From ecological aspect - 2010 Sophomore Composition
... biological diversity and genetic library for future generations… Up to 60000 reef living animals and plants have been described to date. 5. Among these species are keystone process species that regulate ecosystem processes and functions, for example through grazing(牧場) and predation. Others species ...
... biological diversity and genetic library for future generations… Up to 60000 reef living animals and plants have been described to date. 5. Among these species are keystone process species that regulate ecosystem processes and functions, for example through grazing(牧場) and predation. Others species ...
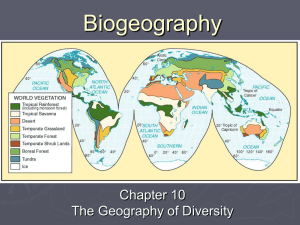
Chapter 10: The Geography of Diversity
... Bushy-tailed woodrat (Neotomoa nicerea), over both geographic space and evolutionary time. ...
... Bushy-tailed woodrat (Neotomoa nicerea), over both geographic space and evolutionary time. ...
Research Vegetation Ecologist
... management for ecological communities at risk in British Columbia. The Vegetation Ecologist contributes to the compilation, analyses, and maintenance of data and information on ecological communities in British Columbia from multiple sources. They maintain and update the list of ecosystems at risk i ...
... management for ecological communities at risk in British Columbia. The Vegetation Ecologist contributes to the compilation, analyses, and maintenance of data and information on ecological communities in British Columbia from multiple sources. They maintain and update the list of ecosystems at risk i ...
Predator-prey relationships
... organisms; so simple food chains are rare in nature. There are also many different species of fish and sharks. So a food chain cannot end with a shark; it must end with a distinct species of shark. A food chain does not contain the general category of "fish," it will contain specific species of fish ...
... organisms; so simple food chains are rare in nature. There are also many different species of fish and sharks. So a food chain cannot end with a shark; it must end with a distinct species of shark. A food chain does not contain the general category of "fish," it will contain specific species of fish ...
Ecology - Fall River Public Schools
... List the levels of ecological organization from largest to smallest. ...
... List the levels of ecological organization from largest to smallest. ...
File
... Predation-one species feeds directly on another Symbiotic Interactions Parasitism-one species uses a another as a host to gain nutrients in a way that it harms the host. Usually on or in the host Mutualism- interactions between two different species in which both species benefit from each othe ...
... Predation-one species feeds directly on another Symbiotic Interactions Parasitism-one species uses a another as a host to gain nutrients in a way that it harms the host. Usually on or in the host Mutualism- interactions between two different species in which both species benefit from each othe ...
File - Ms. D. Science CGPA
... use the same limited resources in the same place, at the same time. Parasite- The organism that benefits by living with, on, or in a host in a parasitism interaction. Host-An organism that a parasite lives with, in, or on, and provides a source of energy or a suitable environment for the parasite to ...
... use the same limited resources in the same place, at the same time. Parasite- The organism that benefits by living with, on, or in a host in a parasitism interaction. Host-An organism that a parasite lives with, in, or on, and provides a source of energy or a suitable environment for the parasite to ...
Chapter 11. Diversification of the Eukaryotes: Animals
... • Describe the sub-discipline of population ecology • Discuss what a life history is. • Explain how ecology influences the evolution of aging in a population. • Describe how the human population is growing. ...
... • Describe the sub-discipline of population ecology • Discuss what a life history is. • Explain how ecology influences the evolution of aging in a population. • Describe how the human population is growing. ...
Biodiversity
... Restoration ecology – seeks to reverse population declines by applying ecological principles in an effort to return ecosystems to their natural state. Techniques such as bioremediation and biological augmentation can help restore degraded ecosystems. The basic assumption is that most environmental d ...
... Restoration ecology – seeks to reverse population declines by applying ecological principles in an effort to return ecosystems to their natural state. Techniques such as bioremediation and biological augmentation can help restore degraded ecosystems. The basic assumption is that most environmental d ...
Brian Gelbach January 22, 2012 20155660 Biology Period 8 Dr
... “The Ecological Niche.” Mikecurtis.org.uk. 22 January 2012..
...
... “The Ecological Niche.” Mikecurtis.org.uk. 22 January 2012.
Biotic Potential and Species Growth Capacity
... Students will be able to: -describe the ways in which populations can change -define carrying capacity and describe factors that affect it. -describe the principles associated with survivorship curves including k- and r- strategists. -describe and explain “S” and “J” population growth curves. ...
... Students will be able to: -describe the ways in which populations can change -define carrying capacity and describe factors that affect it. -describe the principles associated with survivorship curves including k- and r- strategists. -describe and explain “S” and “J” population growth curves. ...
Aquatic Biomes
... • Pioneer organisms modify their environment, thus establishing conditions under which more advanced organisms can live. • (ex. seasonal dieback and erosion, for example, would create pockets of "soil" in the crevices and hollows of the bare rock inhabited by the lichen) ...
... • Pioneer organisms modify their environment, thus establishing conditions under which more advanced organisms can live. • (ex. seasonal dieback and erosion, for example, would create pockets of "soil" in the crevices and hollows of the bare rock inhabited by the lichen) ...
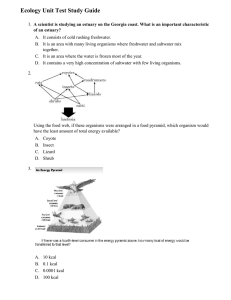
ecology unit study guide
... 24. An example of a symbiotic relationship is found between the clown fish and the sea anemone. The sea anemone provides protection for the fish and the fish provides food for the sea anemone. What category best describes this relationship? A. B. C. D. ...
... 24. An example of a symbiotic relationship is found between the clown fish and the sea anemone. The sea anemone provides protection for the fish and the fish provides food for the sea anemone. What category best describes this relationship? A. B. C. D. ...
Principles of Population Ecology How Do Populations Change in
... 1. Define Population Ecology 2. Define growth rate and explain the factors that produce changes in population size 3. Explain how human population change is calculated 4. Understand how the following terms are related to population growth: intrinsic rate of increase, exponential population growth, e ...
... 1. Define Population Ecology 2. Define growth rate and explain the factors that produce changes in population size 3. Explain how human population change is calculated 4. Understand how the following terms are related to population growth: intrinsic rate of increase, exponential population growth, e ...
File
... Species richness- the number of species in a given area. Species evenness- the measure of whether a particular ecosystem is numerically dominated by one species or are all represented by similar numbers of individuals. ...
... Species richness- the number of species in a given area. Species evenness- the measure of whether a particular ecosystem is numerically dominated by one species or are all represented by similar numbers of individuals. ...
3.2 How Humans Influence Ecosystems
... The Effects of Deforestation Deforestation is the clearing or logging of forests for human use. some land is never reclaimed or replanted. agricultural crops that are planted are often one species = monoculture This reduces biodiversity, and leaves the crop vulnerable to pests or disease. ...
... The Effects of Deforestation Deforestation is the clearing or logging of forests for human use. some land is never reclaimed or replanted. agricultural crops that are planted are often one species = monoculture This reduces biodiversity, and leaves the crop vulnerable to pests or disease. ...
3.2 PPT
... The Effects of Deforestation Deforestation is the clearing or logging of forests for human use. some land is never reclaimed or replanted. agricultural crops that are planted are often one species = monoculture This reduces biodiversity, and leaves the crop vulnerable to pests or disease. ...
... The Effects of Deforestation Deforestation is the clearing or logging of forests for human use. some land is never reclaimed or replanted. agricultural crops that are planted are often one species = monoculture This reduces biodiversity, and leaves the crop vulnerable to pests or disease. ...
16.4 Threats To Biodiversity KEY CONCEPT biodiversity.
... Preserving biodiversity is important to the future of the biosphere. • The loss of biodiversity has long-term effects. – loss of medical and technological advances – extinction of species – loss of ecosystem stability ...
... Preserving biodiversity is important to the future of the biosphere. • The loss of biodiversity has long-term effects. – loss of medical and technological advances – extinction of species – loss of ecosystem stability ...
Chapter 22
... means a tentative explanation. In a scientific context, a theory is a useful, comprehensive, and well-supported explanation for a wide range of observations. n Evolution. In its strict biological meaning, evolution is defined as a change in allele frequencies in a population over time. By this defin ...
... means a tentative explanation. In a scientific context, a theory is a useful, comprehensive, and well-supported explanation for a wide range of observations. n Evolution. In its strict biological meaning, evolution is defined as a change in allele frequencies in a population over time. By this defin ...
SC 118 Human Biology Credit for Prior Learning
... What was the “green revolution”? What was its effect? Do we see S-shaped (sigmoid) population growth in nature? List some species that can replenish their numbers readily after a crash and some species that have very slow population growth. If the number of births per woman in the US stabilized at 2 ...
... What was the “green revolution”? What was its effect? Do we see S-shaped (sigmoid) population growth in nature? List some species that can replenish their numbers readily after a crash and some species that have very slow population growth. If the number of births per woman in the US stabilized at 2 ...
Mentor Invitational – Feb
... 79. an organism which consumes meat and plant material 80. decomposer which eats detritus and dead organisms 81. two caribou fighting for a mate (type of competition) 82. the organisms to inhabit an environment 83. the use of bacteria to clean up oil in water systems 84. the specific relationship be ...
... 79. an organism which consumes meat and plant material 80. decomposer which eats detritus and dead organisms 81. two caribou fighting for a mate (type of competition) 82. the organisms to inhabit an environment 83. the use of bacteria to clean up oil in water systems 84. the specific relationship be ...
Conservation Ecology: Scientific Responsibility and Responsible
... 1995), by integrating some of the approaches of macroecology (Brown 1995) with fine−scale, mechanistic studies, or by using theories of self−organizing processes in ecosystems (e.g., Holling et al. 1996) as a framework for evaluating scale dependency and scaling functions. Baskerville argues that, i ...
... 1995), by integrating some of the approaches of macroecology (Brown 1995) with fine−scale, mechanistic studies, or by using theories of self−organizing processes in ecosystems (e.g., Holling et al. 1996) as a framework for evaluating scale dependency and scaling functions. Baskerville argues that, i ...
Theoretical ecology

Theoretical ecology is the scientific discipline devoted to the study of ecological systems using theoretical methods such as simple conceptual models, mathematical models, computational simulations, and advanced data analysis. Effective models improve understanding of the natural world by revealing how the dynamics of species populations are often based on fundamental biological conditions and processes. Further, the field aims to unify a diverse range of empirical observations by assuming that common, mechanistic processes generate observable phenomena across species and ecological environments. Based on biologically realistic assumptions, theoretical ecologists are able to uncover novel, non-intuitive insights about natural processes. Theoretical results are often verified by empirical and observational studies, revealing the power of theoretical methods in both predicting and understanding the noisy, diverse biological world.The field is broad and includes foundations in applied mathematics, computer science, biology, statistical physics, genetics, chemistry, evolution, and conservation biology. Theoretical ecology aims to explain a diverse range of phenomena in the life sciences, such as population growth and dynamics, fisheries, competition, evolutionary theory, epidemiology, animal behavior and group dynamics, food webs, ecosystems, spatial ecology, and the effects of climate change.Theoretical ecology has further benefited from the advent of fast computing power, allowing the analysis and visualization of large-scale computational simulations of ecological phenomena. Importantly, these modern tools provide quantitative predictions about the effects of human induced environmental change on a diverse variety of ecological phenomena, such as: species invasions, climate change, the effect of fishing and hunting on food network stability, and the global carbon cycle.