correct proportion of carbohydrate, fat and protein. Not enough protein may result in stunted growth. 3. We need min ...
... What a healthy diet must have: 1. Sufficient energy: If you don’t consume enough energy, you may end up using your body protein to stay alive as your fat and carbohydrate run out. 2. Correct proportion of carbohydrate, fat and protein. Not enough protein may result in stunted growth. 3. We need min ...
PP - Chemistry Courses: About
... • DHF must be reduced to THF by DHF reductase • NADPH dependent • Chemotherapy target – DHF analogs such as methotrexate ...
... • DHF must be reduced to THF by DHF reductase • NADPH dependent • Chemotherapy target – DHF analogs such as methotrexate ...
PP076 Allergenicity assessment strategy for novel food proteins and
... the food market, since detailed guidance on how to assess the allergenic potential of novel foods is not available. At present, the approach relies mostly on the guidance of allergenicity assessment for genetically modified (GM) plant foods. However this guidance is difficult to interpret, not compl ...
... the food market, since detailed guidance on how to assess the allergenic potential of novel foods is not available. At present, the approach relies mostly on the guidance of allergenicity assessment for genetically modified (GM) plant foods. However this guidance is difficult to interpret, not compl ...
Chapter 1 Introduction
... genetic information). The 21st century is an era of life science. Lots of wonders are being created, and explosive information is being provided at an unprecedented speed. Biochemistry is a window opening to the world of life science. Thus, the knowledge of biochemistry which involves the study of c ...
... genetic information). The 21st century is an era of life science. Lots of wonders are being created, and explosive information is being provided at an unprecedented speed. Biochemistry is a window opening to the world of life science. Thus, the knowledge of biochemistry which involves the study of c ...
Document
... For proteins, a sequence motif is distinguished from a structural motif, a motif formed by the three dimensional arrangement of amino acids, which may not be adjacent Machine Learning & Bioinformatics ...
... For proteins, a sequence motif is distinguished from a structural motif, a motif formed by the three dimensional arrangement of amino acids, which may not be adjacent Machine Learning & Bioinformatics ...
What is bioinformatics? A proposed definition and overview of the field
... A concept that underpins most research methods in bioinformatics is that much of this data can be grouped together based on biologically meaningful similarities. For example, sequence segments are often repeated at different positions of genomic DNA (27). Genes can be clustered into those with parti ...
... A concept that underpins most research methods in bioinformatics is that much of this data can be grouped together based on biologically meaningful similarities. For example, sequence segments are often repeated at different positions of genomic DNA (27). Genes can be clustered into those with parti ...
10 CODON ANTI- CODON CYTOPLASM RIBOSOME tRNA AMINO
... Coded amino acids in correct order: MET (start) PHE ASP LEU 8. Define the term “mutation” in relation to DNA. A mutation is a change in the DNA sequence. This may result in a change to the mRNA sequence, which could cause a change in the protein and trait. 9. Describe a point mutation. Does it alway ...
... Coded amino acids in correct order: MET (start) PHE ASP LEU 8. Define the term “mutation” in relation to DNA. A mutation is a change in the DNA sequence. This may result in a change to the mRNA sequence, which could cause a change in the protein and trait. 9. Describe a point mutation. Does it alway ...
Ch. 2 Macromolecules
... You are in the fourth quarter of a basketball or football game and you are completely exhausted (and I mean gassed). You slam a bottle of Gatorade and you immediately begin to get your “second wind.” What macromolecule in Gatorade is responsible for this? Carbohydrates because they are the body’s p ...
... You are in the fourth quarter of a basketball or football game and you are completely exhausted (and I mean gassed). You slam a bottle of Gatorade and you immediately begin to get your “second wind.” What macromolecule in Gatorade is responsible for this? Carbohydrates because they are the body’s p ...
European Journal of Biochemistry 1999, 264, 833-839
... Bacteriocins are ribosomally synthesized polypeptides, produced by bacteria that inhibit the growth of other bacteria. Production of bacteriocins is widespread among lactic acid bacteria, a group of Gram-positive organisms used as starters in food fermentation. These compounds potentially fulfil the ...
... Bacteriocins are ribosomally synthesized polypeptides, produced by bacteria that inhibit the growth of other bacteria. Production of bacteriocins is widespread among lactic acid bacteria, a group of Gram-positive organisms used as starters in food fermentation. These compounds potentially fulfil the ...
Amino acids and protein (lec. 2%2c 2015)
... So, all amino acids (except glycine) are optically active because they have four different groups attached to α-carbon Optically active molecules means also they have two isomers ...
... So, all amino acids (except glycine) are optically active because they have four different groups attached to α-carbon Optically active molecules means also they have two isomers ...
Protein structure prediction

Protein structure prediction is the prediction of the three-dimensional structure of a protein from its amino acid sequence — that is, the prediction of its folding and its secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure from its primary structure. Structure prediction is fundamentally different from the inverse problem of protein design. Protein structure prediction is one of the most important goals pursued by bioinformatics and theoretical chemistry; it is highly important in medicine (for example, in drug design) and biotechnology (for example, in the design of novel enzymes). Every two years, the performance of current methods is assessed in the CASP experiment (Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction). A continuous evaluation of protein structure prediction web servers is performed by the community project CAMEO3D.