notes - Austin Community College
... a. Affects the entire brain and is caused by the swirling or twisting movement of the brain within the cranium. b. This category includes concussion and diffuse axonal injury. c. Concussion (p. 1377 box at bottom) 1) Temporary axonal injury that results in an interruption of brain function. 2) Concu ...
... a. Affects the entire brain and is caused by the swirling or twisting movement of the brain within the cranium. b. This category includes concussion and diffuse axonal injury. c. Concussion (p. 1377 box at bottom) 1) Temporary axonal injury that results in an interruption of brain function. 2) Concu ...
Samantha Zarati - A critical review of computational neurological models
... the total input of one neuron by checking whether any presynaptic neurons have spiked (this can be made even more efficient to reduce the number of unnecessary operations); or one can parallelize over synapses, which particularly reduces the number of unnecessary operations with sparse firing, and c ...
... the total input of one neuron by checking whether any presynaptic neurons have spiked (this can be made even more efficient to reduce the number of unnecessary operations); or one can parallelize over synapses, which particularly reduces the number of unnecessary operations with sparse firing, and c ...
The Nervous System and Senses
... Uses reflected light • The eye is covered with a protective layer called the cornea • Muscles around the iris (the colored portion) control the size of the pupil (the black circle), controlling how much light enters the eye • From the pupil, light passes through a lens, which focuses light on the ba ...
... Uses reflected light • The eye is covered with a protective layer called the cornea • Muscles around the iris (the colored portion) control the size of the pupil (the black circle), controlling how much light enters the eye • From the pupil, light passes through a lens, which focuses light on the ba ...
endocrine system
... inner white stuff—axons linking parts of the brain. 180+ billion glial cells, which feed and protect neurons and assist neural transmission. ...
... inner white stuff—axons linking parts of the brain. 180+ billion glial cells, which feed and protect neurons and assist neural transmission. ...
The Nervous System
... • Impulse goes from neuronal axon to another neuron or a receptor – This junction called ---synapse – neurotransmitters ...
... • Impulse goes from neuronal axon to another neuron or a receptor – This junction called ---synapse – neurotransmitters ...
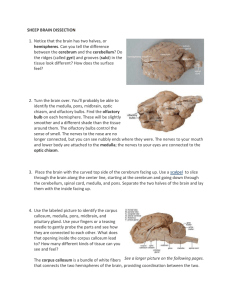
Sheep Brain Dissection Instructions
... pituitary gland. Use your fingers or a teasing needle to gently probe the parts and see how they are connected to each other. What does that opening inside the corpus callosum lead to? How many different kinds of tissue can you see and feel? The corpus callosum is a bundle of white fibers See a larg ...
... pituitary gland. Use your fingers or a teasing needle to gently probe the parts and see how they are connected to each other. What does that opening inside the corpus callosum lead to? How many different kinds of tissue can you see and feel? The corpus callosum is a bundle of white fibers See a larg ...
Crux-Final_Demo_Slideshow
... The long-term objective of this system is to enable any scientist in an executive role (program officers, journal editors, foundation executives) to do more than address the question: ‘were the goals of the project fulfilled?’ We want to provide data management, sharing and analysis so that these in ...
... The long-term objective of this system is to enable any scientist in an executive role (program officers, journal editors, foundation executives) to do more than address the question: ‘were the goals of the project fulfilled?’ We want to provide data management, sharing and analysis so that these in ...
(Grades K-12) Create a model of the brain by using clay, Playdough
... activities and resources. It is our hope that families will use these resources as a springboard for further discussions and activities. Before delving into the book, we will start by sharing some very basic information about the human brain. Building Background: The Human Brain Most of what we know ...
... activities and resources. It is our hope that families will use these resources as a springboard for further discussions and activities. Before delving into the book, we will start by sharing some very basic information about the human brain. Building Background: The Human Brain Most of what we know ...
Biological Basis of behavior
... found themselves unable to name objects that were processed by the right side of the brain, but were able to name objects that were processed by the left-side of the brain. Based on this information, Sperry suggested that language was controlled by the left-side of the brain. The Endocrine System: ...
... found themselves unable to name objects that were processed by the right side of the brain, but were able to name objects that were processed by the left-side of the brain. Based on this information, Sperry suggested that language was controlled by the left-side of the brain. The Endocrine System: ...
Central Nervous System
... 2. The circadian clock: it shifts forwards (in the day) during the teenage years. 3. It’s like a car trying to run on an empty tank. 4. Your mood, your ability to think and your ability to perform and react appropriately. 5. Rapid Eye Movement. Dreaming and learning happens during this time. 6. Whet ...
... 2. The circadian clock: it shifts forwards (in the day) during the teenage years. 3. It’s like a car trying to run on an empty tank. 4. Your mood, your ability to think and your ability to perform and react appropriately. 5. Rapid Eye Movement. Dreaming and learning happens during this time. 6. Whet ...
document
... I) NERVOUS SYSTEM = Master control and communication system of the body. This system works with the ENDOCRINE system to maintain and regulate body HOMEOSTASIS (balance). NERVOUS SYSTEM – Fast action, uses electrical impulses. Changes by this system tend to be fast but temporary. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM – ...
... I) NERVOUS SYSTEM = Master control and communication system of the body. This system works with the ENDOCRINE system to maintain and regulate body HOMEOSTASIS (balance). NERVOUS SYSTEM – Fast action, uses electrical impulses. Changes by this system tend to be fast but temporary. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM – ...
The Cerebral Cortex
... how the cerebral cortex has developed around and above more primitive brain structures. ...
... how the cerebral cortex has developed around and above more primitive brain structures. ...
psych mod 4 terms
... 4. Fragile X Syndrome- cause by a defect in the X chromosome. This defect can result in physical changes, such as a relatively large head with protruding ears, as well as mild to profound levels of mental retardation. 5. Theory of Evolution- says that different species arose from common ancestor and ...
... 4. Fragile X Syndrome- cause by a defect in the X chromosome. This defect can result in physical changes, such as a relatively large head with protruding ears, as well as mild to profound levels of mental retardation. 5. Theory of Evolution- says that different species arose from common ancestor and ...
CNS
... Provides a pathway for communication between muscles and gland and the brain. Integration of automatic, protective reflexes ...
... Provides a pathway for communication between muscles and gland and the brain. Integration of automatic, protective reflexes ...
Philosophy and the Brain
... • “I beseech you tell me how the soul of man (since it is but a thinking substance) can determine the spirits of the body to produce voluntary actions” ...
... • “I beseech you tell me how the soul of man (since it is but a thinking substance) can determine the spirits of the body to produce voluntary actions” ...
Statistical Learning for Resting-State fMRI: Successes and Challenges
... While data-driven methods such as ICA are often called model-free, they rely on the following simple multivariate decomposition model of the signal: Y = U V + N, where Y ∈ Rn×p are the fMRI data: n observations of images with p voxels, U ∈ Rn×k and V ∈ Rk×p are respectively k time series and k spati ...
... While data-driven methods such as ICA are often called model-free, they rely on the following simple multivariate decomposition model of the signal: Y = U V + N, where Y ∈ Rn×p are the fMRI data: n observations of images with p voxels, U ∈ Rn×k and V ∈ Rk×p are respectively k time series and k spati ...
Document
... inner white stuff—axons linking parts of the brain. 180+ billion glial cells, which feed and protect neurons and assist neural transmission. ...
... inner white stuff—axons linking parts of the brain. 180+ billion glial cells, which feed and protect neurons and assist neural transmission. ...
2
... inner white stuff—axons linking parts of the brain. 180+ billion glial cells, which feed and protect neurons and assist neural transmission. ...
... inner white stuff—axons linking parts of the brain. 180+ billion glial cells, which feed and protect neurons and assist neural transmission. ...
brain and cranial nerves
... --they are concerned with the reception and interpretation of sensory impulses. --Sensory areas are: Primary somatosensory area. Primary visual area. Primary auditory area. Primary gustatory area. ii. Motor areas: --control and govern muscular movements --areas are: primary motor area. Broca’s speec ...
... --they are concerned with the reception and interpretation of sensory impulses. --Sensory areas are: Primary somatosensory area. Primary visual area. Primary auditory area. Primary gustatory area. ii. Motor areas: --control and govern muscular movements --areas are: primary motor area. Broca’s speec ...
Neuron Note #3 - WordPress.com
... accident that caused severe nerve damage in her right hand, preventing her from fully moving it or detecting pressure in her fingertips. The branch of the nervous system that she has most likely damaged is the: a) b) c) d) e) ...
... accident that caused severe nerve damage in her right hand, preventing her from fully moving it or detecting pressure in her fingertips. The branch of the nervous system that she has most likely damaged is the: a) b) c) d) e) ...
Article Analysis Form for Hock: Forty Studies that Changed Psychology
... just indicate the variable or variables being measured if it is a descriptive or correlational research design. IV = Type of environment (1) Standard Laboratory, (2) Enriched Environment, (3) Impoverished Environment. DV = Brain Development—The rats’ brains were measured, weighed, and analyzed to de ...
... just indicate the variable or variables being measured if it is a descriptive or correlational research design. IV = Type of environment (1) Standard Laboratory, (2) Enriched Environment, (3) Impoverished Environment. DV = Brain Development—The rats’ brains were measured, weighed, and analyzed to de ...
Chapter Summary Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception • Sensation
... When sounds enter the ear, they move the ear drum, which sets in motion the ossicles. The last of these, the stirrup, vibrates the oval window, setting into motion fluid in the cochlea. Hair cells on the basilar membrane in the cochlea transduce movements along the basilar membrane into neural signa ...
... When sounds enter the ear, they move the ear drum, which sets in motion the ossicles. The last of these, the stirrup, vibrates the oval window, setting into motion fluid in the cochlea. Hair cells on the basilar membrane in the cochlea transduce movements along the basilar membrane into neural signa ...
Biomedical Sciences Option
... breadth to introduce the student to a wide range of disciplines, but is flexible enough so that students can focus, in their last two years, on areas of specific interest. Students interested in a career in a health science profession should consult the Health Professions Advising Office for informa ...
... breadth to introduce the student to a wide range of disciplines, but is flexible enough so that students can focus, in their last two years, on areas of specific interest. Students interested in a career in a health science profession should consult the Health Professions Advising Office for informa ...