Gapped Blast and PSI
... BLAST programs use a threshold value which can be adjusted to alter speed and probability. A higher value of T will give greater speed, but also a larger probability of missing weaker similarities. Can use various substitution matrices such as Blosum(62) or PAM ...
... BLAST programs use a threshold value which can be adjusted to alter speed and probability. A higher value of T will give greater speed, but also a larger probability of missing weaker similarities. Can use various substitution matrices such as Blosum(62) or PAM ...
Chapter 3: Amino Acids and Peptides
... q Proteins are linear polymers of amino acids connected by peptide bonds – amino acids are the building blocks of proteins q There are 20 standard amino acids. Asparagine was first found in 1806 and the last amino acid discovered (Threonine) was in 1938 (over 130 years later!!) q All 20 amino aci ...
... q Proteins are linear polymers of amino acids connected by peptide bonds – amino acids are the building blocks of proteins q There are 20 standard amino acids. Asparagine was first found in 1806 and the last amino acid discovered (Threonine) was in 1938 (over 130 years later!!) q All 20 amino aci ...
8.1 Why Do Cells Divide?
... The nucleotides are held together by hydrogen bonding between the bases in two strands forming a double helix. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education Inc. ...
... The nucleotides are held together by hydrogen bonding between the bases in two strands forming a double helix. Copyright © 2009 Pearson Education Inc. ...
Sigma Xi, Montreal Nov 2004 - Biology Department | UNC Chapel Hill
... variation. However, we do not know how frequently such variations in gene location occur among individuals within populations. Additionally, we do not know the degree to which such differences in chromosomal location affect gene expression at the transposed loci. We are studying this issue using Com ...
... variation. However, we do not know how frequently such variations in gene location occur among individuals within populations. Additionally, we do not know the degree to which such differences in chromosomal location affect gene expression at the transposed loci. We are studying this issue using Com ...
Nucleoside Phosphoramidate Monoesters: Potential
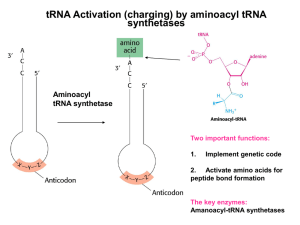
... charging of tRNAs with amino acids 1. tRNA synthetases must link tRNAs with their correct amino acids. 2. tRNA synthetases recognize correct amino acids by specific binding to the active site and proofreading. 3. tRNA synthetases recognize correct tRNAs via by interacting with specific regions of tR ...
... charging of tRNAs with amino acids 1. tRNA synthetases must link tRNAs with their correct amino acids. 2. tRNA synthetases recognize correct amino acids by specific binding to the active site and proofreading. 3. tRNA synthetases recognize correct tRNAs via by interacting with specific regions of tR ...
ICBEnzyEvol
... are obtained from nucleotide sequences by using the universal genetic mapping table. Generating the nucleotide sequences from the amino acid sequences is a concept of reverse process. For a particular amino acid sequences, there can be numerous nucleotide sequences for all the possible combination o ...
... are obtained from nucleotide sequences by using the universal genetic mapping table. Generating the nucleotide sequences from the amino acid sequences is a concept of reverse process. For a particular amino acid sequences, there can be numerous nucleotide sequences for all the possible combination o ...
best
... SU = Rln 920 (2 pts) SF = R ln 2 There are two possible folded states since the helix and strand structures coexist (4 pts) ∆So = SF - SU = R(ln 2 - 20 ln 9) C2: (8 pts) Do one of the following two questions: i) The primary sequence of a 10 residue peptide is being determined using Edman degradation ...
... SU = Rln 920 (2 pts) SF = R ln 2 There are two possible folded states since the helix and strand structures coexist (4 pts) ∆So = SF - SU = R(ln 2 - 20 ln 9) C2: (8 pts) Do one of the following two questions: i) The primary sequence of a 10 residue peptide is being determined using Edman degradation ...
best
... SU = Rln 920 (2 pts) SF = R ln 2 There are two possible folded states since the helix and strand structures coexist (4 pts) So = SF - SU = R(ln 2 - 20 ln 9) C2: (8 pts) Do one of the following two questions: i) The primary sequence of a 10 residue peptide is being determined using Edman degradation ...
... SU = Rln 920 (2 pts) SF = R ln 2 There are two possible folded states since the helix and strand structures coexist (4 pts) So = SF - SU = R(ln 2 - 20 ln 9) C2: (8 pts) Do one of the following two questions: i) The primary sequence of a 10 residue peptide is being determined using Edman degradation ...
Oncomedicine Base Excision Repair Manipulation in Breast
... Next, AP Endonucleases are the next enzyme carrying the in BER pathway. The enzyme APE1 is described as the major AP-endonuclease in mammalian cells and essential for the survival [41]. The role of this enzyme is to generate the 5’-sugar phosphate group (dRP) and 3’-OH ends by incising the phosphodi ...
... Next, AP Endonucleases are the next enzyme carrying the in BER pathway. The enzyme APE1 is described as the major AP-endonuclease in mammalian cells and essential for the survival [41]. The role of this enzyme is to generate the 5’-sugar phosphate group (dRP) and 3’-OH ends by incising the phosphodi ...
a rapid uplc™ - ms/ms method for determining specific
... The results of the two methods (AAA vs LC/MS/MS) were compared by correlation analysis where, for each amino acid, the correlation coefficient (R) was greater than 0.96 . Figure 2 shows the method comparison of three representative analytes. Each of the 75 specimens was classified into the same PKU, ...
... The results of the two methods (AAA vs LC/MS/MS) were compared by correlation analysis where, for each amino acid, the correlation coefficient (R) was greater than 0.96 . Figure 2 shows the method comparison of three representative analytes. Each of the 75 specimens was classified into the same PKU, ...
1-HumanGen Mutations
... which are held together by either intramolecular forces (covalent bonds) or weaker intermolecular forces. • Molecular dimers are often formed by the reaction of two identical compounds • An example of an intermolecular or physical dimer is acetic acid wherein hydrogen bonds hold the two molecules to ...
... which are held together by either intramolecular forces (covalent bonds) or weaker intermolecular forces. • Molecular dimers are often formed by the reaction of two identical compounds • An example of an intermolecular or physical dimer is acetic acid wherein hydrogen bonds hold the two molecules to ...
Perspectives in Nutrition, 8th Edition
... Inorganic substance is oxidized: loss of 1 or more electrons (LEO) b. Inorganic substance is reduced: gain of 1 or more electrons (GER) c. Organic substance is oxidized: gain of oxygen or loss of hydrogen; hydrogen atoms are eventually added to oxygen to form water d. Organic substance is reduced: l ...
... Inorganic substance is oxidized: loss of 1 or more electrons (LEO) b. Inorganic substance is reduced: gain of 1 or more electrons (GER) c. Organic substance is oxidized: gain of oxygen or loss of hydrogen; hydrogen atoms are eventually added to oxygen to form water d. Organic substance is reduced: l ...
Chapter 21 Biochemistry
... • The order of nucleotides on a nucleic acid chain specifies the order of amino acids in the primary protein structure. • A sequence of three nucleotide bases determines which amino acid is next in the chain; this sequence is called a codon. • The sequence of nucleotide bases that code for a particu ...
... • The order of nucleotides on a nucleic acid chain specifies the order of amino acids in the primary protein structure. • A sequence of three nucleotide bases determines which amino acid is next in the chain; this sequence is called a codon. • The sequence of nucleotide bases that code for a particu ...
Some Amino Acids
... • The order of nucleotides on a nucleic acid chain specifies the order of amino acids in the primary protein structure. • A sequence of three nucleotide bases determines which amino acid is next in the chain; this sequence is called a codon. • The sequence of nucleotide bases that code for a particu ...
... • The order of nucleotides on a nucleic acid chain specifies the order of amino acids in the primary protein structure. • A sequence of three nucleotide bases determines which amino acid is next in the chain; this sequence is called a codon. • The sequence of nucleotide bases that code for a particu ...
Essential Biology Topic 3 File
... 29. In the space below, draw and label a diagram explaining the process of DNA replication. Pay attention to the requirements of your assessment level. ...
... 29. In the space below, draw and label a diagram explaining the process of DNA replication. Pay attention to the requirements of your assessment level. ...
Paper - Revision Science
... (PCBs) by the following reaction. 2FeCl 3(aq) + Cu(s) → 2FeCl 2(aq) + CuCl 2(aq) A solution in which [Fe3+(aq)] was originally equal to 1.50 mol dm–3 was re-used several times to dissolve copper from the PCBs, and was then titrated as follows. A 2.50 cm3 sample of the partially-used-up solution was ...
... (PCBs) by the following reaction. 2FeCl 3(aq) + Cu(s) → 2FeCl 2(aq) + CuCl 2(aq) A solution in which [Fe3+(aq)] was originally equal to 1.50 mol dm–3 was re-used several times to dissolve copper from the PCBs, and was then titrated as follows. A 2.50 cm3 sample of the partially-used-up solution was ...
Amino Acids and Peptides
... units of proteins. They form short polymer chains called peptides or polypeptides which in turn form structures called proteins. The process of such formation from an mRNA template is known as translation, which is part of protein synthesis. Phenylalanine is one of the standard amino acids. ...
... units of proteins. They form short polymer chains called peptides or polypeptides which in turn form structures called proteins. The process of such formation from an mRNA template is known as translation, which is part of protein synthesis. Phenylalanine is one of the standard amino acids. ...
Full Text
... understanding of interactions in protein structures. Therefore, we have been interested in developing a representation for biological sequences that can incorporate structural features conferred through dependences among amino acids. We have used Bayesian networks (Neapolitan, 1990; Pearl, 1988) to ...
... understanding of interactions in protein structures. Therefore, we have been interested in developing a representation for biological sequences that can incorporate structural features conferred through dependences among amino acids. We have used Bayesian networks (Neapolitan, 1990; Pearl, 1988) to ...
Biochemistry review
... arachidonic acid, which type of supplement listed would be useful in increasing eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and Omega 3s docosahexanoic acid (DHA) levels? a. glucosamine and chondroitin b. B complex with B6, B12 and folate c. cold water fish oil supplement d. ADEK, the fat soluble vitamins ...
... arachidonic acid, which type of supplement listed would be useful in increasing eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and Omega 3s docosahexanoic acid (DHA) levels? a. glucosamine and chondroitin b. B complex with B6, B12 and folate c. cold water fish oil supplement d. ADEK, the fat soluble vitamins ...
PDF - Andrew Rambaut
... exhibited positive epistasis. This has important implications for the understanding of the evolution of sex, suggesting that RNA recombination is not an adaptation to purge deleterious mutations from viral genomes (Bonhoeffer et al. 2004). However, the generality of these results to viruses other th ...
... exhibited positive epistasis. This has important implications for the understanding of the evolution of sex, suggesting that RNA recombination is not an adaptation to purge deleterious mutations from viral genomes (Bonhoeffer et al. 2004). However, the generality of these results to viruses other th ...
Document
... Used by majority of groups Biopsy at 6-10 cell stage Blastomeres totipotent 1-2 cells for analysis ...
... Used by majority of groups Biopsy at 6-10 cell stage Blastomeres totipotent 1-2 cells for analysis ...
Thursday and Friday
... length of the two sequences under comparison. Algorithms of this nature are not particularly suited to the identification of genes that have evolved by recombination or insertion of unrelated regions of DNA. In instances such as this, a global similarity score will be greatly reduced. In cases where ...
... length of the two sequences under comparison. Algorithms of this nature are not particularly suited to the identification of genes that have evolved by recombination or insertion of unrelated regions of DNA. In instances such as this, a global similarity score will be greatly reduced. In cases where ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.