I can compare 2 different biomes by explaining how they are similar
... 26. Describe the four stages of the demographic transition. 27. Explain why different countries may be at different stages of the demographic transition. 28. Describe three problems caused by rapid human population growth. 29. Compare population growth problems in more-developed countries and less d ...
... 26. Describe the four stages of the demographic transition. 27. Explain why different countries may be at different stages of the demographic transition. 28. Describe three problems caused by rapid human population growth. 29. Compare population growth problems in more-developed countries and less d ...
HUMAN POPULATION ISSUES
... two populations fluctuate with about 10 years between successive high populations. The change in the lynx population usually followed changes in the varying hare population ...
... two populations fluctuate with about 10 years between successive high populations. The change in the lynx population usually followed changes in the varying hare population ...
Lesson 02- Population and Carrying Capacity kw
... 2. How could the moose population change from zero to four from year 1 to year 2? 3. Is there a relationship between moose and wolf populations? If so, explain it. 4. What other factors might be present that might account for changes in the populations? 5. Predict what might happen to the moose ...
... 2. How could the moose population change from zero to four from year 1 to year 2? 3. Is there a relationship between moose and wolf populations? If so, explain it. 4. What other factors might be present that might account for changes in the populations? 5. Predict what might happen to the moose ...
Introduction to Ecology Organisms don`t live in a vacuum!
... The life cycle of common fruit flies (Drosophila melanogaster) takes about seven days under ideal conditions. Starting with one pair of flies, in one year you would have a ball of flies as large as the Earth. Clearly this can’t happen in the real world—something must act to keep populations down. ...
... The life cycle of common fruit flies (Drosophila melanogaster) takes about seven days under ideal conditions. Starting with one pair of flies, in one year you would have a ball of flies as large as the Earth. Clearly this can’t happen in the real world—something must act to keep populations down. ...
Population - Ms. Farrell`s Science Center
... • How large will the rabbit population be in 10 years? • N=1,484 ...
... • How large will the rabbit population be in 10 years? • N=1,484 ...
Exponential Growth
... Pribilof Islands (St. Paul) in the Bering Sea off Alaska. Food was plentiful, and the reindeer encountered no predators on the island. The herd grew exponentially (note the initial J shape) until it reached 2000 reindeer in 1926. At this point, the small island was seriously overgrazed, food was sca ...
... Pribilof Islands (St. Paul) in the Bering Sea off Alaska. Food was plentiful, and the reindeer encountered no predators on the island. The herd grew exponentially (note the initial J shape) until it reached 2000 reindeer in 1926. At this point, the small island was seriously overgrazed, food was sca ...
pop ecol apr18 02
... A fur seal population on St. Paul Island, Alaska The numbers of male fur seals with harems were reduced to very low numbers due to huntin untill 1911. After hunting was banned, the population increased diramatically and now oscillates around an equilibrium number, presumably the islands carrying cap ...
... A fur seal population on St. Paul Island, Alaska The numbers of male fur seals with harems were reduced to very low numbers due to huntin untill 1911. After hunting was banned, the population increased diramatically and now oscillates around an equilibrium number, presumably the islands carrying cap ...
Limits to Growth and Human Carrying Capacity
... 1. Water and soil are valuable resources, which must be used more carefully as the human population grows. 2. Much of the current agricultural practices result in soil degradation and water pollution. Thus our food supply is unsustainable. 3. Nonrenewable energy resources will be consumed at some po ...
... 1. Water and soil are valuable resources, which must be used more carefully as the human population grows. 2. Much of the current agricultural practices result in soil degradation and water pollution. Thus our food supply is unsustainable. 3. Nonrenewable energy resources will be consumed at some po ...
Population Dynamics Populations Organisms do not generally live
... Reproductive age are those persons that are capable of reproduction. Postreproductive age are those persons too old to reproduce. ...
... Reproductive age are those persons that are capable of reproduction. Postreproductive age are those persons too old to reproduce. ...
population dynamics
... of parental caregiving in European kestrels over 5 years. The researchers transferred chicks among nests to produce reduced broods (three or four chicks), normal broods (five or six), and enlarged broods (seven or eight). They then measured the percentage of male and female parent birds that survive ...
... of parental caregiving in European kestrels over 5 years. The researchers transferred chicks among nests to produce reduced broods (three or four chicks), normal broods (five or six), and enlarged broods (seven or eight). They then measured the percentage of male and female parent birds that survive ...
Limits on Populations.
... Species vary in their capacity to reproduce. iotic potential is the maximum number of offspring that a species could produce, if resources were unlimited. You have seen how quickly field mice reproduce, but many animals have a much lower biotic potential. For example, mature female black bears give ...
... Species vary in their capacity to reproduce. iotic potential is the maximum number of offspring that a species could produce, if resources were unlimited. You have seen how quickly field mice reproduce, but many animals have a much lower biotic potential. For example, mature female black bears give ...
PVA
... + allow estimation of extinction probability (run 1,000 simulations, tally number of extinction events) + indicates which factors are most important in declines – requires large amounts of data – not generalizable - build anew for each species ...
... + allow estimation of extinction probability (run 1,000 simulations, tally number of extinction events) + indicates which factors are most important in declines – requires large amounts of data – not generalizable - build anew for each species ...
General Population Change
... population growth controls • Unchecked population growth – Biotic potential – capacity for growth – Intrinsic rate of increase – the rate at which a population would grow if it had unlimited resources ...
... population growth controls • Unchecked population growth – Biotic potential – capacity for growth – Intrinsic rate of increase – the rate at which a population would grow if it had unlimited resources ...
File
... “In the second or two it took to read this sentence, 21 babies were born somewhere in the world and nine people died. The statistics may have changed a bit by the time you read this, but births will still far outnumber death. An imbalance between births and deaths is the cause for population growt ...
... “In the second or two it took to read this sentence, 21 babies were born somewhere in the world and nine people died. The statistics may have changed a bit by the time you read this, but births will still far outnumber death. An imbalance between births and deaths is the cause for population growt ...
SBI4U Population Dynamics
... What is the formula that is used to determine “population growth” or “population change”? A population of 2000 seals produces 950 young in one year. In the same period of time, 150 seals die. If 50 seals leave the population to join another population, and 30 seals join the population under study, w ...
... What is the formula that is used to determine “population growth” or “population change”? A population of 2000 seals produces 950 young in one year. In the same period of time, 150 seals die. If 50 seals leave the population to join another population, and 30 seals join the population under study, w ...
Document
... b) more people live in Mexico than in Sweden. c) birth rates and death rates do not appear to be correlated. d) a Swedish person born in 1900 is more likely to be dead than a Mexican person born in 1900. e) these populations are probably far away from their carrying capacity. ...
... b) more people live in Mexico than in Sweden. c) birth rates and death rates do not appear to be correlated. d) a Swedish person born in 1900 is more likely to be dead than a Mexican person born in 1900. e) these populations are probably far away from their carrying capacity. ...
Document
... • What is Earth’s carrying capacity for human’s? • Have we already exceeded K? • What are consequences of human population growth for other species on this ...
... • What is Earth’s carrying capacity for human’s? • Have we already exceeded K? • What are consequences of human population growth for other species on this ...
Chapter 8 - TeacherWeb
... A. Populations change in size, density, and age distribution, most members of populations live together in clumps or groups 1. Three general patterns of population distribution occur in a habitat: clumping, uniform distribution and random dispersion. Most species live in clumps or groups. a. Availab ...
... A. Populations change in size, density, and age distribution, most members of populations live together in clumps or groups 1. Three general patterns of population distribution occur in a habitat: clumping, uniform distribution and random dispersion. Most species live in clumps or groups. a. Availab ...
Population Ecology
... A. Populations change in size, density, and age distribution, most members of populations live together in clumps or groups 1. Three general patterns of population distribution occur in a habitat: clumping, uniform distribution and random dispersion. Most species live in clumps or groups. a. Availab ...
... A. Populations change in size, density, and age distribution, most members of populations live together in clumps or groups 1. Three general patterns of population distribution occur in a habitat: clumping, uniform distribution and random dispersion. Most species live in clumps or groups. a. Availab ...
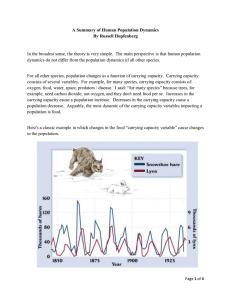
a Summary of Human Population Dynamics
... The incontrovertible truth was that ever-increasing hare-meat was the fuel enabling the reality of lynx population growth. However, the mal-distribution of hare-meat was just as real; and, it simulated the circumstances of a hare-meat shortage to the lynx that saw their fellow lynx starve. Not surpr ...
... The incontrovertible truth was that ever-increasing hare-meat was the fuel enabling the reality of lynx population growth. However, the mal-distribution of hare-meat was just as real; and, it simulated the circumstances of a hare-meat shortage to the lynx that saw their fellow lynx starve. Not surpr ...
Prentice Hall Biology
... stable. Then, as advances in medicine, agriculture, and technology occurred, the human population began growing very rapidly. Today, the world’s human population is greater than 6 billion people, and it continues to grow, but at a slower rate. ...
... stable. Then, as advances in medicine, agriculture, and technology occurred, the human population began growing very rapidly. Today, the world’s human population is greater than 6 billion people, and it continues to grow, but at a slower rate. ...
國立臺南大學 生態科學與技術學系 生態學期末考題 (A 卷)
... exhibit either logistic growth, dampened oscillations, or fluctuate forever in a stable limit cycle. Whichever one of these patterns is actually exhibited by a population depends upon the product of the ___________ and the ____________. (A) Population growth rate under ideal conditions; starting pop ...
... exhibit either logistic growth, dampened oscillations, or fluctuate forever in a stable limit cycle. Whichever one of these patterns is actually exhibited by a population depends upon the product of the ___________ and the ____________. (A) Population growth rate under ideal conditions; starting pop ...
Les populations et les communautés
... b) Recapturing took place in May, when it was observed that many females were about to give birth. In light of this information, is the groundhog population more likely to grow or decrease? ...
... b) Recapturing took place in May, when it was observed that many females were about to give birth. In light of this information, is the groundhog population more likely to grow or decrease? ...
Population Ecology - School of Environmental and Forest Sciences
... • Density dependence tends to push populations toward carrying capacity, K • Consequently, populations do not grow indefinitely (over long term) • Yet they often don’t rest at K either – i.e., density dependence doesn’t always lead to a static equilibrium ...
... • Density dependence tends to push populations toward carrying capacity, K • Consequently, populations do not grow indefinitely (over long term) • Yet they often don’t rest at K either – i.e., density dependence doesn’t always lead to a static equilibrium ...
Biological populations and communities
... • Population growth curves graph how populations grow and are used to determine: how fast a population could grow the population size now and in the future ...
... • Population growth curves graph how populations grow and are used to determine: how fast a population could grow the population size now and in the future ...
World population
In demographics and general statistics, the term world population refers to the total number of living humans on Earth. The United States Census Bureau estimates that the world population exceeded 7 billion on March 12, 2012. According to a separate estimate by the United Nations Population Fund, it reached this milestone on October 31, 2011. In July 2015, the Population Division of the United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs estimated the world population at approximately 7.3 billion.The world population has experienced continuous growth since the end of the Great Famine and the Black Death in 1350, when it was near 370 million. The highest growth rates – global population increases above 1.8% per year – occurred briefly during the 1950s, and for longer during the 1960s and 1970s. The global growth rate peaked at 2.2% in 1963, and has declined to 1.1% as of 2012. Total annual births were highest in the late 1980s at about 139 million, and are now expected to remain essentially constant at their 2011 level of 135 million, while deaths number 56 million per year, and are expected to increase to 80 million per year by 2040.The 2012 UN projections show a continued increase in population in the near future with a steady decline in population growth rate; the global population is expected to reach between 8.3 and 10.9 billion by 2050. 2003 UN Population Division population projections for the year 2150 range between 3.2 and 24.8 billion. One of many independent mathematical models supports the lower estimate, while a 2014 estimate forecasts between 9.3 and 12.6 billion in 2100, and continued growth thereafter. Some analysts have questioned the sustainability of further world population growth, highlighting the growing pressures on the environment, global food supplies, and energy resources.Various scholarly estimates have been made of the total number of humans who have ever lived, giving figures ranging from approximately 100 billion to 115 billion.