Ecology: Lecture 1
... similar species scarcely ever occupy similar niches, but displace each other in such a manner that each takes possession of certainly particular kinds of food and modes of life in which it has an advantage over its competitor.” ...
... similar species scarcely ever occupy similar niches, but displace each other in such a manner that each takes possession of certainly particular kinds of food and modes of life in which it has an advantage over its competitor.” ...
Biology I Jeopardy Chapters 2-5: Ecology
... Density-dependent factors: have an increasing effect as the population increases. Ex: disease, competition, predators, predation, food Density-independent factors: affect populations regardless of their density. Ex: volcanic eruptions, temperature, ...
... Density-dependent factors: have an increasing effect as the population increases. Ex: disease, competition, predators, predation, food Density-independent factors: affect populations regardless of their density. Ex: volcanic eruptions, temperature, ...
Microsoft Word - Activity4.doc
... ______ As a result of resource partitioning, certain characteristics may enable individuals to obtain resources in their partitions more successfully. Selection of these characteristics (or characters) reduces competition with individual in other partitions and leads to a divergence of features. ___ ...
... ______ As a result of resource partitioning, certain characteristics may enable individuals to obtain resources in their partitions more successfully. Selection of these characteristics (or characters) reduces competition with individual in other partitions and leads to a divergence of features. ___ ...
Biodiversity Index
... When scientists speak of the variety of organisms (and their genes) in an ecosystem, they refer to it as biodiversity. A biologically diverse ecosystem, such as an old growth forest or tropical rain forest, is healthy, complex and stable. Nature tends to increase diversity through the process of suc ...
... When scientists speak of the variety of organisms (and their genes) in an ecosystem, they refer to it as biodiversity. A biologically diverse ecosystem, such as an old growth forest or tropical rain forest, is healthy, complex and stable. Nature tends to increase diversity through the process of suc ...
Credit III Geography as the Study of Environment
... 2. What is an ecosystem, name its broad types and define any one. ...
... 2. What is an ecosystem, name its broad types and define any one. ...
Population Ecology notes
... 1. The population experiences exponential growth. 2. Population size (and density) increases, the growth rate decreases as a result of density-dependent factors. 3. The population approaches the carrying capacity, K, the number of individuals that the environment can support ...
... 1. The population experiences exponential growth. 2. Population size (and density) increases, the growth rate decreases as a result of density-dependent factors. 3. The population approaches the carrying capacity, K, the number of individuals that the environment can support ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Limits to Growth
... hypothesis to explain this shift. • According to this hypothesis, these countries have completed the demographic transition, a dramatic change in birth and death rates. ...
... hypothesis to explain this shift. • According to this hypothesis, these countries have completed the demographic transition, a dramatic change in birth and death rates. ...
Ecosystems
... species that an ecosystem can support over time When areas exceed carrying capacity leads to competition for resources ...
... species that an ecosystem can support over time When areas exceed carrying capacity leads to competition for resources ...
ICS Final Exam Study Guide
... Emigration- the movement of individuals out of an area, can cause a population to decrease in size. Exponential growth- occur when the individuals in a population reproduce at a constant rate. Logistic growth- occurs when a population’s growth slows or stops following a period of exponential growth. ...
... Emigration- the movement of individuals out of an area, can cause a population to decrease in size. Exponential growth- occur when the individuals in a population reproduce at a constant rate. Logistic growth- occurs when a population’s growth slows or stops following a period of exponential growth. ...
Unit 1 - Cook County Schools
... SEV1. Students will investigate the flow of energy and cycling of matter within an ecosystem and relate these phenomena to human society. a. Interpret biogeochemical cycles including hydrologic, nitrogen, phosphorus, oxygen, and carbon cycles. Recognize that energy is not recycled in ecosystems. b. ...
... SEV1. Students will investigate the flow of energy and cycling of matter within an ecosystem and relate these phenomena to human society. a. Interpret biogeochemical cycles including hydrologic, nitrogen, phosphorus, oxygen, and carbon cycles. Recognize that energy is not recycled in ecosystems. b. ...
Study Guide – Interactions of Living Things
... 2. What does a food chain show? Energy flow between specific organisms. (A food web shows energy flow between organisms from many different food chains) ...
... 2. What does a food chain show? Energy flow between specific organisms. (A food web shows energy flow between organisms from many different food chains) ...
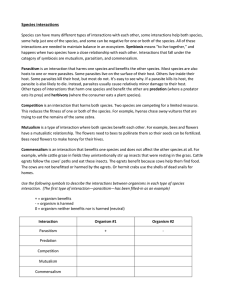
Species interactions
... Species can have many different types of interactions with each other, some interactions help both species, some help just one of the species, and some can be negative for one or both of the species. All of these interactions are needed to maintain balance in an ecosystem. Symbiosis means “to live t ...
... Species can have many different types of interactions with each other, some interactions help both species, some help just one of the species, and some can be negative for one or both of the species. All of these interactions are needed to maintain balance in an ecosystem. Symbiosis means “to live t ...
Priceless or worthless?
... Scientifically, of course, this is true. Yet science is rarely the sole measurement that we humans use to make our global decisions. As humans, we see the world from our own point of view. Game birds are protected by gamekeepers not for their own intrinsic value, but so that they can be shot. We lik ...
... Scientifically, of course, this is true. Yet science is rarely the sole measurement that we humans use to make our global decisions. As humans, we see the world from our own point of view. Game birds are protected by gamekeepers not for their own intrinsic value, but so that they can be shot. We lik ...
Complexity and Stability - Powerpoint for Nov. 2.
... 1) Non-interactors - species does not affect population of those species with which it interacts 2) weak interactors - species only influences those species with which it interacts directly - effects may be large 3) strong interactors - species that directly and indirectly effects other species - th ...
... 1) Non-interactors - species does not affect population of those species with which it interacts 2) weak interactors - species only influences those species with which it interacts directly - effects may be large 3) strong interactors - species that directly and indirectly effects other species - th ...
6.2 An ecosystem is composed of all the populations
... 5. Food chains are models that show how materials and energy are transferred from one organism to another in an ecosystem. The basis of every food chain is the energy stored in green plants. Food webs are models that show the complex variety of energy sources available to most organisms in an ecosys ...
... 5. Food chains are models that show how materials and energy are transferred from one organism to another in an ecosystem. The basis of every food chain is the energy stored in green plants. Food webs are models that show the complex variety of energy sources available to most organisms in an ecosys ...
Ecology Powerpoint
... (for photosynthesis), providing shelter and food for other organisms (e.g. bees, ants, etc.), and giving off oxygen into the atmosphere. ...
... (for photosynthesis), providing shelter and food for other organisms (e.g. bees, ants, etc.), and giving off oxygen into the atmosphere. ...
DINEEnv Science Chapter 1 Science and the Environment Section 1
... ______________________________________ is an undesirable change in the natural environment that is caused by the introduction of substances that are harmful to living organisms or by excessive wastes, heat, noise, or radiation ...
... ______________________________________ is an undesirable change in the natural environment that is caused by the introduction of substances that are harmful to living organisms or by excessive wastes, heat, noise, or radiation ...
Limiting Factors…
... Exponential Growth Rate • Occurs when organisms have ideal conditions • More individuals = faster growth ...
... Exponential Growth Rate • Occurs when organisms have ideal conditions • More individuals = faster growth ...
Confusing Ecology with Environmentalism 1
... concerned about, and, more importantly, to act on issues of environmental protection. Ecologists can provide information needed by decision-makers. Hence, environmentalists' and ecologists' efforts are complimentary. Many ecologists are becoming environmentalists and are using their scientific exper ...
... concerned about, and, more importantly, to act on issues of environmental protection. Ecologists can provide information needed by decision-makers. Hence, environmentalists' and ecologists' efforts are complimentary. Many ecologists are becoming environmentalists and are using their scientific exper ...
Florida 4-H Environmental Education Activities
... population size of the predator in an inverse relationship. Under controlled laboratory conditions, situations have been observed in which both the predator and the prey may be eliminated. In natural systems, extinction of populations caused by predation is much more rare. Extinction of an organism ...
... population size of the predator in an inverse relationship. Under controlled laboratory conditions, situations have been observed in which both the predator and the prey may be eliminated. In natural systems, extinction of populations caused by predation is much more rare. Extinction of an organism ...
Theoretical ecology

Theoretical ecology is the scientific discipline devoted to the study of ecological systems using theoretical methods such as simple conceptual models, mathematical models, computational simulations, and advanced data analysis. Effective models improve understanding of the natural world by revealing how the dynamics of species populations are often based on fundamental biological conditions and processes. Further, the field aims to unify a diverse range of empirical observations by assuming that common, mechanistic processes generate observable phenomena across species and ecological environments. Based on biologically realistic assumptions, theoretical ecologists are able to uncover novel, non-intuitive insights about natural processes. Theoretical results are often verified by empirical and observational studies, revealing the power of theoretical methods in both predicting and understanding the noisy, diverse biological world.The field is broad and includes foundations in applied mathematics, computer science, biology, statistical physics, genetics, chemistry, evolution, and conservation biology. Theoretical ecology aims to explain a diverse range of phenomena in the life sciences, such as population growth and dynamics, fisheries, competition, evolutionary theory, epidemiology, animal behavior and group dynamics, food webs, ecosystems, spatial ecology, and the effects of climate change.Theoretical ecology has further benefited from the advent of fast computing power, allowing the analysis and visualization of large-scale computational simulations of ecological phenomena. Importantly, these modern tools provide quantitative predictions about the effects of human induced environmental change on a diverse variety of ecological phenomena, such as: species invasions, climate change, the effect of fishing and hunting on food network stability, and the global carbon cycle.