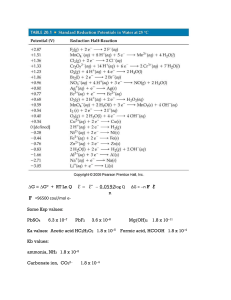
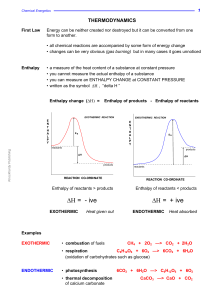
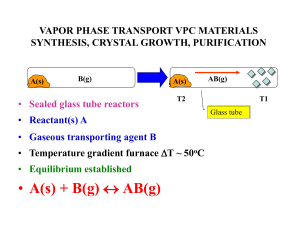
Reactions of Plutonium Dioxide with Water and Oxygen
... container. The oxide was outgassed to constant mass in vacuum at 400eC and was then exposed to water pressure at 15 tom as the temperature was increased stepwise from 25°C to 50, 100, 150, and 250°C over a period in excess of 110 hours. Water vapor was introduced into the evacuated balantxtchamber v ...
... container. The oxide was outgassed to constant mass in vacuum at 400eC and was then exposed to water pressure at 15 tom as the temperature was increased stepwise from 25°C to 50, 100, 150, and 250°C over a period in excess of 110 hours. Water vapor was introduced into the evacuated balantxtchamber v ...
15equil1pp
... “If the concentrations of all the substances present at equilibrium are raised to the power of the number of moles they appear in the equation, the product of the concentrations of the products divided by the product of the concentrations of the reactants is a constant, provided the temperature rema ...
... “If the concentrations of all the substances present at equilibrium are raised to the power of the number of moles they appear in the equation, the product of the concentrations of the products divided by the product of the concentrations of the reactants is a constant, provided the temperature rema ...
101
... elements, such as Cu and Zn, and with ions containing a single element, such as Cu2+ and Zn2+ . In these cases, you could use ionic charges to describe the transfer of electrons. However, many redox reactions involve reactants or products with covalent bonds, including elements that exist as covalen ...
... elements, such as Cu and Zn, and with ions containing a single element, such as Cu2+ and Zn2+ . In these cases, you could use ionic charges to describe the transfer of electrons. However, many redox reactions involve reactants or products with covalent bonds, including elements that exist as covalen ...
File
... A) Addition of HCl to the solution B) Addition of Pb(NO3)2 to the solution C) An increase in temperature D) All of these. ______2. AgCl would be LEAST soluble in a solution of 1.00 molar A) HNO3 B) AgNO3 C) HCl D) BaCl2 ______3. Methanol,CH3OH, is a liquid at room temperature, 298 K. For the phase c ...
... A) Addition of HCl to the solution B) Addition of Pb(NO3)2 to the solution C) An increase in temperature D) All of these. ______2. AgCl would be LEAST soluble in a solution of 1.00 molar A) HNO3 B) AgNO3 C) HCl D) BaCl2 ______3. Methanol,CH3OH, is a liquid at room temperature, 298 K. For the phase c ...
2(g)
... RXN Limitations • RXNS don’t communicate temp. and pressure • RXNS don’t communicate progress or process • RXNS don’t communicate measurable quantities of substances (can’t really weigh or calculate moles, atoms, molecules, ions, etc. without a calculation first) ...
... RXN Limitations • RXNS don’t communicate temp. and pressure • RXNS don’t communicate progress or process • RXNS don’t communicate measurable quantities of substances (can’t really weigh or calculate moles, atoms, molecules, ions, etc. without a calculation first) ...
Kinetics Presentation - Chemistrybyscott.org
... Also note that trans-butene is MORE STABLE than cis-butene by about 4 kJ/mol. ...
... Also note that trans-butene is MORE STABLE than cis-butene by about 4 kJ/mol. ...
m - DepositOnce
... generating further defects. This is done by doping with cations of lower valence. These substitute the cations in the lattice and introduce large amounts of point defects. An example for doping MO2 with a trivalent impurity is given in reaction 2-5: ...
... generating further defects. This is done by doping with cations of lower valence. These substitute the cations in the lattice and introduce large amounts of point defects. An example for doping MO2 with a trivalent impurity is given in reaction 2-5: ...
Η - Knockhardy
... 25cm3 of 2.0M HCl was added to 25cm3 of 2.0M NaOH in an insulated beaker. The initial temperature of both solutions was 20°C. The reaction mixture was stirred to ensure mixing and the highest temperature reached by the solution was 33°C. Calculate the Molar Enthalpy of Neutralisation. Temperature ri ...
... 25cm3 of 2.0M HCl was added to 25cm3 of 2.0M NaOH in an insulated beaker. The initial temperature of both solutions was 20°C. The reaction mixture was stirred to ensure mixing and the highest temperature reached by the solution was 33°C. Calculate the Molar Enthalpy of Neutralisation. Temperature ri ...
Mechanistic and Computational Studies of Ferroin, Simple Organic
... Before the year 1950, many chemists in their ‘right mind’ held the archaic belief that all chemical reactions proceed strictly from reactants to products, though some could be coaxed into reverse. What we now know colloquially as a potential energy surface was only visualized in more than two dimens ...
... Before the year 1950, many chemists in their ‘right mind’ held the archaic belief that all chemical reactions proceed strictly from reactants to products, though some could be coaxed into reverse. What we now know colloquially as a potential energy surface was only visualized in more than two dimens ...
pdf version - Joliet Junior College
... symbols alert the student to the following: Represents a key fact or other piece of information, such as the definitions of an element and a compound. Represents a useful trick the student will likely find useful, such as an 'EZ' way to convert between grams and moles for a substance Alerts the stud ...
... symbols alert the student to the following: Represents a key fact or other piece of information, such as the definitions of an element and a compound. Represents a useful trick the student will likely find useful, such as an 'EZ' way to convert between grams and moles for a substance Alerts the stud ...
Equilibrium
... ______________ (the process of dissolving) equals the rate of _______________]. At this instance, ___________ equilibrium has been established. ...
... ______________ (the process of dissolving) equals the rate of _______________]. At this instance, ___________ equilibrium has been established. ...
Kinetics Workbook - School District 67
... Even though there are more than four billion collisions per second between N and O the amount of product after a year is too small to detect. Using the collision theory, give two reasons why this reaction might be slow. i) ii) ...
... Even though there are more than four billion collisions per second between N and O the amount of product after a year is too small to detect. Using the collision theory, give two reasons why this reaction might be slow. i) ii) ...
Unit 8: Reactions
... When you write Cl2, that states there is ONE molecule of diatomic (2 atoms) chlorine. Diatomic molecules of (Br2, I2, N2, Cl2, H2, O2, & F2) exist whenever these elements are not in a compound with another element. In NaCl, there is one Cl-1 ion (due to Na’s+1 charge), but when Cl-1 is separated f ...
... When you write Cl2, that states there is ONE molecule of diatomic (2 atoms) chlorine. Diatomic molecules of (Br2, I2, N2, Cl2, H2, O2, & F2) exist whenever these elements are not in a compound with another element. In NaCl, there is one Cl-1 ion (due to Na’s+1 charge), but when Cl-1 is separated f ...
Stoichiometry Notes
... At STP/NTP one mole of any gas contains 22.4 L i.e. at 273 K and 1 atm pressure. Mole concept is based on balanced chemical reaction. If amounts of both reactants are given then find the limiting reagent. It is that reagent which is consumed completely in a irreversible chemical reaction. Class Disc ...
... At STP/NTP one mole of any gas contains 22.4 L i.e. at 273 K and 1 atm pressure. Mole concept is based on balanced chemical reaction. If amounts of both reactants are given then find the limiting reagent. It is that reagent which is consumed completely in a irreversible chemical reaction. Class Disc ...
406 K (English version)
... The teacher should take note of intermolecular forces such as hydrogen bonding and the van de Waals forces. The size of an atom, molecule or ion is not constant and depends on various factors such as the level to which the electron cloud in the particle is deformed through interaction. ...
... The teacher should take note of intermolecular forces such as hydrogen bonding and the van de Waals forces. The size of an atom, molecule or ion is not constant and depends on various factors such as the level to which the electron cloud in the particle is deformed through interaction. ...
Chapter 3 Stoichiometry STOICHIOMETRY: The chemical arithmetic
... With a 50 % Yield, How many moles of NH3 are produced from (a) 3 grams of H2 and ½ mole of N2? ½ mole = (½ mole)x(17 g/mole) grams of NH3 (b) 3 grams of H2 and 28 grams of N2? ...
... With a 50 % Yield, How many moles of NH3 are produced from (a) 3 grams of H2 and ½ mole of N2? ½ mole = (½ mole)x(17 g/mole) grams of NH3 (b) 3 grams of H2 and 28 grams of N2? ...
organonitrogen compounds i. amines
... There is, though, a major difference in the way that amines and alcohols behave toward oxidizing agents. Amines generally show more complex behavior on oxidation because, as we shall see, nitrogen has a larger number of stable ...
... There is, though, a major difference in the way that amines and alcohols behave toward oxidizing agents. Amines generally show more complex behavior on oxidation because, as we shall see, nitrogen has a larger number of stable ...
Topic 9 Oxidation and Reduction Answers - slider-dpchemistry-11
... Rule/s: Three rules are used here. Firstly, hydrogen always has an oxidation of +1 (except in combination with reactive metals such as Na when it is -1). Secondly, oxygen always has an oxidation state of –2 (except in H2O2 where it is -1). These known values are used first. Finally, as all these mol ...
... Rule/s: Three rules are used here. Firstly, hydrogen always has an oxidation of +1 (except in combination with reactive metals such as Na when it is -1). Secondly, oxygen always has an oxidation state of –2 (except in H2O2 where it is -1). These known values are used first. Finally, as all these mol ...
Answers - Pearson-Global
... impression often given at GCSE, such compounds are very common – although in the great majority of cases, there are more than 8 electrons around one atom rather than fewer. Students might ask why it doesn’t form ionic bonds. The amount of energy needed to remove 3 electrons so close to the boron nuc ...
... impression often given at GCSE, such compounds are very common – although in the great majority of cases, there are more than 8 electrons around one atom rather than fewer. Students might ask why it doesn’t form ionic bonds. The amount of energy needed to remove 3 electrons so close to the boron nuc ...
Collected Essays chapter 13 answers
... (c) In a different experiment, NH3 gas and H2S gas are introduced into an empty 1.00-liter vessel at 25°C. The initial partial pressure of each gas is 0.500 atmosphere. Calculate the number of moles of solid NH4HS that is present when equilibrium is established. 6.95 x 10-3 moles 1981 - #9c & d PCl5 ...
... (c) In a different experiment, NH3 gas and H2S gas are introduced into an empty 1.00-liter vessel at 25°C. The initial partial pressure of each gas is 0.500 atmosphere. Calculate the number of moles of solid NH4HS that is present when equilibrium is established. 6.95 x 10-3 moles 1981 - #9c & d PCl5 ...
Full-Text PDF
... All these over potential values are maintained on the lower side to minimize the band gap energy. The oxygen over potential control is slightly difficult than the other factors. In electrolytic oxygen evolution on metals, at first chemisorbed water molecule reacts with a hole (h+ ) and generate HO• ...
... All these over potential values are maintained on the lower side to minimize the band gap energy. The oxygen over potential control is slightly difficult than the other factors. In electrolytic oxygen evolution on metals, at first chemisorbed water molecule reacts with a hole (h+ ) and generate HO• ...
Chapter 1 – Reaction Kinetics Answer Key
... 3. The concentrations of pure solids and liquids are fixed. That is they do not change (appreciably for the liquid if it is the solvent and at all for the solid) during a chemical reaction. ...
... 3. The concentrations of pure solids and liquids are fixed. That is they do not change (appreciably for the liquid if it is the solvent and at all for the solid) during a chemical reaction. ...
COMPOUNDS OF CARBON CONTAINING NITROGEN
... (v) Reaction with nitrous acid : Primary aromatic amines react with nitrous acid to give diazonium salts and this reaction is known as diazotisation. Nitrous acid is an unstable compound and can not be stored, so it is prepared during the reaction by mixing sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid. The ...
... (v) Reaction with nitrous acid : Primary aromatic amines react with nitrous acid to give diazonium salts and this reaction is known as diazotisation. Nitrous acid is an unstable compound and can not be stored, so it is prepared during the reaction by mixing sodium nitrite and hydrochloric acid. The ...