Module Number- 3181
... Written evidence of the ability to give the required representations of amino acids and proteins and to describe specified properties, role of proteins and the role of enzyme given with performance Criteria (a) to (d) respectively. Performance evidence of the ability to analyse amino acids which wil ...
... Written evidence of the ability to give the required representations of amino acids and proteins and to describe specified properties, role of proteins and the role of enzyme given with performance Criteria (a) to (d) respectively. Performance evidence of the ability to analyse amino acids which wil ...
Proteins and amino acids
... It drives the folding of a protein The sticky amino acids glue together The non-sticky amino acids point to the water The waters must be ‘happy’ ...
... It drives the folding of a protein The sticky amino acids glue together The non-sticky amino acids point to the water The waters must be ‘happy’ ...
Amino Acid Metabolism
... regardless of whether they are released from dietary or intracellular proteins • The metabolism of the resulting amino group and nitrogen excretion are a central part of nitrogen metabolism ...
... regardless of whether they are released from dietary or intracellular proteins • The metabolism of the resulting amino group and nitrogen excretion are a central part of nitrogen metabolism ...
Sathgudi Sweet orange
... microscopy and PCR. 2. The complete genome of CMBVSON consisted of 7558 nucleotide containing for 6 open reading frames (ORFs). High variability (87.4% to 96%) observed in ORF 4 and 5 infecting sathgudi sweet orange, rangpur lime acid lime and pummelo. 3. The intergenic region (non coding region) ha ...
... microscopy and PCR. 2. The complete genome of CMBVSON consisted of 7558 nucleotide containing for 6 open reading frames (ORFs). High variability (87.4% to 96%) observed in ORF 4 and 5 infecting sathgudi sweet orange, rangpur lime acid lime and pummelo. 3. The intergenic region (non coding region) ha ...
Chapter 3 Notes
... 3.12 Proteins have a wide range of functions and structures • Proteins are • involved in nearly every dynamic function in your body and • very diverse, with tens of thousands of different proteins, each with a specific structure and function, in the human body. ...
... 3.12 Proteins have a wide range of functions and structures • Proteins are • involved in nearly every dynamic function in your body and • very diverse, with tens of thousands of different proteins, each with a specific structure and function, in the human body. ...
Beginner`s Guide to Real-Time PCR
... experience to interpret correctly. It is crucial to interpret the melt curve along side the amplification plot in order to work with your data. Things to consider: Target abundance Because of its inherent lack of specificity, intercalating dyes are less effective when your target of interest is rare ...
... experience to interpret correctly. It is crucial to interpret the melt curve along side the amplification plot in order to work with your data. Things to consider: Target abundance Because of its inherent lack of specificity, intercalating dyes are less effective when your target of interest is rare ...
Supplemental Methods and Figure Legends
... Supplemental Methods and Figure Legends Supplemental methods. Plasmids for expressing P. angusta H3 and H4 in S. cerevisiae: The S. cerevisiae HHT2 and HHF2 genes (respectively, chr. XIV coordinates 575,265-576,092 and 576,046-577,238) were amplified by PCR and cloned separately into pGEM-T (Promega ...
... Supplemental Methods and Figure Legends Supplemental methods. Plasmids for expressing P. angusta H3 and H4 in S. cerevisiae: The S. cerevisiae HHT2 and HHF2 genes (respectively, chr. XIV coordinates 575,265-576,092 and 576,046-577,238) were amplified by PCR and cloned separately into pGEM-T (Promega ...
CRISPR/Cas9: Tools and Applications for Eukaryotic Genome Editing
... Knowing now that Cas9 works well, one of the immediate concerns in everyone’s mind was the specificity of the system. Figure 12 shows that Cas9 does have off-target activities and these tend to occur when there are mismatches between the guide RNA and the target DNA on the PAM-distal side of Cas9. ...
... Knowing now that Cas9 works well, one of the immediate concerns in everyone’s mind was the specificity of the system. Figure 12 shows that Cas9 does have off-target activities and these tend to occur when there are mismatches between the guide RNA and the target DNA on the PAM-distal side of Cas9. ...
Biology Study List - MCAT Prep Course
... Biology Study List for the MCAT Molecular Biology ¾ Understand the basic functions and structures of the major chemical components of living cells and their surroundings: proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, nucleotides, water and minerals (in order of importance) Enzymes: ¾ Understand the function and ...
... Biology Study List for the MCAT Molecular Biology ¾ Understand the basic functions and structures of the major chemical components of living cells and their surroundings: proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, nucleotides, water and minerals (in order of importance) Enzymes: ¾ Understand the function and ...
Slide 1
... – Energy level of the diet • Energy and C-skeletons needed by rumen bacteria to produce microbial protein from ruminal NH3 ...
... – Energy level of the diet • Energy and C-skeletons needed by rumen bacteria to produce microbial protein from ruminal NH3 ...
Amino acids used in Animal Nutrition
... Categories of Amino Acids While there are 22 in total, only 20 are of primary interest for animals In 1938, Rose divided these amino acids into two groups: Essential (indispensable): • Those that cannot be synthesized by the animal in quantities sufficient for optimum performance and must be supp ...
... Categories of Amino Acids While there are 22 in total, only 20 are of primary interest for animals In 1938, Rose divided these amino acids into two groups: Essential (indispensable): • Those that cannot be synthesized by the animal in quantities sufficient for optimum performance and must be supp ...
Cloning and characterization of the
... pseudouridine formation even at the highest concentration of recombinant spPus1p tested (data not shown). These results demonstrate that spPus1p is capable of forming Ψ at positions 27, 28, 34, 35 and 36, the efficiency of the modification being dependent on the position of the uridine in the tRNA m ...
... pseudouridine formation even at the highest concentration of recombinant spPus1p tested (data not shown). These results demonstrate that spPus1p is capable of forming Ψ at positions 27, 28, 34, 35 and 36, the efficiency of the modification being dependent on the position of the uridine in the tRNA m ...
Comparison of the separation of Candida albicans chromosome
... Princeton, NJ) (15). Plasmids pCaActl containing the C. albicans actin gene and plasmid pE2 containing a 10 kbp Eco RI fragment of the C. albicans mitochondrial genome (12) were kindly provided by Dr. Stuart Riggsby. The C. albicans genes for TRP1 in plasmid pAR84-2 and HIS3 in plasmid pAR84-3 were ...
... Princeton, NJ) (15). Plasmids pCaActl containing the C. albicans actin gene and plasmid pE2 containing a 10 kbp Eco RI fragment of the C. albicans mitochondrial genome (12) were kindly provided by Dr. Stuart Riggsby. The C. albicans genes for TRP1 in plasmid pAR84-2 and HIS3 in plasmid pAR84-3 were ...
RNA 3`-terminal phosphate cyclases and cyclase
... Chakravarty and Shuman [39] extended the known substrate specificity of RtcA even further. They demonstrated that at the slow rate the E. coli RtcA can convert, in a reaction involving an RctA-AMP covalent intermediate, the 5’-phosphates in RNA and DNA into A5’pp5’N structures. This modification opt ...
... Chakravarty and Shuman [39] extended the known substrate specificity of RtcA even further. They demonstrated that at the slow rate the E. coli RtcA can convert, in a reaction involving an RctA-AMP covalent intermediate, the 5’-phosphates in RNA and DNA into A5’pp5’N structures. This modification opt ...
PPT File
... The average gene consists of 3000 bases, but sizes vary greatly, with the largest known human gene being dystrophin at 2.4 million bases. The total number of genes is estimated at 30,000 ...
... The average gene consists of 3000 bases, but sizes vary greatly, with the largest known human gene being dystrophin at 2.4 million bases. The total number of genes is estimated at 30,000 ...
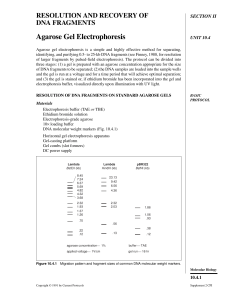
Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
... While this has a slight effect on the mobility of the DNA (Fig. 10.4.2D), it eliminates the need to stain the gel upon completion of the separation. An added advantage to running gels with ethidium bromide is that the mobility of the DNA can be monitored throughout the run until the desired separati ...
... While this has a slight effect on the mobility of the DNA (Fig. 10.4.2D), it eliminates the need to stain the gel upon completion of the separation. An added advantage to running gels with ethidium bromide is that the mobility of the DNA can be monitored throughout the run until the desired separati ...
Predictable Alteration of Sequence Recognition by RNA
... can be found in all eukaryotes, from humans to algae, although they differ greatly in number between organisms. This protein family has massively expanded in terrestrial plants, which contain from ;100 (Physcomitrella) to over 1000 (Selaginella) PPR proteins (Fujii and Small, 2011). PPR proteins are ...
... can be found in all eukaryotes, from humans to algae, although they differ greatly in number between organisms. This protein family has massively expanded in terrestrial plants, which contain from ;100 (Physcomitrella) to over 1000 (Selaginella) PPR proteins (Fujii and Small, 2011). PPR proteins are ...
Glycolic Acid Labeling During Photosynthesis
... the rate of the hydrogen transport reaction were significant compared to the biosynthesis of glycolic acid from CO, one might expect a significantly higher ratio of tritium to :'C in glycolic acid than in other intermediates of the photosynthetic carbol redutction cycle, after a short period of phot ...
... the rate of the hydrogen transport reaction were significant compared to the biosynthesis of glycolic acid from CO, one might expect a significantly higher ratio of tritium to :'C in glycolic acid than in other intermediates of the photosynthetic carbol redutction cycle, after a short period of phot ...
Dynamic epigenetic responses to childhood exposure to violence
... optimal research methods are still being developed. In undertaking epigenetic research (or when interpreting previously published data) it is important to take into account a number of biological, technical and methodological issues 37. It is unlikely that the simple “brute-force” approaches that ha ...
... optimal research methods are still being developed. In undertaking epigenetic research (or when interpreting previously published data) it is important to take into account a number of biological, technical and methodological issues 37. It is unlikely that the simple “brute-force” approaches that ha ...
How do bacteria respond to their environment?
... Experiment • Add uncharged tRNA to ribosomes • See if pppGpp increases Need: • In vitro system where charging of tRNA can be controlled • Assay for level of pppGpp ...
... Experiment • Add uncharged tRNA to ribosomes • See if pppGpp increases Need: • In vitro system where charging of tRNA can be controlled • Assay for level of pppGpp ...
A novel DNA modification by sulphur
... related NifS (ni trogen f ixation) proteins of nitrogen-fixing bacteria (e.g. Klebsiella pneumoniae and Rhodobacter capsulatus). The functions of IscS and NifS are related in that they provide the sulphur via an L-cysteine desulphurase activity. All of these proteins, including DndA, have a conserve ...
... related NifS (ni trogen f ixation) proteins of nitrogen-fixing bacteria (e.g. Klebsiella pneumoniae and Rhodobacter capsulatus). The functions of IscS and NifS are related in that they provide the sulphur via an L-cysteine desulphurase activity. All of these proteins, including DndA, have a conserve ...
Proteinogenic amino acid
... polypeptide as a whole. It is used by many proteins as a regulatory mechanism, changing the conformation and behavior of the polypeptide in acidic regions such as the late endosome or lysosome, enforcing conformation change in enzymes. However only a few histidines are needed for this, so it is comp ...
... polypeptide as a whole. It is used by many proteins as a regulatory mechanism, changing the conformation and behavior of the polypeptide in acidic regions such as the late endosome or lysosome, enforcing conformation change in enzymes. However only a few histidines are needed for this, so it is comp ...
PRODUCTION, CHARACTERIZATION AND MOLECULAR DOCKING OF MYCOPHENOLIC ACID BYSSOCHLAMYS NIVEA Original Article
... was analyzed using HPLC with C18 coloumn [14]. The identification of the acid was performed with a linear elution gradient by using 33 mM acetic acid (solvent A) and acetonitrile (solvent B) according to the method described by [12]. For the identification of mycophenolic acid, the gradient program ...
... was analyzed using HPLC with C18 coloumn [14]. The identification of the acid was performed with a linear elution gradient by using 33 mM acetic acid (solvent A) and acetonitrile (solvent B) according to the method described by [12]. For the identification of mycophenolic acid, the gradient program ...
Mistranslation and its control by tRNA synthetases
... [35]. The amino acid attachment site is a terminal adenosine at the 30 -end of one arm (the ‘acceptor arm’) of the L, which ends in the sequence NCCA30 OH. The anticodon is at the end of the other arm of the L, separated by 76 Å from the amino acid acceptor site. A single G:U base pair, located pro ...
... [35]. The amino acid attachment site is a terminal adenosine at the 30 -end of one arm (the ‘acceptor arm’) of the L, which ends in the sequence NCCA30 OH. The anticodon is at the end of the other arm of the L, separated by 76 Å from the amino acid acceptor site. A single G:U base pair, located pro ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.