Chapter12
... typically measured in grams or moles, but could be expressed in liters and molecules as well. We track the amounts of reactants and products using ratios of moles of each substance from the balanced chemical equation. 3. Interpreting Chemical Equations - Consider the Haber process which turns N2 fro ...
... typically measured in grams or moles, but could be expressed in liters and molecules as well. We track the amounts of reactants and products using ratios of moles of each substance from the balanced chemical equation. 3. Interpreting Chemical Equations - Consider the Haber process which turns N2 fro ...
- Vijay Education Academy
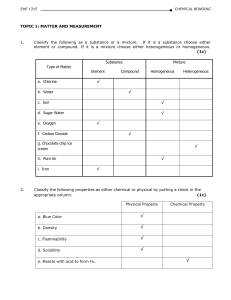
... (b) What method would you suggest for the separation of metal in the following mixtures? (i) Zinc and iron. (ii) Copper and magnesium ...
... (b) What method would you suggest for the separation of metal in the following mixtures? (i) Zinc and iron. (ii) Copper and magnesium ...
Photosynthesis in Hydrogen-Dominated Atmospheres
... photosynthesis in allowing Earth to develop an abundant biosphere [25,30,32] and its potential role in enabling complex life based on aerobic metabolism [2,30] have also been studied. Biosignatures generated from a photosynthetic biosphere like Earth’s, primarily oxygen and ozone, but also the oxyge ...
... photosynthesis in allowing Earth to develop an abundant biosphere [25,30,32] and its potential role in enabling complex life based on aerobic metabolism [2,30] have also been studied. Biosignatures generated from a photosynthetic biosphere like Earth’s, primarily oxygen and ozone, but also the oxyge ...
Student Review packet
... From the mechanism represented above, a student correctly deduces that the rate law for the reaction is rate = k[NO]2[H2]. The student then concludes that (1) the reaction is third-order and (2) the mechanism involves the simultaneous collision ...
... From the mechanism represented above, a student correctly deduces that the rate law for the reaction is rate = k[NO]2[H2]. The student then concludes that (1) the reaction is third-order and (2) the mechanism involves the simultaneous collision ...
CHEM181H1_06_2013_Y_P1
... The enthalpy for the formation of CO2(g) from C(s) is -393.5 kJ mol-1 ...
... The enthalpy for the formation of CO2(g) from C(s) is -393.5 kJ mol-1 ...
Ryoji Noyori - Nobel Lecture
... such as amino acids, tartaric and lactic acids, carbohydrates, terpenes, or alkaloids. Even though stereoselective conversion of a prochiral compound to a chiral product, namely, through an asymmetric reaction is the most attractive approach, practical access to pure enantiomers relied largely on bi ...
... such as amino acids, tartaric and lactic acids, carbohydrates, terpenes, or alkaloids. Even though stereoselective conversion of a prochiral compound to a chiral product, namely, through an asymmetric reaction is the most attractive approach, practical access to pure enantiomers relied largely on bi ...
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY, CFS, IIUM
... variety of matter is recognized is called a property. A characteristic that depends upon the amount of matter in the sample is called an extensive property. A characteristic that does not depend upon the amount of matter is called an intensive property. A characteristic that can be observed without ...
... variety of matter is recognized is called a property. A characteristic that depends upon the amount of matter in the sample is called an extensive property. A characteristic that does not depend upon the amount of matter is called an intensive property. A characteristic that can be observed without ...
chemistry writing team
... for n, l and ml provided their spins are opposite (ms is different). An orbital can have at the most two electrons if they have opporite spins. Hund’s Rule of maximum Multiplicity : ‘‘The electrons start pairing only when all the degenerate orbitals of a subshell are singly occupied with parrallel s ...
... for n, l and ml provided their spins are opposite (ms is different). An orbital can have at the most two electrons if they have opporite spins. Hund’s Rule of maximum Multiplicity : ‘‘The electrons start pairing only when all the degenerate orbitals of a subshell are singly occupied with parrallel s ...
Chemical Reactions
... In Chapter 1, we learned that chemistry is mainly concerned with two things: the structure of matter and the transformations of one form of matter to another. In Chapters 2 and 3, we discussed the first of these topics, and now we are ready to turn our attention to the second. In a chemical change, ...
... In Chapter 1, we learned that chemistry is mainly concerned with two things: the structure of matter and the transformations of one form of matter to another. In Chapters 2 and 3, we discussed the first of these topics, and now we are ready to turn our attention to the second. In a chemical change, ...
CBSE Living Science Chemistry Class X
... 1. Change in colour 2. Change in temperature 3. Evolution of a gas 4. Formation of a precipitate 5. Change of state. These changes indicate that chemical reactions have occurred. In our daily life, we find that there occurs a large variety of chemical reactions within our body and in our s ...
... 1. Change in colour 2. Change in temperature 3. Evolution of a gas 4. Formation of a precipitate 5. Change of state. These changes indicate that chemical reactions have occurred. In our daily life, we find that there occurs a large variety of chemical reactions within our body and in our s ...
SQA CfE Higher Chemistry Unit 1: Chemical Changes and Structure
... of successful collisions which occur. Collision theory can be stated thus: • particles must collide to react. • not all collisions are successful. • sufficient energy is needed. • orientation must be correct. In the picture shown above the single step formation of products in the reaction is a simpl ...
... of successful collisions which occur. Collision theory can be stated thus: • particles must collide to react. • not all collisions are successful. • sufficient energy is needed. • orientation must be correct. In the picture shown above the single step formation of products in the reaction is a simpl ...
Chapter 17: Reaction Energy and Reaction Kinetics
... If a large amount of energy is released when a compound is formed, the compound has a high negative heat of formation. Such compounds are very stable. Once they start, the reactions forming them usually proceed vigorously and without outside assistance. Elements in their standard states are defined ...
... If a large amount of energy is released when a compound is formed, the compound has a high negative heat of formation. Such compounds are very stable. Once they start, the reactions forming them usually proceed vigorously and without outside assistance. Elements in their standard states are defined ...
Entropy (Part I)
... • Entropy increases markedly at the temperature of a phase change. • Boiling corresponds to a much greater change in entropy than melting. • Entropy will increase when: liquids or solutions are formed from solids, gases are formed from solids or liquids, the number of gas molecules ...
... • Entropy increases markedly at the temperature of a phase change. • Boiling corresponds to a much greater change in entropy than melting. • Entropy will increase when: liquids or solutions are formed from solids, gases are formed from solids or liquids, the number of gas molecules ...
Syllabus - Chemistry
... The Chemistry of Excited State Molecules: Photochemical laws & quantum yield. Kinetics & quantum yield of photo-physical (radiative) and photo-chemical processes. Photochemical processes: primary, secondary, adiabatic & non- adiabatic. Properties of thexi states; Determination of dipole moments & ac ...
... The Chemistry of Excited State Molecules: Photochemical laws & quantum yield. Kinetics & quantum yield of photo-physical (radiative) and photo-chemical processes. Photochemical processes: primary, secondary, adiabatic & non- adiabatic. Properties of thexi states; Determination of dipole moments & ac ...
Learning Outcomes
... (b) describe the formation of ionic bonds between metals and non-metals, e.g. NaCl; MgCl2 ... 17 (c) state that ionic materials contain a giant lattice in which the ions are held by electrostatic attraction, e.g. NaCl (candidates will not be required to draw diagrams of ionic lattices) ........... 1 ...
... (b) describe the formation of ionic bonds between metals and non-metals, e.g. NaCl; MgCl2 ... 17 (c) state that ionic materials contain a giant lattice in which the ions are held by electrostatic attraction, e.g. NaCl (candidates will not be required to draw diagrams of ionic lattices) ........... 1 ...
Energy is the essence of chemistry It determines which reaction can
... • A negative ion is next to a positive ion. The strong attraction between these ions causes a high melting and boiling temperature. Many ionic solids are soluble in water An electrolyte solution. It conducts electricity Many are also sparingly soluble in water Calcium phosphate in bones is very spar ...
... • A negative ion is next to a positive ion. The strong attraction between these ions causes a high melting and boiling temperature. Many ionic solids are soluble in water An electrolyte solution. It conducts electricity Many are also sparingly soluble in water Calcium phosphate in bones is very spar ...
Answer
... • One of the most important reactions in living cells is the splitting of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and free phosphate (Pi): ...
... • One of the most important reactions in living cells is the splitting of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and free phosphate (Pi): ...
Osmium(VIII) Catalyzed Oxidation of 6-Aminopenicillanic Acid
... [6-8]. Copper(III) is involved in many biological electron transfer reactions [9]. When copper(III) periodate complex is the oxidant and multiple equilibria between different copper(III) species are involved, it would be interesting to know which of the species is the active oxidant. The reactions c ...
... [6-8]. Copper(III) is involved in many biological electron transfer reactions [9]. When copper(III) periodate complex is the oxidant and multiple equilibria between different copper(III) species are involved, it would be interesting to know which of the species is the active oxidant. The reactions c ...
Chapter 9 Reaction Energetics
... friend's account is the reference, ΔB = +$50 as money flowed into that account. Finally, if the bank is the reference, ΔB = 0 as no money entered or left the bank; the money you exchanged with your friend stayed in the bank. A thermodynamic problem would be set up the same way. Suppose that 50 J of ...
... friend's account is the reference, ΔB = +$50 as money flowed into that account. Finally, if the bank is the reference, ΔB = 0 as no money entered or left the bank; the money you exchanged with your friend stayed in the bank. A thermodynamic problem would be set up the same way. Suppose that 50 J of ...
Experimental Study of Closed System in the Chlorine Dioxide
... at 350 nm and 297 nm for triiodide ion. The curve of absorbance along with the reaction time can also be gotten at 460 nm for iodine. Figure 3 represents the absorbance changing with the reaction time at 297 nm for triiodide ion. When the mole ratio r is less than or equal to 3.00 (see curves 1 and ...
... at 350 nm and 297 nm for triiodide ion. The curve of absorbance along with the reaction time can also be gotten at 460 nm for iodine. Figure 3 represents the absorbance changing with the reaction time at 297 nm for triiodide ion. When the mole ratio r is less than or equal to 3.00 (see curves 1 and ...
CHAPTER 21 NONMETALLIC ELEMENTS AND THEIR COMPOUNDS
... The density of a gas depends on temperature, pressure, and the molar mass of the substance. When two gases are at the same pressure and temperature, the ratio of their densities should be the same as the ratio of their molar masses. The molar mass of ammonium chloride is 53.5 g/mol, and the ratio of ...
... The density of a gas depends on temperature, pressure, and the molar mass of the substance. When two gases are at the same pressure and temperature, the ratio of their densities should be the same as the ratio of their molar masses. The molar mass of ammonium chloride is 53.5 g/mol, and the ratio of ...
Part-1
... No. of octahendral voids present in a lattice = Number of close packed particles No. of tetrahedral voids present in a lattice = 2 × number of close packed particles In ionic solids, the larger ions (usually anions) form close packed structure and the smaller ions (usually cations) occupy voids. If ...
... No. of octahendral voids present in a lattice = Number of close packed particles No. of tetrahedral voids present in a lattice = 2 × number of close packed particles In ionic solids, the larger ions (usually anions) form close packed structure and the smaller ions (usually cations) occupy voids. If ...
CHAPTER I
... Electron spin. Three quantum numbers (n, ℓ , and mℓ ) allow us to define the orbital for an electron. To describe completely an electron in an atom with many electrons, however, we still need one more quantum number, the electron spin quantum number, ms. In approximately 1920, theoretical chemists r ...
... Electron spin. Three quantum numbers (n, ℓ , and mℓ ) allow us to define the orbital for an electron. To describe completely an electron in an atom with many electrons, however, we still need one more quantum number, the electron spin quantum number, ms. In approximately 1920, theoretical chemists r ...
5 organic chemistry: functional groups
... Root beer hasn’t tasted the same since the use of sassafras oil as a food additive was outlawed because sassafras oil is 80% safrole, which has been shown to cause cancer in rats and mice. Identify the functional groups in the structure of safrole. OOCH2 i O Safrole ...
... Root beer hasn’t tasted the same since the use of sassafras oil as a food additive was outlawed because sassafras oil is 80% safrole, which has been shown to cause cancer in rats and mice. Identify the functional groups in the structure of safrole. OOCH2 i O Safrole ...