Habitats - Wenatchee High School
... – Natural populations do not exhibit exponential growth all the time… – Cases when growth slows or stops: • As resources decrease • Deathrate = birthrate • Immigration = emigration ...
... – Natural populations do not exhibit exponential growth all the time… – Cases when growth slows or stops: • As resources decrease • Deathrate = birthrate • Immigration = emigration ...
CH 5 Overview Notes
... • certain human activities—such as damming rivers and clear-cutting forests ...
... • certain human activities—such as damming rivers and clear-cutting forests ...
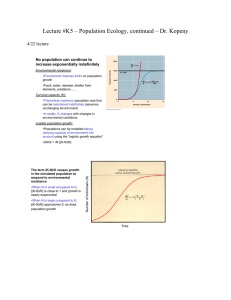
Lecture #K5 – Population Ecology, continued – Dr
... •Hypothetical example: food becomes limiting, but birthrate not immediately affected because females use energy reserves to continue producing eggs for a period; population may then overshoot carrying capacity •Real life: In many of the populations that show sigmoidal-type growth, they oscillate aro ...
... •Hypothetical example: food becomes limiting, but birthrate not immediately affected because females use energy reserves to continue producing eggs for a period; population may then overshoot carrying capacity •Real life: In many of the populations that show sigmoidal-type growth, they oscillate aro ...
What are some of the factors that limit population growth?
... Determined by: The species itself and the environment (resources available, predation, etc…) ...
... Determined by: The species itself and the environment (resources available, predation, etc…) ...
Slide 1
... Equal catchability of all individuals in all samples Equal probability of survival Marks are not lost Sampling time is negligible compared to intervals between samples ...
... Equal catchability of all individuals in all samples Equal probability of survival Marks are not lost Sampling time is negligible compared to intervals between samples ...
Population Dynamics in Ecosystems and Human Impact
... • Density Dependent Factors: Factors that limit the size of a population and only exist when populations get too big ...
... • Density Dependent Factors: Factors that limit the size of a population and only exist when populations get too big ...
Chapter 8
... organisms) or volume (for aquatic organisms) At low population densities, individuals are spaced well apart. Examples: territorial, solitary mammalian species such as tigers and plant species in marginal environments. At high population densities, individuals are crowded together. Examples: colonial ...
... organisms) or volume (for aquatic organisms) At low population densities, individuals are spaced well apart. Examples: territorial, solitary mammalian species such as tigers and plant species in marginal environments. At high population densities, individuals are crowded together. Examples: colonial ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... world’s population every year. – Current doubling time is 56 years • (length of time it takes for population size to double) ...
... world’s population every year. – Current doubling time is 56 years • (length of time it takes for population size to double) ...
Chapter 4 Population and Environment
... Dying-off population If birth rate decreases pre-reproductive group decreases, correspondingly other two groups also decreases • there is low percentage of young people Developing and under-developed countries have rapid population growth. Ex. India, China Dispersion The spatial pattern of individua ...
... Dying-off population If birth rate decreases pre-reproductive group decreases, correspondingly other two groups also decreases • there is low percentage of young people Developing and under-developed countries have rapid population growth. Ex. India, China Dispersion The spatial pattern of individua ...
Inquiry into Life, Eleventh Edition
... Patterns of population growth cont’d. • More-developed versus less-developed countries – MDC’s • Population growth is low and standard of living high • Increased rapidly between 1850 and 1950 due to decreased death rate • This was followed by a decrease in birth rate-demographic transition • Has st ...
... Patterns of population growth cont’d. • More-developed versus less-developed countries – MDC’s • Population growth is low and standard of living high • Increased rapidly between 1850 and 1950 due to decreased death rate • This was followed by a decrease in birth rate-demographic transition • Has st ...
population ecology 2010
... births and deaths) – There is a dynamic balance between biotic potential and environmental resistance ...
... births and deaths) – There is a dynamic balance between biotic potential and environmental resistance ...
Population Ecology
... i) ΔN = change in population size ii) Δ t = time interval iii) B = number of births iv) D = number of deaths IV) Per Capita (Per individual0 Growth Rate a) Now express B as average birth (bN) per capita (per individual) per year → i) b= per capita birth rate → number offspring produced per year by a ...
... i) ΔN = change in population size ii) Δ t = time interval iii) B = number of births iv) D = number of deaths IV) Per Capita (Per individual0 Growth Rate a) Now express B as average birth (bN) per capita (per individual) per year → i) b= per capita birth rate → number offspring produced per year by a ...
lecture_ch14_Population Ecology1
... produce many offspring, beginning just after birth, continuing every year, while growing tremendously large, to reduce the predation risk and living forever. ...
... produce many offspring, beginning just after birth, continuing every year, while growing tremendously large, to reduce the predation risk and living forever. ...
Marine Ecology 2011-final Lecture 2, pop
... • Fixed amounts of energy (investing energy in one will take it from another) The goal of theory of life history strategies: to predict the characteristics of any organism that you should expect to find under any given set of conditions ...
... • Fixed amounts of energy (investing energy in one will take it from another) The goal of theory of life history strategies: to predict the characteristics of any organism that you should expect to find under any given set of conditions ...
Human population overshoot what went wrong?
... In Kenya, we do use electricity (hydro / diesel), if we can. We have constant power cuts. But that‟s not the only limit. In fact, the vast majority of us, even the so-called middleclass, build our lives around limits. Limits are the basis for every decision we make, business or otherwise. It is, you ...
... In Kenya, we do use electricity (hydro / diesel), if we can. We have constant power cuts. But that‟s not the only limit. In fact, the vast majority of us, even the so-called middleclass, build our lives around limits. Limits are the basis for every decision we make, business or otherwise. It is, you ...
Population Ecology
... There are about 3 humans added to the world’s population every second Every 20 minutes, there are 3,600 new humans added to the world Every 20 minutes, there is one species of plant or animal that becomes extinct The human population is expected to continue increasing for at least the next several d ...
... There are about 3 humans added to the world’s population every second Every 20 minutes, there are 3,600 new humans added to the world Every 20 minutes, there is one species of plant or animal that becomes extinct The human population is expected to continue increasing for at least the next several d ...
Chapter 52 - Canyon ISD
... • Demographic transition: a shift from zero population growth in which birth rates and death rates are high to zero population growth characterized by low birth and death rates ...
... • Demographic transition: a shift from zero population growth in which birth rates and death rates are high to zero population growth characterized by low birth and death rates ...
Organismal Biology/52D-PopultionLimtngFactrs
... • Waste accumulation is another component that can regulate population size. • In wine, as yeast populations increase, they make more alcohol during fermentation. • However, yeast can only withstand an alcohol percentage of approximately 13% before they begin to die. • Disease can also regulate pop ...
... • Waste accumulation is another component that can regulate population size. • In wine, as yeast populations increase, they make more alcohol during fermentation. • However, yeast can only withstand an alcohol percentage of approximately 13% before they begin to die. • Disease can also regulate pop ...
12.4 - Factors Affecting Population Growth
... sustain itself. This is known as the Allee Effect, where some plants and animals which reach a population size too small (density) so they will see a decrease in their per capita growth rate, the population will continue to decrease in size, which in turn will lead to an increase in extinction rate ...
... sustain itself. This is known as the Allee Effect, where some plants and animals which reach a population size too small (density) so they will see a decrease in their per capita growth rate, the population will continue to decrease in size, which in turn will lead to an increase in extinction rate ...
FOUR (4) FACTORS AFFECTING DENSITY • IMMIGRATION
... POPULATION SIZE • IF r < 1--DECREASE IN SIZE • IF r > 1--INCREASE IN SIZE • ORDER OF MAGNITUDE OF r DETERMINES RATE OF CHANGE • IF r REMAINS CONSTANT, THEN RATE OF CHANGE IS CONSTANT ...
... POPULATION SIZE • IF r < 1--DECREASE IN SIZE • IF r > 1--INCREASE IN SIZE • ORDER OF MAGNITUDE OF r DETERMINES RATE OF CHANGE • IF r REMAINS CONSTANT, THEN RATE OF CHANGE IS CONSTANT ...
BIOLOGY 154: ECOLOGY and ENVIRONMENTAL ISSUES
... • Use Chi2 to determine if the deviations between the observed and predicted numbers are likely due to chance ...
... • Use Chi2 to determine if the deviations between the observed and predicted numbers are likely due to chance ...
The Lesson of the Kaibab
... hunting. In addition, in 1907, The Forest Service tried to exterminate the predators of the deer. Between 1907 and 1939, 816 mountain lions, 20 wolves, 7388 coyotes and more than 500 bobcats were killed. Signs that the deer population was out of control began to appear as early as 1920 - the range w ...
... hunting. In addition, in 1907, The Forest Service tried to exterminate the predators of the deer. Between 1907 and 1939, 816 mountain lions, 20 wolves, 7388 coyotes and more than 500 bobcats were killed. Signs that the deer population was out of control began to appear as early as 1920 - the range w ...
Slide 1
... Succession of one community by another goes on until a mature, stable community develops. Such a community is called a climax community. In an ecosystem with climax community, the conditions continue to be suitable for all members. The climax community remains until an event such as, fire, flood, ...
... Succession of one community by another goes on until a mature, stable community develops. Such a community is called a climax community. In an ecosystem with climax community, the conditions continue to be suitable for all members. The climax community remains until an event such as, fire, flood, ...
Chapter 4 Notes - Riverton High School
... Principles of Population Growth • A population is a group of organisms, all of the same species, that live in a specific area. • A healthy population will grow and die at a steady rate unless it runs out of food or space, or is attacked in some way by disease or predators. • Scientists study changes ...
... Principles of Population Growth • A population is a group of organisms, all of the same species, that live in a specific area. • A healthy population will grow and die at a steady rate unless it runs out of food or space, or is attacked in some way by disease or predators. • Scientists study changes ...
World population
In demographics and general statistics, the term world population refers to the total number of living humans on Earth. The United States Census Bureau estimates that the world population exceeded 7 billion on March 12, 2012. According to a separate estimate by the United Nations Population Fund, it reached this milestone on October 31, 2011. In July 2015, the Population Division of the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs estimated the world population at approximately 7.3 billion.The world population has experienced continuous growth since the end of the Great Famine and the Black Death in 1350, when it was near 370 million. The highest growth rates – global population increases above 1.8% per year – occurred briefly during the 1950s, and for longer during the 1960s and 1970s. The global growth rate peaked at 2.2% in 1963, and has declined to 1.1% as of 2012. Total annual births were highest in the late 1980s at about 139 million, and are now expected to remain essentially constant at their 2011 level of 135 million, while deaths number 56 million per year, and are expected to increase to 80 million per year by 2040.The 2012 UN projections show a continued increase in population in the near future with a steady decline in population growth rate; the global population is expected to reach between 8.3 and 10.9 billion by 2050. 2003 UN Population Division population projections for the year 2150 range between 3.2 and 24.8 billion. One of many independent mathematical models supports the lower estimate, while a 2014 estimate forecasts between 9.3 and 12.6 billion in 2100, and continued growth thereafter. Some analysts have questioned the sustainability of further world population growth, highlighting the growing pressures on the environment, global food supplies, and energy resources.Various scholarly estimates have been made of the total number of humans who have ever lived, giving figures ranging from approximately 100 billion to 115 billion.