Surface chemistry and Catalysis
... Action • catalyst and reactants are in the same phase • reaction proceeds through an intermediate species with lower energy • there is usually more than one reaction step • transition metal ions are often involved - oxidation state changes ...
... Action • catalyst and reactants are in the same phase • reaction proceeds through an intermediate species with lower energy • there is usually more than one reaction step • transition metal ions are often involved - oxidation state changes ...
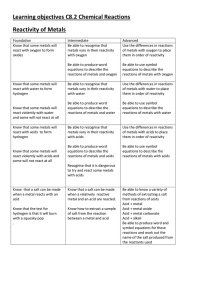
Learning objectives C8.2 Chemical Reactions Reactivity of Metals
... methods of extracting a salt from reactions of acids Acid + metal Acid + metal oxide Acid + metal carbonate Acid + alkali Be able to produce word and symbol equations for these reactions and work out the name of the salt produced from the reactants used ...
... methods of extracting a salt from reactions of acids Acid + metal Acid + metal oxide Acid + metal carbonate Acid + alkali Be able to produce word and symbol equations for these reactions and work out the name of the salt produced from the reactants used ...
Chemistry I Exams and Keys Corrected 2016 Season
... 18. Joseph Proust(1754 to 1826) was the chemist to first formally state that: Rejected: because simple memorization. Also, student may not have read about Proust. All full credit. A) When two elements combine with each other to form more than one compound, the weights of one element that combine wi ...
... 18. Joseph Proust(1754 to 1826) was the chemist to first formally state that: Rejected: because simple memorization. Also, student may not have read about Proust. All full credit. A) When two elements combine with each other to form more than one compound, the weights of one element that combine wi ...
Theoretical Competition - Austrian Chemistry Olympiad
... 5.2. Write down a balanced equation for the reaction of I- with H2O2! H2O2 + 2 H+ + 2 I- ⇌ 2 H2O + I2 5.3. Calculate the potential difference for the reaction in 5.2.. ΔEƟ = EƟ2 - EƟ1 = 1.763 – 0.535 = 1.228 V 5.4. Calculate the free standard enthalpy and the equilibrium constant for the reaction in ...
... 5.2. Write down a balanced equation for the reaction of I- with H2O2! H2O2 + 2 H+ + 2 I- ⇌ 2 H2O + I2 5.3. Calculate the potential difference for the reaction in 5.2.. ΔEƟ = EƟ2 - EƟ1 = 1.763 – 0.535 = 1.228 V 5.4. Calculate the free standard enthalpy and the equilibrium constant for the reaction in ...
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... These reactions will be further discussed in Chapter 8 2. Neutralization: The most important reaction of acids and bases is called neutralization. In these reactions an acid combines with a base to form a salt and water. For example: ...
... These reactions will be further discussed in Chapter 8 2. Neutralization: The most important reaction of acids and bases is called neutralization. In these reactions an acid combines with a base to form a salt and water. For example: ...
O usually has oxidation number of -2, except in peroxides where it is
... The sum of the oxidation numbers of the elements in a polyatomic ion must equal the ion charge. Consider these examples. If there are two poly atomic ions in a compound deal with them first. ...
... The sum of the oxidation numbers of the elements in a polyatomic ion must equal the ion charge. Consider these examples. If there are two poly atomic ions in a compound deal with them first. ...
Gas phase chemistry of neutral metal clusters
... for clusters with ionization energies larger than 10.5 eV is additionally possible, but should also not cause fragmentation of high ionization energy clusters. In general, for the majority of systems, the true neutral cluster distribution is obtained through 118 nm (or similar) single photon ionizat ...
... for clusters with ionization energies larger than 10.5 eV is additionally possible, but should also not cause fragmentation of high ionization energy clusters. In general, for the majority of systems, the true neutral cluster distribution is obtained through 118 nm (or similar) single photon ionizat ...
chemical reaction
... Factors Affecting Rates of Reactions, continued • Concentration In general, a high concentration of reactants causes a fast rate of reaction. Concentration is a measure of the amount of one substance when it is dissolved in another substance. • When concentration is high, there are many reactant par ...
... Factors Affecting Rates of Reactions, continued • Concentration In general, a high concentration of reactants causes a fast rate of reaction. Concentration is a measure of the amount of one substance when it is dissolved in another substance. • When concentration is high, there are many reactant par ...
Chemistry 2008–2012 Written examination – November Examination Specifications
... • Check that your name and student number as printed on your answer sheet for multiple-choice questions are correct, and sign your name in the space provided to verify this. • All written responses must be in English. At the end of the examination • Place the answer sheet for multiple-choice questio ...
... • Check that your name and student number as printed on your answer sheet for multiple-choice questions are correct, and sign your name in the space provided to verify this. • All written responses must be in English. At the end of the examination • Place the answer sheet for multiple-choice questio ...
Size-Selective Hydrogenation of Olefins by Dendrimer
... altering the periphery. Indeed, others have previously recognized that dendritic structures have the potential to function as selective moieties in catalytic processes. For example, dendrons grafted onto metalloporphyrins were shown to be selective for differentshaped ligands17 as well as for epoxid ...
... altering the periphery. Indeed, others have previously recognized that dendritic structures have the potential to function as selective moieties in catalytic processes. For example, dendrons grafted onto metalloporphyrins were shown to be selective for differentshaped ligands17 as well as for epoxid ...
Example: Writing a Thermochemical Equation
... heat. If you wanted the result in kilocalories, you would have to concert using the relationship 1 cal = 4.184 J. Lets look at one last example. Calculating the Heat of Reaction Using Stoichiometry ...
... heat. If you wanted the result in kilocalories, you would have to concert using the relationship 1 cal = 4.184 J. Lets look at one last example. Calculating the Heat of Reaction Using Stoichiometry ...
A reaction - 固体表面物理化学国家重点实验室
... concentration of one or more intermediate species. • In other cases the rate expression may be involve the concentration of some species which do not appear in the stoichiometric equation; such species are known as catalysts. In still other cases, the concentration of product molecules may appear in ...
... concentration of one or more intermediate species. • In other cases the rate expression may be involve the concentration of some species which do not appear in the stoichiometric equation; such species are known as catalysts. In still other cases, the concentration of product molecules may appear in ...
2015 Academic Challenge CHEMISTRY TEST – STATE
... The reaction will proceed from left to right. The reaction will proceed from right to left. Not enough information is available to make a prediction. The reaction is already at equilibrium. All of the above statements are correct. ...
... The reaction will proceed from left to right. The reaction will proceed from right to left. Not enough information is available to make a prediction. The reaction is already at equilibrium. All of the above statements are correct. ...
Review AGº = -RTlnKº Calculate the equilibrium constant Kc at 25 ºC
... Chemistry 103 Spring 2011 ...
... Chemistry 103 Spring 2011 ...
g moles molarity
... Example : The principal ingredient of certain commercial antacids is calcium carbonate, CaCO3. A student titrates an antacid tablet weighting 0.542 g with hydrochloric acid; the reaction is ...
... Example : The principal ingredient of certain commercial antacids is calcium carbonate, CaCO3. A student titrates an antacid tablet weighting 0.542 g with hydrochloric acid; the reaction is ...
Slide 1
... the proper movement of ions to maintain electrical neutrality. When Zn is oxidized some anions must enter (or cations must leave) the Zn half-cell to compensate for the added positive charge of the Zn2+ produced. Also when Ag+ reduced cations must enter (or anions must leave) the Ag half-cell. Let’s ...
... the proper movement of ions to maintain electrical neutrality. When Zn is oxidized some anions must enter (or cations must leave) the Zn half-cell to compensate for the added positive charge of the Zn2+ produced. Also when Ag+ reduced cations must enter (or anions must leave) the Ag half-cell. Let’s ...
Enzymes: “Helper” Protein molecules
... Each enzyme is the specific helper to a specific reaction each enzyme needs to be the right shape for the job enzymes are named for the reaction they help ...
... Each enzyme is the specific helper to a specific reaction each enzyme needs to be the right shape for the job enzymes are named for the reaction they help ...
Ch. 02 - HCC Learning Web
... • A molecule consists of two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds • A single covalent bond, or single bond, is the sharing of one pair of valence electrons • A double covalent bond, or double bond, is the sharing of two pairs of valence electrons ...
... • A molecule consists of two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds • A single covalent bond, or single bond, is the sharing of one pair of valence electrons • A double covalent bond, or double bond, is the sharing of two pairs of valence electrons ...
Unit 9 Chemical Equations and Reactions Balancing Equations Notes
... Single Replacement- a metal will _________________ a less active metal in an ionic compound OR a nonmetal will replace a less active nonmetal. Double Replacement- the metals in ionic compounds _________________ places. Combustion- an ____________________ compound containing carbon, hydrogen and some ...
... Single Replacement- a metal will _________________ a less active metal in an ionic compound OR a nonmetal will replace a less active nonmetal. Double Replacement- the metals in ionic compounds _________________ places. Combustion- an ____________________ compound containing carbon, hydrogen and some ...
Lecture two
... • if it isn’t favorable for an atom to gain or lose an electron - it will have to share it with another • covalent bond = bond in which atoms share electrons • atoms that like to form covalent bonds • oxygen • nitrogen • carbon ...
... • if it isn’t favorable for an atom to gain or lose an electron - it will have to share it with another • covalent bond = bond in which atoms share electrons • atoms that like to form covalent bonds • oxygen • nitrogen • carbon ...