video slide - Buena Park High School
... (a) Insertion sequences, the simplest transposable elements in bacteria, contain a single gene that encodes transposase, which catalyzes movement within the genome. The inverted repeats are backward, upside-down versions of each other; only a portion is shown. The inverted repeat sequence varies fro ...
... (a) Insertion sequences, the simplest transposable elements in bacteria, contain a single gene that encodes transposase, which catalyzes movement within the genome. The inverted repeats are backward, upside-down versions of each other; only a portion is shown. The inverted repeat sequence varies fro ...
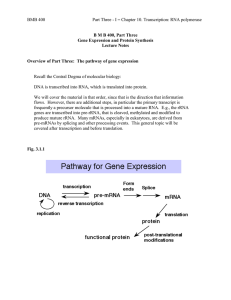
Genes Code for Proteins
... provided a wild-type copy of each gene. The heterozygote has wild phenotype, and thus the two genes are said to complement. The complementation test is shown in more detail in FIGURE 2.3. The basic test consists of the comparison shown in the top part of the figure. If two mutations lie in the same ...
... provided a wild-type copy of each gene. The heterozygote has wild phenotype, and thus the two genes are said to complement. The complementation test is shown in more detail in FIGURE 2.3. The basic test consists of the comparison shown in the top part of the figure. If two mutations lie in the same ...
Presentation
... blunt ends – DNA-PK is activated on binding DNA – Autophosphorylation aids binding of other repair proteins Polymerases that lay down the nucleotide structure – Pol X family members and and TdT that have varying degrees of template dependency. pol can add nucleotides randomly to generate micro ...
... blunt ends – DNA-PK is activated on binding DNA – Autophosphorylation aids binding of other repair proteins Polymerases that lay down the nucleotide structure – Pol X family members and and TdT that have varying degrees of template dependency. pol can add nucleotides randomly to generate micro ...
Chpt10_TxnRNAPol.doc
... from purified eukaryotic polymerases. These specificity factors are present in crude nuclear extracts, because when such crude extracts were added to the purified polymerases, specific initiation at promoters was observed. Biochemists purified several transcription initiation factors by fractionatin ...
... from purified eukaryotic polymerases. These specificity factors are present in crude nuclear extracts, because when such crude extracts were added to the purified polymerases, specific initiation at promoters was observed. Biochemists purified several transcription initiation factors by fractionatin ...
Chem 100 Unit 5 Biochemistry
... hydrophilic head. One of the major functions of Sphingolipids and phosphoglycerides is forming the “lipid bilayer” of cell membranes. Glycolipids are found in brain and nervous tissue. ...
... hydrophilic head. One of the major functions of Sphingolipids and phosphoglycerides is forming the “lipid bilayer” of cell membranes. Glycolipids are found in brain and nervous tissue. ...
Document
... This can be seen from Figure 2.Absorbance of vitamin K3 at 265 nm remains relatively constant. Photostability test for folic acid showed similar results. Figure 4 shows absorbance spectra of folic acid solution with cyclodextrin. In comparison to Figure 3, solution of folic acid, under the same cond ...
... This can be seen from Figure 2.Absorbance of vitamin K3 at 265 nm remains relatively constant. Photostability test for folic acid showed similar results. Figure 4 shows absorbance spectra of folic acid solution with cyclodextrin. In comparison to Figure 3, solution of folic acid, under the same cond ...
Molecular Basis of Polymorphisms of Human Complement
... of the C3 F allele has been reported in patients with partial lipodystrophy, IgA nephropathy, and Indian childhood hepatic cirrhosis. Studies of the genomic organization of the human C3 gene led to the identification of a single change (C to G) between C3 S and C3 F at nucleotide 364 in exon 3 . Thi ...
... of the C3 F allele has been reported in patients with partial lipodystrophy, IgA nephropathy, and Indian childhood hepatic cirrhosis. Studies of the genomic organization of the human C3 gene led to the identification of a single change (C to G) between C3 S and C3 F at nucleotide 364 in exon 3 . Thi ...
lecture4
... We turn now from the metabolism of carbohydrates to that of fatty acids. A fatty acid contains a long hydrocarbon chain and a terminal carboxylate group. Fatty acids have four major physiological roles. First, fatty acids are building blocks of phospholipids and glycolipids. These amphipathic molecu ...
... We turn now from the metabolism of carbohydrates to that of fatty acids. A fatty acid contains a long hydrocarbon chain and a terminal carboxylate group. Fatty acids have four major physiological roles. First, fatty acids are building blocks of phospholipids and glycolipids. These amphipathic molecu ...
CHAPTER 3 The Molecules of Cells
... The 4 single bonds of carbon point to the corners of a tetrahedron. Figure 3.1, top part Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... The 4 single bonds of carbon point to the corners of a tetrahedron. Figure 3.1, top part Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Co-dominance • WT protein will make WT phenotype. Mutant gene
... • Repression of genes involved in the lytic cycle. Bound c1 repressor blocks expression of genes either side of it on the λ chromosome, thus blocking the lytic cycle (stops expression of genes to make more phage & lyse cell). It is now undergoing the lysogenic pathway. • Production of integrase ...
... • Repression of genes involved in the lytic cycle. Bound c1 repressor blocks expression of genes either side of it on the λ chromosome, thus blocking the lytic cycle (stops expression of genes to make more phage & lyse cell). It is now undergoing the lysogenic pathway. • Production of integrase ...
Diversity of DNA methyltransferases that recognize asymmetric
... DNA methyltransferases (MTases) are a group of enzymes that catalyze the methyl group transfer from S-adenosyl-L-methionine in a sequence-specific manner. Orthodox Type II DNA MTases usually recognize palindromic DNA sequences and add a methyl group to the target base (either adenine or cytosine) on ...
... DNA methyltransferases (MTases) are a group of enzymes that catalyze the methyl group transfer from S-adenosyl-L-methionine in a sequence-specific manner. Orthodox Type II DNA MTases usually recognize palindromic DNA sequences and add a methyl group to the target base (either adenine or cytosine) on ...
BIOLOGY
... The 4 single bonds of carbon point to the corners of a tetrahedron. Figure 3.1, top part Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... The 4 single bonds of carbon point to the corners of a tetrahedron. Figure 3.1, top part Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Homework # 9 Citric Acid Cycle, electron transport Chain, and
... In addition, alcohol directly contributes to malnutrition since a pint of 86 proof alcohol (not an unusual daily intake for an alcoholic) represents about half of the daily energy requirement. However, ethanol does not have any minerals, vitamins, carbohydrates, fats or protein associated with it. A ...
... In addition, alcohol directly contributes to malnutrition since a pint of 86 proof alcohol (not an unusual daily intake for an alcoholic) represents about half of the daily energy requirement. However, ethanol does not have any minerals, vitamins, carbohydrates, fats or protein associated with it. A ...
Stabilizing synthetic data in the DNA of living organisms
... Moreover, when more than three synthetic DNA oligomers are used for data storage, there is a high potential for correction of the identified data breakage points (Fig. 4). The natural DNA error rate in the genome of a living organism or in laboratorial experiments is not as high as the error rate as ...
... Moreover, when more than three synthetic DNA oligomers are used for data storage, there is a high potential for correction of the identified data breakage points (Fig. 4). The natural DNA error rate in the genome of a living organism or in laboratorial experiments is not as high as the error rate as ...
Searching in Applications Containing Bio-Sequences
... Search Request Considerations: How much substitution does the claim allow ? ...
... Search Request Considerations: How much substitution does the claim allow ? ...
Lecture 2
... or cations with d electrons not available for π-bonding Soft acids are cations with a moderate positive charge (2+ or lower), Or cations with d electrons readily availbale for π-bonding ...
... or cations with d electrons not available for π-bonding Soft acids are cations with a moderate positive charge (2+ or lower), Or cations with d electrons readily availbale for π-bonding ...
Fundementals I
... Two cysteine side-chains react to form Cystine. Two disulfide bonds oxidized to join and form from cysteine and cysteine to form cystine. Oxidation in biochemistry usually means taking away a hydrogen atom. (take away proton and it’s associated electron) Have left: 2 protons and 2 electrons. Have ta ...
... Two cysteine side-chains react to form Cystine. Two disulfide bonds oxidized to join and form from cysteine and cysteine to form cystine. Oxidation in biochemistry usually means taking away a hydrogen atom. (take away proton and it’s associated electron) Have left: 2 protons and 2 electrons. Have ta ...
Plasma Nucleic Acids in the Diagnosis and Management
... quantifying small amounts of circulating proteins that were relatively specific for certain types of cancer. The application of immunodiffusion techniques and subsequently RIAs and ELISAs led to the discovery of several circulating tumor markers, many of which have now entered routine clinical pract ...
... quantifying small amounts of circulating proteins that were relatively specific for certain types of cancer. The application of immunodiffusion techniques and subsequently RIAs and ELISAs led to the discovery of several circulating tumor markers, many of which have now entered routine clinical pract ...
The Study of Genetics: A Historical Perspective Ross Edwards
... hybridization' did not receive much attention until the early 20th century when it was allegedly rediscovered by three scientists: Hugo de Vries, Carl Correns, and Erik Von Tschermak. From this re-discovery arose the birth of modern genetics, which was studied by pioneers like William Bateson (who e ...
... hybridization' did not receive much attention until the early 20th century when it was allegedly rediscovered by three scientists: Hugo de Vries, Carl Correns, and Erik Von Tschermak. From this re-discovery arose the birth of modern genetics, which was studied by pioneers like William Bateson (who e ...
BB30055: Genes and genomes
... Microsatellite genotyping design PCR primers unique to one locus in the genome .a single pair of PCR primers will produce different sized products for each of the different length microsatellites ...
... Microsatellite genotyping design PCR primers unique to one locus in the genome .a single pair of PCR primers will produce different sized products for each of the different length microsatellites ...
Paper Title
... Up to this point, all experiments were processed with the properties mentioned in 2.1. In this section we are focusing on the question, if the accuracy can be further increased by choosing a different set of physicochemical properties from AAindex database [19]. This is a multidimensional problem as ...
... Up to this point, all experiments were processed with the properties mentioned in 2.1. In this section we are focusing on the question, if the accuracy can be further increased by choosing a different set of physicochemical properties from AAindex database [19]. This is a multidimensional problem as ...
Self-Referential Encoding on Modules of Anticodon Pairs—Roots of
... indication on the process. Dimers are considered mimics of the ribosomes—structures that hold tRNAs together and facilitate the transferase reaction, and of the translation process—anticodons are at the same time codons for each other. The primitive protein synthesis system gets stabilized when the ...
... indication on the process. Dimers are considered mimics of the ribosomes—structures that hold tRNAs together and facilitate the transferase reaction, and of the translation process—anticodons are at the same time codons for each other. The primitive protein synthesis system gets stabilized when the ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.