nervous system
... Body: Contains nucleus, control center of the cell. Regulates production of protein within the cell. Neurons ...
... Body: Contains nucleus, control center of the cell. Regulates production of protein within the cell. Neurons ...
Unit 3A Notes
... pressure, blood sugar, and slows digestion. It gets you ready for action. 2. The parasympathetic nervous system kicks in when the “crisis” is over – it calms you down by doing the opposite things. It helps you chill out. 6. The central nervous system 1. Our bodies are amazing, but without the brain, ...
... pressure, blood sugar, and slows digestion. It gets you ready for action. 2. The parasympathetic nervous system kicks in when the “crisis” is over – it calms you down by doing the opposite things. It helps you chill out. 6. The central nervous system 1. Our bodies are amazing, but without the brain, ...
action potential
... •Action potentials are based on the movements of ions between the outside and inside of the cell •When an action potential occurs, a molecular message is sent to neighboring neurons ...
... •Action potentials are based on the movements of ions between the outside and inside of the cell •When an action potential occurs, a molecular message is sent to neighboring neurons ...
Ch 10 Brain Damage & Neuroplasticity (pt2)
... Regrowth of damaged neurons Not as successful in mammals as in lower ...
... Regrowth of damaged neurons Not as successful in mammals as in lower ...
vocabulary worksheet
... 27. The _______________ is the outermost covering of the brain consisting of densely packed neurons, responsible for higher thought processes and interpretation of sensory input. 28. The thick band of neurons that connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres is called the _________________ _____ ...
... 27. The _______________ is the outermost covering of the brain consisting of densely packed neurons, responsible for higher thought processes and interpretation of sensory input. 28. The thick band of neurons that connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres is called the _________________ _____ ...
Exam 3 Review KEY
... body which is the most common type. 10) The bipolar neuron has one dendrite and one axon with the cell body in between, these are rare and found only in specialized sense organs. 11) Most synapses, are chemical synapses in which the neurotransmitter is secreted by the pre-synaptic cell which then di ...
... body which is the most common type. 10) The bipolar neuron has one dendrite and one axon with the cell body in between, these are rare and found only in specialized sense organs. 11) Most synapses, are chemical synapses in which the neurotransmitter is secreted by the pre-synaptic cell which then di ...
Central Nervous System Control of Energy and Glucose
... became the first FDA-approved diet pill in the last 15 years. However, the cellular mechanisms for the beneficial metabolic effects of serotonin have remained largely unknown. In the first part of my talk, I will discuss my recent findings that 5-HT2CRs excite arcuate POMC neurons via the activation ...
... became the first FDA-approved diet pill in the last 15 years. However, the cellular mechanisms for the beneficial metabolic effects of serotonin have remained largely unknown. In the first part of my talk, I will discuss my recent findings that 5-HT2CRs excite arcuate POMC neurons via the activation ...
Module 04
... Tens of billions of neurons, each communicating with thousands of other neurons, yield an everchanging wiring diagram. The complexity of the central nervous system allows or makes possible (enables) our thinking, feeling, and behavior. In this way, it is similar to the electronic circuitry (wiring ...
... Tens of billions of neurons, each communicating with thousands of other neurons, yield an everchanging wiring diagram. The complexity of the central nervous system allows or makes possible (enables) our thinking, feeling, and behavior. In this way, it is similar to the electronic circuitry (wiring ...
The biological basis of behavior
... • Synapse: area composed of the axon terminal of one neuron, the synaptic space, and the dendrite or cell body of the next neuron. • Neurotransmitters: chemicals released by the synaptic vesicles that travel across the synaptic space and affect adjacent neurons. • Synaptic vesicles: tiny sacs in a t ...
... • Synapse: area composed of the axon terminal of one neuron, the synaptic space, and the dendrite or cell body of the next neuron. • Neurotransmitters: chemicals released by the synaptic vesicles that travel across the synaptic space and affect adjacent neurons. • Synaptic vesicles: tiny sacs in a t ...
Chapter 33 Nervous System
... i. Those that cause changes in the nervous system work in one or more of the following ways 1. Cause an increase in amount of neurotransmitter released into synapse 2. Block receptor site on a dendrite, preventing neurotransmitter from binding 3. Prevent neurotransmitter from leaving synapse 4. Imit ...
... i. Those that cause changes in the nervous system work in one or more of the following ways 1. Cause an increase in amount of neurotransmitter released into synapse 2. Block receptor site on a dendrite, preventing neurotransmitter from binding 3. Prevent neurotransmitter from leaving synapse 4. Imit ...
The Nervous System
... o “fight or flight”- triggered under stress • Accelerated breathing & heart rate (increases blood flow) • Inhibition or slowing of digestion • Pupils Dilate • Tunnel vision • Increased muscle tension for extra strength & speed ...
... o “fight or flight”- triggered under stress • Accelerated breathing & heart rate (increases blood flow) • Inhibition or slowing of digestion • Pupils Dilate • Tunnel vision • Increased muscle tension for extra strength & speed ...
The Nervous System: Overview The nervous system Divisions of the
... processes, and contains two types of neuron: Motor neurons Sensory neurons ...
... processes, and contains two types of neuron: Motor neurons Sensory neurons ...
Nervous System Cells
... • Neurons – excitable cells that conduct the impulses that make possible all nervous system functions • Glia – (glial cells) support the function of neurons in various ways ...
... • Neurons – excitable cells that conduct the impulses that make possible all nervous system functions • Glia – (glial cells) support the function of neurons in various ways ...
File
... that are sensitive to a particular stimuli such as heat, pressure or light called Receptors. • Messages are sent as an electrical impulse along the neuron. • This carries the messages from the axon of one neuron to the dendrite of the next ...
... that are sensitive to a particular stimuli such as heat, pressure or light called Receptors. • Messages are sent as an electrical impulse along the neuron. • This carries the messages from the axon of one neuron to the dendrite of the next ...
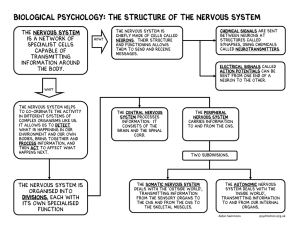
Biological Psychology: The structure of the nervous system
... in different systems of complex organisms like us. It allows us to detect what is happening in our environment and our own bodies, bring together and process information, and ...
... in different systems of complex organisms like us. It allows us to detect what is happening in our environment and our own bodies, bring together and process information, and ...
Organization of the Nervous System
... Dendrites: Increase the surface area for receiving incoming information. Axon: Carries information from the cell body to a neighboring neuron. Myelin Sheath: Insulating fat cells that increase the rate of signal transmissions. Node of Ranvier: Bare axon; allows action potential to jump from node to ...
... Dendrites: Increase the surface area for receiving incoming information. Axon: Carries information from the cell body to a neighboring neuron. Myelin Sheath: Insulating fat cells that increase the rate of signal transmissions. Node of Ranvier: Bare axon; allows action potential to jump from node to ...
Organization of the Nervous System
... Dendrites: Increase the surface area for receiving incoming information. Axon: Carries information from the cell body to a neighboring neuron. Myelin Sheath: Insulating fat cells that increase the rate of signal transmissions. Node of Ranvier: Bare axon; allows action potential to jump from node to ...
... Dendrites: Increase the surface area for receiving incoming information. Axon: Carries information from the cell body to a neighboring neuron. Myelin Sheath: Insulating fat cells that increase the rate of signal transmissions. Node of Ranvier: Bare axon; allows action potential to jump from node to ...
Bio 17 – Nervous & Endocrine Systems
... IPSP = Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential EPSP = Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential ...
... IPSP = Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential EPSP = Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential ...
The Nervous System
... • Membrane potentials arise from differences in ion concentrations between a cell’s contents and the extracellular fluid. • An action potential is an all-or-none change in the membrane potential. • Action potentials travel along an axon because they are self-propagating. • Chemical or electrical com ...
... • Membrane potentials arise from differences in ion concentrations between a cell’s contents and the extracellular fluid. • An action potential is an all-or-none change in the membrane potential. • Action potentials travel along an axon because they are self-propagating. • Chemical or electrical com ...
The Nervous System - OCPS TeacherPress
... Integration center: synapse between sensory/motor neurons Motor neurons: Effector organ – muscle/gland that responds (the reflex) ...
... Integration center: synapse between sensory/motor neurons Motor neurons: Effector organ – muscle/gland that responds (the reflex) ...
Nerves Part 1 Powerpoint
... • Interneurons form the central nervous system (CNS) • Sensory and motor neurons form the peripheral nervous system (PNS) ...
... • Interneurons form the central nervous system (CNS) • Sensory and motor neurons form the peripheral nervous system (PNS) ...
KS4_nervous_models_Pupil_Sheets
... An electrical impulse cannot travel across a gap so another mechanism needs to be used. When the impulse reaches the end of the neuron chemicals called neurotransmitters are released into the gap. These diffuse across and bind to receptors in the next neuron which sets off a new impulse. ...
... An electrical impulse cannot travel across a gap so another mechanism needs to be used. When the impulse reaches the end of the neuron chemicals called neurotransmitters are released into the gap. These diffuse across and bind to receptors in the next neuron which sets off a new impulse. ...
Key Stage 4 – Nervous models Pupil worksheet
... An electrical impulse cannot travel across a gap so another mechanism needs to be used. When the impulse reaches the end of the neuron chemicals called neurotransmitters are released into the gap. These diffuse across and bind to receptors in the next neuron which sets off a new impulse. ...
... An electrical impulse cannot travel across a gap so another mechanism needs to be used. When the impulse reaches the end of the neuron chemicals called neurotransmitters are released into the gap. These diffuse across and bind to receptors in the next neuron which sets off a new impulse. ...
How is the Nervous System Organized? a Class Objectives a What
... The neurotransmitters are like pieces of a puzzle, and the receptor sites on the next neuron are differently shaped spaces. - ________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ _ ...
... The neurotransmitters are like pieces of a puzzle, and the receptor sites on the next neuron are differently shaped spaces. - ________________________________________________ ________________________________________________ _ ...
Neurotoxin
Neurotoxins are substances that are poisonous or destructive to nerve tissue. Neurotoxins are an extensive class of exogenous chemical neurological insults that can adversely affect function in both developing and mature nervous tissue. The term can also be used to classify endogenous compounds, which, when abnormally contact, can prove neurologically toxic. Though neurotoxins are often neurologically destructive, their ability to specifically target neural components is important in the study of nervous systems. Common examples of neurotoxins include lead, ethanol (drinking alcohol), Manganese glutamate, nitric oxide (NO), botulinum toxin (e.g. Botox), tetanus toxin, and tetrodotoxin. Some substances such as nitric oxide and glutamate are in fact essential for proper function of the body and only exert neurotoxic effects at excessive concentrations.Neurotoxins inhibit neuron control over ion concentrations across the cell membrane, or communication between neurons across a synapse. Local pathology of neurotoxin exposure often includes neuron excitotoxicity or apoptosis but can also include glial cell damage. Macroscopic manifestations of neurotoxin exposure can include widespread central nervous system damage such as intellectual disability, persistent memory impairments, epilepsy, and dementia. Additionally, neurotoxin-mediated peripheral nervous system damage such as neuropathy or myopathy is common. Support has been shown for a number of treatments aimed at attenuating neurotoxin-mediated injury, such as antioxidant, and antitoxin administration.