Primary Sequence of Ovomucoid Messenger RNA
... 25% glycerol) andadded to 200 pCi of dry [y-'P]dATP. T, polynucleotide kinase (2-4pl) was added, and the reaction incubated at 37°C for 30 min. Alternatively, labeling of the 3' ends of restriction sites containing singlestranded 5' termini was accomplished by incubation of the digested DNA with 130 ...
... 25% glycerol) andadded to 200 pCi of dry [y-'P]dATP. T, polynucleotide kinase (2-4pl) was added, and the reaction incubated at 37°C for 30 min. Alternatively, labeling of the 3' ends of restriction sites containing singlestranded 5' termini was accomplished by incubation of the digested DNA with 130 ...
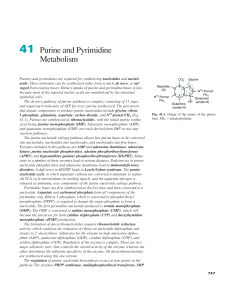
41 Purine and Pyrimidine Metabolism
... bases to generate nucleotides for RNA and DNA synthesis. For certain cell types, such as the lymphocytes, the salvage of bases is the major form of nucleotide generation. The overall picture of salvage is shown in Figure 41.10. The pathways allow free bases, nucleosides, and nucleotides to be easily ...
... bases to generate nucleotides for RNA and DNA synthesis. For certain cell types, such as the lymphocytes, the salvage of bases is the major form of nucleotide generation. The overall picture of salvage is shown in Figure 41.10. The pathways allow free bases, nucleosides, and nucleotides to be easily ...
5-Metabolism of Pyrimidine Nucleotides
... significance than that of the purines, owing to the solubility of the by-products of pyrimidine catabolism. ...
... significance than that of the purines, owing to the solubility of the by-products of pyrimidine catabolism. ...
NON-CANONICAL TRANSCRIPTION INITIATION: THE EXPANDING
... of auxiliary factors associate with RNAP and modulate its activity (Helmann, 2009). Transcription initiation When RNAP recognizes the promoter DNA, it first forms the so called closed complex in which the two DNA strands are still unwound. Subsequently, RNAP isomerizes and forms the open complex in ...
... of auxiliary factors associate with RNAP and modulate its activity (Helmann, 2009). Transcription initiation When RNAP recognizes the promoter DNA, it first forms the so called closed complex in which the two DNA strands are still unwound. Subsequently, RNAP isomerizes and forms the open complex in ...
"Dot and Slot Blotting of DNA". In: Current Protocols in Molecular
... carried out to determine the relative abundance of target sequences in the blotted DNA preparations. Dot and slot blots differ only in the geometry of the blot, a series of spots giving a hybridization pattern that is amenable to analysis by densitometric scanning. Samples are usually applied to the ...
... carried out to determine the relative abundance of target sequences in the blotted DNA preparations. Dot and slot blots differ only in the geometry of the blot, a series of spots giving a hybridization pattern that is amenable to analysis by densitometric scanning. Samples are usually applied to the ...
Summary and Discussion English
... euchromatic and heterochromatic regions in interphase and the mechanisms underlying the formation of interchanges between homologous chromosomes containing heterochromatic regions. The results obtained in this study are summerized below and also presented in Table 1. In chapter 2 we examined the mec ...
... euchromatic and heterochromatic regions in interphase and the mechanisms underlying the formation of interchanges between homologous chromosomes containing heterochromatic regions. The results obtained in this study are summerized below and also presented in Table 1. In chapter 2 we examined the mec ...
Chapter 1 (6 questions)
... Refer to the illustration above. The rate of growth of a population is represented by r. During which time period will r = 0? a. ...
... Refer to the illustration above. The rate of growth of a population is represented by r. During which time period will r = 0? a. ...
Chapter 17 Recombinant DNA and Biotechnology
... • Many restriction enzymes make staggered cuts in the two strands of DNA, creating “sticky ends” with unpaired bases. • The sticky ends can be used to create recombinant DNA if DNA molecules from different species are cut with the same restriction enzyme. ...
... • Many restriction enzymes make staggered cuts in the two strands of DNA, creating “sticky ends” with unpaired bases. • The sticky ends can be used to create recombinant DNA if DNA molecules from different species are cut with the same restriction enzyme. ...
LIPIDS
... consist of a phosphatidyl group attached to a polar head group. These mechanisms involve activation of either the phosphatidyl group or the head group with CDP. In the case of phosphatidyl choline (lecithin) there is the intermediate formation of CDP-choline. Phospholipases selectively hydrolyze spe ...
... consist of a phosphatidyl group attached to a polar head group. These mechanisms involve activation of either the phosphatidyl group or the head group with CDP. In the case of phosphatidyl choline (lecithin) there is the intermediate formation of CDP-choline. Phospholipases selectively hydrolyze spe ...
Appendix AC - Substances and Materials
... Yes. You will be required to obtain a CDC Registration and Biosafety Committee approval prior to obtaining the agent and beginning your studies. 3. Infectious Agents: If bacterial, viral, rickettsial, fungal, protozoal, or other infectious agents will be used in animals, complete items 3.a. 3.b, and ...
... Yes. You will be required to obtain a CDC Registration and Biosafety Committee approval prior to obtaining the agent and beginning your studies. 3. Infectious Agents: If bacterial, viral, rickettsial, fungal, protozoal, or other infectious agents will be used in animals, complete items 3.a. 3.b, and ...
06 Classification and modern methods of diagnostics
... Primers are complementary to segments of opposite strands of that flank the target sequence. Only the segments of target DNA between the primers will be ...
... Primers are complementary to segments of opposite strands of that flank the target sequence. Only the segments of target DNA between the primers will be ...
Legal status of products derived from « new techniques of genetic
... I – 2. The other techniques. Cisgenesis / intragenesis are “techniques involving the direct introduction into an organism of heritable material prepared outside the organism including micro-injection, macro-injection and micro-encapsulation” considered to give rise to GMOs in accordance with Annex 1 ...
... I – 2. The other techniques. Cisgenesis / intragenesis are “techniques involving the direct introduction into an organism of heritable material prepared outside the organism including micro-injection, macro-injection and micro-encapsulation” considered to give rise to GMOs in accordance with Annex 1 ...
The Euglena gracilis chloroplast rpoB gene
... We are interested in the relationship between chloroplast genes for RNA polymerase subunits and the known chloroplast polymerase activities. Antibodies against fusion proteins that contained fragments of the chloroplast genes rpoA from spinach, rpoB from tobacco, and rpoC2 from Euglena, were able to ...
... We are interested in the relationship between chloroplast genes for RNA polymerase subunits and the known chloroplast polymerase activities. Antibodies against fusion proteins that contained fragments of the chloroplast genes rpoA from spinach, rpoB from tobacco, and rpoC2 from Euglena, were able to ...
chapter 3: the cell - CM
... (H2O2); oxidizes toxic chemicals to less toxic compounds that can be eliminated from body before causing damage • Catabolic reactions; break down fatty acids into smaller molecules that can be used for energy production or other anabolic reactions ...
... (H2O2); oxidizes toxic chemicals to less toxic compounds that can be eliminated from body before causing damage • Catabolic reactions; break down fatty acids into smaller molecules that can be used for energy production or other anabolic reactions ...
Oxford Nanopore Technologies
... – a adaptor molecule ( e.g. Cyclodextrin). – Tunnelling electrodes based detectors. – Capacitive detectors – Graphene based nano-gap or edge state detectors. ...
... – a adaptor molecule ( e.g. Cyclodextrin). – Tunnelling electrodes based detectors. – Capacitive detectors – Graphene based nano-gap or edge state detectors. ...
Metabolism of bilirubin and bile salts synthesis (uronic acid pathway
... Hemoglobin, myoglobin, cytochromes and other heme containing proteins ...
... Hemoglobin, myoglobin, cytochromes and other heme containing proteins ...
Diapositiva 1 - Universidad de Sevilla
... HIV-1 RNA copies per mL, depending upon the assay used.At low plasma HIV-1 RNA levels, genotypic resistance testing is likely to be sequencing only a small number of circulating virus variants. ...
... HIV-1 RNA copies per mL, depending upon the assay used.At low plasma HIV-1 RNA levels, genotypic resistance testing is likely to be sequencing only a small number of circulating virus variants. ...
B2 - Revision World
... A as the heart rate increases the concentration of lactic acid increases B as the concentration of lactic acid increases the heart rate decreases C the concentration of lactic acid increases as running speed increases D the concentration of lactic acid is not dependent on heart rate (iv) Explain why ...
... A as the heart rate increases the concentration of lactic acid increases B as the concentration of lactic acid increases the heart rate decreases C the concentration of lactic acid increases as running speed increases D the concentration of lactic acid is not dependent on heart rate (iv) Explain why ...
std. xii - cbse board test (57/2)
... (i) Satellite DNA consists of very large arrays of tandemly repeating, non-coding DNA. (ii) Depending on base composition (A : T rich or G : C rich), length of segment and number of repetitive units, the satellite DNA is classified into many categories such as micro-satellites, mini-satellites etc. ...
... (i) Satellite DNA consists of very large arrays of tandemly repeating, non-coding DNA. (ii) Depending on base composition (A : T rich or G : C rich), length of segment and number of repetitive units, the satellite DNA is classified into many categories such as micro-satellites, mini-satellites etc. ...
Lecture4 Biol302 Spring2012
... Each of the 20 amino acids in proteins is specified by one or more nucleotide triplets in mRNA. (20 amino acids refers to what is attached to the tRNAs!) Of the 64 possible triplets, given the four bases in mRNA, 61 specify amino acids and 3 signal chain termination. (have no tRNAs!) ...
... Each of the 20 amino acids in proteins is specified by one or more nucleotide triplets in mRNA. (20 amino acids refers to what is attached to the tRNAs!) Of the 64 possible triplets, given the four bases in mRNA, 61 specify amino acids and 3 signal chain termination. (have no tRNAs!) ...
Chapter 12 Translation and the Genetic Code
... Each of the 20 amino acids in proteins is specified by one or more nucleotide triplets in mRNA. (20 amino acids refers to what is attached to the tRNAs!) Of the 64 possible triplets, given the four bases in mRNA, 61 specify amino acids and 3 signal chain termination. (have no tRNAs!) ...
... Each of the 20 amino acids in proteins is specified by one or more nucleotide triplets in mRNA. (20 amino acids refers to what is attached to the tRNAs!) Of the 64 possible triplets, given the four bases in mRNA, 61 specify amino acids and 3 signal chain termination. (have no tRNAs!) ...
version 2
... Indicate whether each of the statements in COLUMN I applies to A ONLY, B ONLY, BOTH A and B or NONE of the items in COLUMN II. Write A only, B only, both A and B, or none next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.6) in the ANSWER BOOK. COLUMN I 1.3.1 Have a single set of chromosomes 1.3.2 The number, s ...
... Indicate whether each of the statements in COLUMN I applies to A ONLY, B ONLY, BOTH A and B or NONE of the items in COLUMN II. Write A only, B only, both A and B, or none next to the question number (1.3.1–1.3.6) in the ANSWER BOOK. COLUMN I 1.3.1 Have a single set of chromosomes 1.3.2 The number, s ...
103 Final Exam Win06
... e) Suppose a cosmic ray strikes the DNA and removes the A. Write the new amino acid sequence that would result. ...
... e) Suppose a cosmic ray strikes the DNA and removes the A. Write the new amino acid sequence that would result. ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.