Chapter 3 - Victoria College
... makes smooth/controlled movements • Ataxia = loss of muscle coordination due to trauma/disease – unable to coordinate movement w/ sense of body position – altered speech patterns – XS alcohol can cause ataxia also (slurred speech/decreased breathing rate) ...
... makes smooth/controlled movements • Ataxia = loss of muscle coordination due to trauma/disease – unable to coordinate movement w/ sense of body position – altered speech patterns – XS alcohol can cause ataxia also (slurred speech/decreased breathing rate) ...
L03 Brain Script Addendum
... other areas of the brain including the hypothalamus, hippocampus, thalamus, and the cerebral cortex. We know that the amygdala is important for emotions, especially fear. This has been examined in an experiment wherein cats had their amygdala electrically stimulated which resulted in them arching th ...
... other areas of the brain including the hypothalamus, hippocampus, thalamus, and the cerebral cortex. We know that the amygdala is important for emotions, especially fear. This has been examined in an experiment wherein cats had their amygdala electrically stimulated which resulted in them arching th ...
Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves
... • The two cerebral hemispheres share many functions • Each hemisphere also performs unique functions • Functional specialization of each hemisphere is more pronounced in men • Females generally have larger connections between 2 sides ...
... • The two cerebral hemispheres share many functions • Each hemisphere also performs unique functions • Functional specialization of each hemisphere is more pronounced in men • Females generally have larger connections between 2 sides ...
doc - Shoreline Community College
... 37. The ______________ system consists of several glands that are located throughout the body. This system communicates information by secreting ___________ into the blood stream. 38. What are the respective general functions of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems? 39. According to l ...
... 37. The ______________ system consists of several glands that are located throughout the body. This system communicates information by secreting ___________ into the blood stream. 38. What are the respective general functions of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems? 39. According to l ...
ANPS 019 Beneyto-Santonja 10-24
... o Relays sensory information to thalamus and to other portions of the brain stem o Autonomic centers for regulation of visceral function (cardiovascular, respiratory, and digestive system activities) Cerebellum o Coordinates complex somatic motor patterns o Adjusts output of other somatic motor ce ...
... o Relays sensory information to thalamus and to other portions of the brain stem o Autonomic centers for regulation of visceral function (cardiovascular, respiratory, and digestive system activities) Cerebellum o Coordinates complex somatic motor patterns o Adjusts output of other somatic motor ce ...
Oct2011_Computers_Brains_Extra_Mural
... Artificial Neural Networks Artificial neural networks emulate threshold behaviour, simulate co-operative phenomenon by a network of 'simple' switches and are used in a variety of applications, like banking, currency trading, robotics, and experimental and animal psychology studies. These information ...
... Artificial Neural Networks Artificial neural networks emulate threshold behaviour, simulate co-operative phenomenon by a network of 'simple' switches and are used in a variety of applications, like banking, currency trading, robotics, and experimental and animal psychology studies. These information ...
Brain Anatomy - Southwest High School
... • Occipital lobe: in the back of the brain and it is the vision center • Frontal lobe: The front of the brain. This is what makes you you. This is where you interpret and control emotions, make decisions and carry out plans. In the back of the frontal lobe, you work the voluntary muscles. • Parietal ...
... • Occipital lobe: in the back of the brain and it is the vision center • Frontal lobe: The front of the brain. This is what makes you you. This is where you interpret and control emotions, make decisions and carry out plans. In the back of the frontal lobe, you work the voluntary muscles. • Parietal ...
Nervous System Guided Notes
... Following a stroke, a person develops the symptoms listed below. In each case, which part of the brain was injured? ...
... Following a stroke, a person develops the symptoms listed below. In each case, which part of the brain was injured? ...
A nerve cell
... Anatomy, Institute of Basic Medical Sciences & Centre for Molecular Biology and Neuroscience ...
... Anatomy, Institute of Basic Medical Sciences & Centre for Molecular Biology and Neuroscience ...
Chapter 40
... b) Long-term memory involves encoding information and then consolidating, a process that depends on the hippocampus and involves the expression of genes c) Memory circuits are formed throughout the brain d) No particular area can be labeled as the site of memory, rather memories may be stored in var ...
... b) Long-term memory involves encoding information and then consolidating, a process that depends on the hippocampus and involves the expression of genes c) Memory circuits are formed throughout the brain d) No particular area can be labeled as the site of memory, rather memories may be stored in var ...
The Body and the Brain neurons first
... The Testes produce testosterone and small amounts or estrogen and progesterone in males. It is responsible for pushing boys through puberty so that they are ready to reproduce. The ovaries produce estrogen and progesterone and small amounts of testosterone in women. Again, the ovaries prepare women ...
... The Testes produce testosterone and small amounts or estrogen and progesterone in males. It is responsible for pushing boys through puberty so that they are ready to reproduce. The ovaries produce estrogen and progesterone and small amounts of testosterone in women. Again, the ovaries prepare women ...
The Body and the Brain neurons first
... The Testes produce testosterone and small amounts or estrogen and progesterone in males. It is responsible for pushing boys through puberty so that they are ready to reproduce. The ovaries produce estrogen and progesterone and small amounts of testosterone in women. Again, the ovaries prepare women ...
... The Testes produce testosterone and small amounts or estrogen and progesterone in males. It is responsible for pushing boys through puberty so that they are ready to reproduce. The ovaries produce estrogen and progesterone and small amounts of testosterone in women. Again, the ovaries prepare women ...
The Nervous System
... Connects brain + Spinal cord to the rest of the body 12 pairs of cranial nerves-from your brain 31 pairs of spinal nerves—from your spinal cord Made up of sensory and motor neurons Can have several impulses going at the same time ...
... Connects brain + Spinal cord to the rest of the body 12 pairs of cranial nerves-from your brain 31 pairs of spinal nerves—from your spinal cord Made up of sensory and motor neurons Can have several impulses going at the same time ...
Wilfred`s talk
... • Use of Opal WS wrapper for rapid application deployment – Possible to add data type mapping – Leverage semantic web technology for interoperability ...
... • Use of Opal WS wrapper for rapid application deployment – Possible to add data type mapping – Leverage semantic web technology for interoperability ...
File
... occurs, physical changes take place in the brain at a neuronal level • The most prominent change is at the synapse • Learning changes the strength of connections between neurons at the synapse • Learning can cause new synapses to form • Neurotransmitter forms the basis of these connections ...
... occurs, physical changes take place in the brain at a neuronal level • The most prominent change is at the synapse • Learning changes the strength of connections between neurons at the synapse • Learning can cause new synapses to form • Neurotransmitter forms the basis of these connections ...
Neural Networks A Statistical View
... Data mining Natural language recognition OCR including Kanji ...
... Data mining Natural language recognition OCR including Kanji ...
Studying the Well-Trained Mind
... very strong emphasis on refining the attention, enhancing attention skills, and developing very sophisticated means for investigating the nature of the mind from a firstBuddhist monks and Western scientists are comparing notes on how the mind person perspective,” says Buddhist scholar works and coll ...
... very strong emphasis on refining the attention, enhancing attention skills, and developing very sophisticated means for investigating the nature of the mind from a firstBuddhist monks and Western scientists are comparing notes on how the mind person perspective,” says Buddhist scholar works and coll ...
Overview of brain anatomy
... Memory is a complex process that includes three phases: encoding (deciding what information is important), storing, and recalling. Different areas of the brain are involved in memory depending on the type of memory. Short-term memory, also called working memory, occurs in the prefrontal cortex. It s ...
... Memory is a complex process that includes three phases: encoding (deciding what information is important), storing, and recalling. Different areas of the brain are involved in memory depending on the type of memory. Short-term memory, also called working memory, occurs in the prefrontal cortex. It s ...
Brain Anatomy Overview
... Memory is a complex process that includes three phases: encoding (deciding what information is important), storing, and recalling. Different areas of the brain are involved in memory depending on the type of memory. Short-term memory, also called working memory, occurs in the prefrontal cortex. It s ...
... Memory is a complex process that includes three phases: encoding (deciding what information is important), storing, and recalling. Different areas of the brain are involved in memory depending on the type of memory. Short-term memory, also called working memory, occurs in the prefrontal cortex. It s ...
The Body and the Brain
... The Testes produce testosterone and small amounts or estrogen and progesterone in males. It is responsible for pushing boys through puberty so that they are ready to reproduce. The ovaries produce estrogen and progesterone and small amounts of testosterone in women. Again, the ovaries prepare women ...
... The Testes produce testosterone and small amounts or estrogen and progesterone in males. It is responsible for pushing boys through puberty so that they are ready to reproduce. The ovaries produce estrogen and progesterone and small amounts of testosterone in women. Again, the ovaries prepare women ...
The Structure Of The Brain - The Life Management Alliance
... syndrome all the way over to negatively affecting one’s physical health (e.g. the immune system is thrown out of whack). Any one thing that occurs and is seen by the brain elicits an incredibly complex set of reactions from all the brains – and we need to gain more and more control over them so that ...
... syndrome all the way over to negatively affecting one’s physical health (e.g. the immune system is thrown out of whack). Any one thing that occurs and is seen by the brain elicits an incredibly complex set of reactions from all the brains – and we need to gain more and more control over them so that ...
QMIN: Introduction
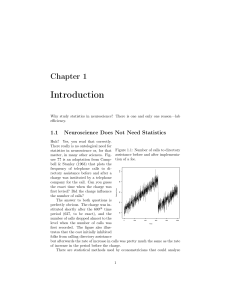
... If a neuroscientist were interested in whether a treatment alters a response, then several methods are available to assess the hypothesis without using statistics. If the response could be measured over many time points, then a plot like the one in Figure ?? be constructed for every animal tested. T ...
... If a neuroscientist were interested in whether a treatment alters a response, then several methods are available to assess the hypothesis without using statistics. If the response could be measured over many time points, then a plot like the one in Figure ?? be constructed for every animal tested. T ...
the brain - Mayfield City Schools
... The main function is to wake you up. This is made of neurons networking together through different parts of the brain to alert and “wake up” higher parts of the brain. A secondary function is that it helps decide what we should pay attention to. ...
... The main function is to wake you up. This is made of neurons networking together through different parts of the brain to alert and “wake up” higher parts of the brain. A secondary function is that it helps decide what we should pay attention to. ...
Spinal Cord - Northside Middle School
... poles of the cell soma. Can you identify the structure curving into the field from the upper left? It is a blood capillary with several astrocyte processes attached ...
... poles of the cell soma. Can you identify the structure curving into the field from the upper left? It is a blood capillary with several astrocyte processes attached ...