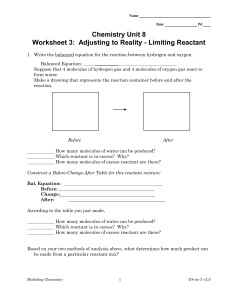
CO Oxidation on Palladium. 2. A Combined
... The temperature dependence of the COz formation rate on a Pd( 111) catalyst was studied in the temperature range of 470600Kusing a C 0 / 0 2 = 2/ 1reactant gas mixture a t a total pressure of 1.5 Torr. The total pressure change (APT)during the course of reaction is a very convenient and reliable way ...
... The temperature dependence of the COz formation rate on a Pd( 111) catalyst was studied in the temperature range of 470600Kusing a C 0 / 0 2 = 2/ 1reactant gas mixture a t a total pressure of 1.5 Torr. The total pressure change (APT)during the course of reaction is a very convenient and reliable way ...
[A], [B], [C], [D] - Wits Structural Chemistry
... For this system to be at equilibrium when [Cl-] is added, the [Pb2+] decreases (reverse reaction). ...
... For this system to be at equilibrium when [Cl-] is added, the [Pb2+] decreases (reverse reaction). ...
Chemical Reactions and Energy
... II. Two Laws of Thermodynamics • Increased disorder (entropy) is offset by biological processes that maintain order. • Living systems do not violate the _2nd Law (States that entropy increases with time) • How is order maintained? • By coupling (stacking) processes that increase entropy with those ...
... II. Two Laws of Thermodynamics • Increased disorder (entropy) is offset by biological processes that maintain order. • Living systems do not violate the _2nd Law (States that entropy increases with time) • How is order maintained? • By coupling (stacking) processes that increase entropy with those ...
MS PowerPoint - Catalysis Eprints database
... Point of the catalyst that facilitates strong interaction with reactant Number of molecules reacting per active site per second ...
... Point of the catalyst that facilitates strong interaction with reactant Number of molecules reacting per active site per second ...
Energetics of the primary electron transfer reaction revealed by
... The solution of the molecular structure of photosynthetic reaction centers [ l-31 provides detailed information on the organization of this pigmentprotein complex, in which a series of light-induced electron transfer steps initiates bacterial photosynthesis. The dynamics of this process has been inv ...
... The solution of the molecular structure of photosynthetic reaction centers [ l-31 provides detailed information on the organization of this pigmentprotein complex, in which a series of light-induced electron transfer steps initiates bacterial photosynthesis. The dynamics of this process has been inv ...
Experimental and Computational Evidence of Metal‑O2 Activation
... upon exposure to the H2O2 product of enzyme turnover. Previous works have neglected this reaction and assumed that neither CoII nor CuII undergoes a change in redox state during enzyme catalysis.32 The Ered in eq 2 may involve complex internal redox chemistry in certain copper amine oxidases,33−36 w ...
... upon exposure to the H2O2 product of enzyme turnover. Previous works have neglected this reaction and assumed that neither CoII nor CuII undergoes a change in redox state during enzyme catalysis.32 The Ered in eq 2 may involve complex internal redox chemistry in certain copper amine oxidases,33−36 w ...
File
... Sketching and evaluation of potential energy profiles in determining whether reactants or products are more stable and if the reaction is exothermic or endothermic ...
... Sketching and evaluation of potential energy profiles in determining whether reactants or products are more stable and if the reaction is exothermic or endothermic ...
Chemistry COS 2011-2012
... Science Course of Study TOPIC: Kinetic Theory: Solids, Liquids and Gases CONTENT STATEMENT Atoms and molecules are constantly in motion, as a substance changes phase, the movement of the atoms or molecules that make up that substance also changes. ...
... Science Course of Study TOPIC: Kinetic Theory: Solids, Liquids and Gases CONTENT STATEMENT Atoms and molecules are constantly in motion, as a substance changes phase, the movement of the atoms or molecules that make up that substance also changes. ...
i principi di base - Structural Biology
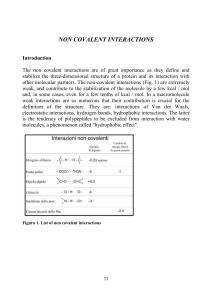
... The dipole-dipole interaction depends on the orientation of a dipole over the other (parallel, linear, opposite) and is maximum when the two dipoles are linear or opposed. The analysis of a molecule such as HCl (Fig. 4) allows us to understand what is a dipole moment. The distance between the H and ...
... The dipole-dipole interaction depends on the orientation of a dipole over the other (parallel, linear, opposite) and is maximum when the two dipoles are linear or opposed. The analysis of a molecule such as HCl (Fig. 4) allows us to understand what is a dipole moment. The distance between the H and ...
Kinetics
... o If the reaction is zero order, changing the concentration has no effect on rate o If the reaction is first order, doubling the concentration will double the rate( change is directly proportional) What if concentration is halved? o If the reaction is second order, doubling the concentration will re ...
... o If the reaction is zero order, changing the concentration has no effect on rate o If the reaction is first order, doubling the concentration will double the rate( change is directly proportional) What if concentration is halved? o If the reaction is second order, doubling the concentration will re ...
A reaction - 固体表面物理化学国家重点实验室
... • Since Ea is a positive energy quantity, the majority of reactions have k increasing with temperature. • For some reactions, however, the rate decreases with increasing temperature, implying a negative activation energy. Such reactions are generally complex, involving the formation of a weakly bou ...
... • Since Ea is a positive energy quantity, the majority of reactions have k increasing with temperature. • For some reactions, however, the rate decreases with increasing temperature, implying a negative activation energy. Such reactions are generally complex, involving the formation of a weakly bou ...
Enzyme catalysis

Enzyme catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction by the active site of a protein. The protein catalyst (enzyme) may be part of a multi-subunit complex, and/or may transiently or permanently associate with a Cofactor (e.g. adenosine triphosphate). Catalysis of biochemical reactions in the cell is vital due to the very low reaction rates of the uncatalysed reactions. A key driver of protein evolution is the optimization of such catalytic activities via protein dynamics.The mechanism of enzyme catalysis is similar in principle to other types of chemical catalysis. By providing an alternative reaction route the enzyme reduces the energy required to reach the highest energy transition state of the reaction. The reduction of activation energy (Ea) increases the amount of reactant molecules that achieve a sufficient level of energy, such that they reach the activation energy and form the product. As with other catalysts, the enzyme is not consumed during the reaction (as a substrate is) but is recycled such that a single enzyme performs many rounds of catalysis.





![[A], [B], [C], [D] - Wits Structural Chemistry](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000095863_1-918f0427052f54159a7c908528a2e159-300x300.png)