Characterization of a cDNA Clone Encoding Multiple Copies of the
... clones were screened on Hybond-N membranes (Amersham Intemational Corp.), at a density of 5000 plaque-forming units 135 mm filter. Plaque lifts were done as recommended by the manufacturer. The membranes were hybridized in 6 x SSC (1 x SSC: 0.15 M NaCl and 0.0 15 M Na-citrate), 5 x Denhardt’s (accor ...
... clones were screened on Hybond-N membranes (Amersham Intemational Corp.), at a density of 5000 plaque-forming units 135 mm filter. Plaque lifts were done as recommended by the manufacturer. The membranes were hybridized in 6 x SSC (1 x SSC: 0.15 M NaCl and 0.0 15 M Na-citrate), 5 x Denhardt’s (accor ...
CHAPTER 6 Gene Expression: Translation
... 1. The relationship between codons and amino acids was determined by Nirenberg and Khorana (1968) using cell-free, protein-synthesizing systems from E. coli that included ribosomes and required protein factors, along with tRNAs carrying radiolabeled amino acids. 2. To begin determining the genetic c ...
... 1. The relationship between codons and amino acids was determined by Nirenberg and Khorana (1968) using cell-free, protein-synthesizing systems from E. coli that included ribosomes and required protein factors, along with tRNAs carrying radiolabeled amino acids. 2. To begin determining the genetic c ...
10529_2013_1416_MOESM1_ESM
... containing 50 μg mL-1 apramycin, 25 μg mL-1 nalidixic acid for 5 days to confirm resistance. To eliminate autonomously replicating plasmid pTG2003, the exconjugants were incubated in YEME culture containing 20 µg mL-1 apramycin, 25 μg mL-1 nalidixic acid for 3 days. The strains of exconjugants were ...
... containing 50 μg mL-1 apramycin, 25 μg mL-1 nalidixic acid for 5 days to confirm resistance. To eliminate autonomously replicating plasmid pTG2003, the exconjugants were incubated in YEME culture containing 20 µg mL-1 apramycin, 25 μg mL-1 nalidixic acid for 3 days. The strains of exconjugants were ...
Molecular analysis of an operon in Bacillus subtilis
... present. In addition, between the Walker motifs I and 11, EcsA contains a glutamine- and glycine-rich motif (consensus L/FSGGQQ/R/KQR) that is well-conserved in the ATP-binding components of ABC-transporters (Ames e t al., 1992). Homology that extends beyond the ATP-binding motifs was observed betwe ...
... present. In addition, between the Walker motifs I and 11, EcsA contains a glutamine- and glycine-rich motif (consensus L/FSGGQQ/R/KQR) that is well-conserved in the ATP-binding components of ABC-transporters (Ames e t al., 1992). Homology that extends beyond the ATP-binding motifs was observed betwe ...
Slide 1
... human leukocyte antigen (HLA) loci on the short arm of chromosome 6. Age at onset, clinical features, and course of the disease are described. Although the mean age of onset was 34 years in this family, in 6 of 41 affected individuals onset was below 15 years of age and was accompanied by the unique ...
... human leukocyte antigen (HLA) loci on the short arm of chromosome 6. Age at onset, clinical features, and course of the disease are described. Although the mean age of onset was 34 years in this family, in 6 of 41 affected individuals onset was below 15 years of age and was accompanied by the unique ...
SQA Higher Biology Unit 1 Cell Biology
... Unicellular organisms carry out all the functions of life within a single cell (Figure 1.1). Eukaryotic unicells are divided into compartments called organelles that carry out different functions. Eukaryotic multicellular organisms are composed of many types of cell that are differentiated to carry ...
... Unicellular organisms carry out all the functions of life within a single cell (Figure 1.1). Eukaryotic unicells are divided into compartments called organelles that carry out different functions. Eukaryotic multicellular organisms are composed of many types of cell that are differentiated to carry ...
475 S07 background questions
... polypeptide” hypothesis and explain why the original hypothesis was changed. 20. Explain how RNA differs from DNA. 21. Briefly explain how information flows from gene to protein. 22. Distinguish between transcription and translation. 23. Compare where transcription and translation occur in prokaryot ...
... polypeptide” hypothesis and explain why the original hypothesis was changed. 20. Explain how RNA differs from DNA. 21. Briefly explain how information flows from gene to protein. 22. Distinguish between transcription and translation. 23. Compare where transcription and translation occur in prokaryot ...
science - Madison Central High
... on a journey that will cover two fascinating centuries of scientific discovery in the field of genetics, filled with twists, turns, and the occasional dead end. I’m Eric Yang, resident science nerd and Honors Decathlete at The Colony High School. Ever since I was a toddler, genetics has captured my ...
... on a journey that will cover two fascinating centuries of scientific discovery in the field of genetics, filled with twists, turns, and the occasional dead end. I’m Eric Yang, resident science nerd and Honors Decathlete at The Colony High School. Ever since I was a toddler, genetics has captured my ...
Single Amino Acids as Additives Modulating CaCO3 Mineralization
... that CaCO3 is the predominant mineral composition utilized, but have completely different structural features from its geological counterparts. It is this same geological mineral, which is usually brittle and very unstable under shear forces, that provides strength and structure to invertebrates. Th ...
... that CaCO3 is the predominant mineral composition utilized, but have completely different structural features from its geological counterparts. It is this same geological mineral, which is usually brittle and very unstable under shear forces, that provides strength and structure to invertebrates. Th ...
Bacterial Transformation Using Fluorescent Protein
... genome). In addition, bacteria naturally contain one or more significantly smaller circular pieces of DNA called plasmids. Plasmid DNA contains genes for traits that may be beneficial to bacterial survival under certain environmental conditions. In nature, bacteria can transfer plasmids back and for ...
... genome). In addition, bacteria naturally contain one or more significantly smaller circular pieces of DNA called plasmids. Plasmid DNA contains genes for traits that may be beneficial to bacterial survival under certain environmental conditions. In nature, bacteria can transfer plasmids back and for ...
Red Blood Cell Membrane Fatty Acids as a
... few clinical institutions in the U.S.A. performing this test. The test is very complex and involves lipid extraction, methylation, separation steps and final analysis by gas chromatography. Plasma fatty acids can also be measured. However, the RBC profile is preferred because RBC fatty acids reveal ...
... few clinical institutions in the U.S.A. performing this test. The test is very complex and involves lipid extraction, methylation, separation steps and final analysis by gas chromatography. Plasma fatty acids can also be measured. However, the RBC profile is preferred because RBC fatty acids reveal ...
Microcin B17 Blocks DNA Replication and Induces
... Trimethoprim selection of ThyA- mutants and P 1 vir-mediated transduction were carried out as described by Miller (1972). The marker recA56 was routinely introduced into strains by cotransduction with the marker srl: :TnlO. Tetracycline resistant bacteria were selected. Clones which were also recA.5 ...
... Trimethoprim selection of ThyA- mutants and P 1 vir-mediated transduction were carried out as described by Miller (1972). The marker recA56 was routinely introduced into strains by cotransduction with the marker srl: :TnlO. Tetracycline resistant bacteria were selected. Clones which were also recA.5 ...
Basic Concepts
... 2. If reactant side has more moles of gas a. Increase in denominator is greater than increase in numerator and Qc < Kc b. To return to equilibrium, Qc must increase; the numerator of the Qc expression must increase and denominator must decrease—it shifts toward fewer moles of gas (reactants to produ ...
... 2. If reactant side has more moles of gas a. Increase in denominator is greater than increase in numerator and Qc < Kc b. To return to equilibrium, Qc must increase; the numerator of the Qc expression must increase and denominator must decrease—it shifts toward fewer moles of gas (reactants to produ ...
Basic Concepts - Department of Chemistry
... 2. If reactant side has more moles of gas a. Increase in denominator is greater than increase in numerator and Qc < Kc b. To return to equilibrium, Qc must increase; the numerator of the Qc expression must increase and denominator must decrease—it shifts toward fewer moles of gas (reactants to produ ...
... 2. If reactant side has more moles of gas a. Increase in denominator is greater than increase in numerator and Qc < Kc b. To return to equilibrium, Qc must increase; the numerator of the Qc expression must increase and denominator must decrease—it shifts toward fewer moles of gas (reactants to produ ...
BMI 731 Chapter1: SNP Analysis
... • The particular order of the bases arranged along the sugar - phosphate backbone is called the DNA sequence ...
... • The particular order of the bases arranged along the sugar - phosphate backbone is called the DNA sequence ...
Tuning Biphenyl Dioxygenase for Extended Substrate Specificity
... product from PCBs. For quantitative analysis, cells were grown at 37°C in 1 mL of the supplemented M9 medium in the presence of 20 g mL−1 kanamycin until an OD600 of 0.8 was reached. Cultures were then induced with 1 mM IPTG and incubated for another 2 h. Five microliters of 100 mM biphenyl or PCB ...
... product from PCBs. For quantitative analysis, cells were grown at 37°C in 1 mL of the supplemented M9 medium in the presence of 20 g mL−1 kanamycin until an OD600 of 0.8 was reached. Cultures were then induced with 1 mM IPTG and incubated for another 2 h. Five microliters of 100 mM biphenyl or PCB ...
PDF
... Attachment of DNA to both the magnetic bead and the surface of the flow cell is essential for single molecule studies. This is achieved by combining together an unmodified DNA with derivatized DNA handles. Such handles can be prepared in a variety of ways. Perhaps the easiest way involves PCR using ...
... Attachment of DNA to both the magnetic bead and the surface of the flow cell is essential for single molecule studies. This is achieved by combining together an unmodified DNA with derivatized DNA handles. Such handles can be prepared in a variety of ways. Perhaps the easiest way involves PCR using ...
DNA - CS.Duke
... the cutAndSplice method. The code given to you will pop-‐up a file-‐dialog box — when run you can use this to navigate to either ecolimed.dat, which is a smaller strand of DNA ...
... the cutAndSplice method. The code given to you will pop-‐up a file-‐dialog box — when run you can use this to navigate to either ecolimed.dat, which is a smaller strand of DNA ...
Explaining the Likelihood Ratio in DNA Mixture
... reporting on DNA evidence. There are several reasons for its relative unpopularity. First, outside of the DNA area, most forensic science disciplines do not yet have a LR available. Moreover, within DNA identification, forensic analysts sometimes find the LR hard to explain. However, all DNA match s ...
... reporting on DNA evidence. There are several reasons for its relative unpopularity. First, outside of the DNA area, most forensic science disciplines do not yet have a LR available. Moreover, within DNA identification, forensic analysts sometimes find the LR hard to explain. However, all DNA match s ...
video slide - Mrs. H-D
... 2 Entry of phage DNA and degradation of host DNA. The sheath of the tail contracts, injecting the phage DNA into the cell and leaving an empty capsid outside. The cell’s DNA is hydrolyzed. ...
... 2 Entry of phage DNA and degradation of host DNA. The sheath of the tail contracts, injecting the phage DNA into the cell and leaving an empty capsid outside. The cell’s DNA is hydrolyzed. ...
Explaining the Likelihood Ratio in DNA Mixture Interpretation
... reporting on DNA evidence. There are several reasons for its relative unpopularity. First, outside of the DNA area, most forensic science disciplines do not yet have a LR available. Moreover, within DNA identification, forensic analysts sometimes find the LR hard to explain. However, all DNA match s ...
... reporting on DNA evidence. There are several reasons for its relative unpopularity. First, outside of the DNA area, most forensic science disciplines do not yet have a LR available. Moreover, within DNA identification, forensic analysts sometimes find the LR hard to explain. However, all DNA match s ...
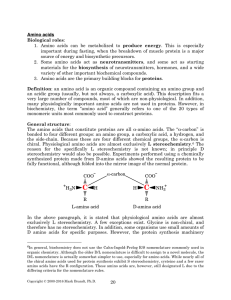
Amino Acids: An Introduction to Their Structure, Functions and
... The peptide bond is formed between the carboxyl group of the first amino acid and the amino group of the second amino acid to form a dipeptide. The peptide bond is unique in that it appears to be a single bond, but has the characteristic of a double bond, i.e., it is a rigid bond. This kind of bond ...
... The peptide bond is formed between the carboxyl group of the first amino acid and the amino group of the second amino acid to form a dipeptide. The peptide bond is unique in that it appears to be a single bond, but has the characteristic of a double bond, i.e., it is a rigid bond. This kind of bond ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.