Sample Final November 2007 File - Moodle
... ____ 17. Which of the following are considered benefits of multicellularity? a. Reduced mass-specific metabolic rate c. Improved ability to escape predation b. Differentiation into specialized tissues d. All of the above ____ 18. Liverworts and hornworts share most of their life cycle characteristic ...
... ____ 17. Which of the following are considered benefits of multicellularity? a. Reduced mass-specific metabolic rate c. Improved ability to escape predation b. Differentiation into specialized tissues d. All of the above ____ 18. Liverworts and hornworts share most of their life cycle characteristic ...
to the syllabus for Biology 15, Spring
... secondary succession 7. The student will be able to describe the biological regulation factors of populations such as competition, predation, symbiosis, mutualism, commensalism, parasitism and discuss r and K selection. 8. The student will be able to access current human population statistics such a ...
... secondary succession 7. The student will be able to describe the biological regulation factors of populations such as competition, predation, symbiosis, mutualism, commensalism, parasitism and discuss r and K selection. 8. The student will be able to access current human population statistics such a ...
udc 349.6 feature of maintenance of ecological function of the state
... In this riverbed, Constitution of Ukraine at one time fastened the duty of the state to provide an ecological function at constitutional level. So, article 16 of Basic Law proclaims, that providing of the ecological safety and maintenance of the ecological equilibrium on the territory of Ukraine, o ...
... In this riverbed, Constitution of Ukraine at one time fastened the duty of the state to provide an ecological function at constitutional level. So, article 16 of Basic Law proclaims, that providing of the ecological safety and maintenance of the ecological equilibrium on the territory of Ukraine, o ...
Nov 8 - University of San Diego
... Question – Can these results be extrapolated to other systems and time/space scales? Nutrient retention ...
... Question – Can these results be extrapolated to other systems and time/space scales? Nutrient retention ...
Biodiversity_and_Conservation
... What is biodiversity? Biodiversity, or Biological Diversity, is a term used to describe the variety of life in an ecosystem. This includes all species of animal, plant and invertebrate life. It can be described at many levels from species diversity (how many different species there are) to ecosystem ...
... What is biodiversity? Biodiversity, or Biological Diversity, is a term used to describe the variety of life in an ecosystem. This includes all species of animal, plant and invertebrate life. It can be described at many levels from species diversity (how many different species there are) to ecosystem ...
Global-scale modelling of atmosphere
... This studentship will contribute towards the EU project PEGASOS (Pan-European GasAeroSOls-climate interaction Study). There are two overall aims of the studentship: (i) to develop and evaluate the atmosphere-biosphere exchange scheme within the UK ChemistryAerosol model (UKCA); and (ii) to apply UKC ...
... This studentship will contribute towards the EU project PEGASOS (Pan-European GasAeroSOls-climate interaction Study). There are two overall aims of the studentship: (i) to develop and evaluate the atmosphere-biosphere exchange scheme within the UK ChemistryAerosol model (UKCA); and (ii) to apply UKC ...
The “bottom up” view of Ecosystem production The
... Reasons why we might not ‘see’ top down cascades in terrestrial ecosystems • Plants have complex tissues and anti-herbivore compounds • Terrestrial may have more complex and more detritus based food webs, less direct grazing. • Many terrestrial apex predators have been hunted to near or local extin ...
... Reasons why we might not ‘see’ top down cascades in terrestrial ecosystems • Plants have complex tissues and anti-herbivore compounds • Terrestrial may have more complex and more detritus based food webs, less direct grazing. • Many terrestrial apex predators have been hunted to near or local extin ...
chapter 5
... Briefly describe the evolution of life from chemical evolution to the development of eukaryotic cells. ...
... Briefly describe the evolution of life from chemical evolution to the development of eukaryotic cells. ...
Ecology Notes
... 1. _________________- consumer that eats only plants Ex: grasshoppers, mice, rabbits, deer, beavers, moose, cows, sheep, goats and groundhogs 2. _________________- consumer that eats only other animals. Ex: Foxes, frogs, snakes, hawks, and spiders. 3. _________________– consumer that eat the remains ...
... 1. _________________- consumer that eats only plants Ex: grasshoppers, mice, rabbits, deer, beavers, moose, cows, sheep, goats and groundhogs 2. _________________- consumer that eats only other animals. Ex: Foxes, frogs, snakes, hawks, and spiders. 3. _________________– consumer that eat the remains ...
Appendix_GCB-formatted
... similar results were derived independently by Ohlberger et al. (2011) using more sophisticated data on perch Perca fluvitatilis physiological rates, which incorporated a more realistic, hump-shaped relationship between energy gain rate and temperature (i.e., temperature optimum). This suggests that, ...
... similar results were derived independently by Ohlberger et al. (2011) using more sophisticated data on perch Perca fluvitatilis physiological rates, which incorporated a more realistic, hump-shaped relationship between energy gain rate and temperature (i.e., temperature optimum). This suggests that, ...
Interactions between Organisms
... These ‘epiphytes’ gain support & grow nearer the light then they would have done on the ground. Examples of e_______ are lichens, some algae, mosses, ferns & orchids, it seems that the trees are not greatly affected by their presence. d) Transport Where one species may use another to, in effect, hit ...
... These ‘epiphytes’ gain support & grow nearer the light then they would have done on the ground. Examples of e_______ are lichens, some algae, mosses, ferns & orchids, it seems that the trees are not greatly affected by their presence. d) Transport Where one species may use another to, in effect, hit ...
Ch 17.1 Communities - Elmwood Park Public Schools
... Canadian lynx & snowshoe hare Coupled oscillation ...
... Canadian lynx & snowshoe hare Coupled oscillation ...
Sixth Extinction
... • Because of human actions, natural habitats are becoming increasingly isolated and island-like. • By identifying potential mechanisms underlying the loss of species diversity, Island Biogeography Theory may help suggest ways in which we can design nature reserves to maximize their ability to mainta ...
... • Because of human actions, natural habitats are becoming increasingly isolated and island-like. • By identifying potential mechanisms underlying the loss of species diversity, Island Biogeography Theory may help suggest ways in which we can design nature reserves to maximize their ability to mainta ...
NOTES: Chapter 8.1 - How Populations Change In Size
... Some species have much higher reproductive potentials than others. Darwin calculated that it could take 750 years for a pair of elephants to produce 19 million descendants. While bacteria could produce that in a few days or weeks. ...
... Some species have much higher reproductive potentials than others. Darwin calculated that it could take 750 years for a pair of elephants to produce 19 million descendants. While bacteria could produce that in a few days or weeks. ...
Design of rain forest reserves
... grounds for these extrapolation techniques. In fact, large-scale censuses of plants in several vegetation types have shown that real species-area curves often strongly depart from the power-law shape [36] for plant species. Likewise, the predictive power of indicator taxa for estimating biodiversity ...
... grounds for these extrapolation techniques. In fact, large-scale censuses of plants in several vegetation types have shown that real species-area curves often strongly depart from the power-law shape [36] for plant species. Likewise, the predictive power of indicator taxa for estimating biodiversity ...
Chapter1Env - cmorganscience
... - Reveal causal relationships: changes in independent variables cause changes in dependent variables - But many things can’t be manipulated: long-term or large-scale questions (e.g., global climate change) • Natural experiments show real-world complexity - Only feasible approach for ecosystem or pla ...
... - Reveal causal relationships: changes in independent variables cause changes in dependent variables - But many things can’t be manipulated: long-term or large-scale questions (e.g., global climate change) • Natural experiments show real-world complexity - Only feasible approach for ecosystem or pla ...
Endangered Species teachers guide
... species are not the only factors involved in this dilemma. Endangerment is a broad issue, one that involves the habitats and environments where species live and interact with one another. Although some measures are being taken to help specific cases of endangerment, the universal problem cannot be s ...
... species are not the only factors involved in this dilemma. Endangerment is a broad issue, one that involves the habitats and environments where species live and interact with one another. Although some measures are being taken to help specific cases of endangerment, the universal problem cannot be s ...
Predators and Prey • Predator – an organism that hunts and kills
... In response, the vines have imprinted their leaves with spots that look like butterfly eggs o Butterflies, believing that the vine’s leaves are already inundated with eggs, lay their eggs elsewhere They don’t want to lay their eggs on a leaf where there will be competition for sustenance This back-a ...
... In response, the vines have imprinted their leaves with spots that look like butterfly eggs o Butterflies, believing that the vine’s leaves are already inundated with eggs, lay their eggs elsewhere They don’t want to lay their eggs on a leaf where there will be competition for sustenance This back-a ...
Succession study guide
... The change of an ecosystem over a period of time. This includes Primary and secondary succession ...
... The change of an ecosystem over a period of time. This includes Primary and secondary succession ...
Review for Exam 3
... 1. What is ecological succession? Why are roots so important to primary succession? 2. What is a species niche? 3. Explain resource partitioning– what causes it? 4. Tropic structure is related to the 2 laws of energy – how? 5. Why is a food web better at describing relationships than a food chain? 6 ...
... 1. What is ecological succession? Why are roots so important to primary succession? 2. What is a species niche? 3. Explain resource partitioning– what causes it? 4. Tropic structure is related to the 2 laws of energy – how? 5. Why is a food web better at describing relationships than a food chain? 6 ...
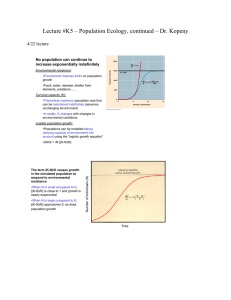
Lecture #K5 – Population Ecology, continued – Dr
... A fur seal population on St. Paul Island, Alaska The numbers of male fur seals with harems were reduced to very low numbers due to hunting until 1911. After hunting was banned, the population increased dramatically and now oscillates around an equilibrium number, presumably the islands carrying capa ...
... A fur seal population on St. Paul Island, Alaska The numbers of male fur seals with harems were reduced to very low numbers due to hunting until 1911. After hunting was banned, the population increased dramatically and now oscillates around an equilibrium number, presumably the islands carrying capa ...
The Balance of Nature: What Is It and Why Care?
... atively constant competitive communities. Variation at the plant population level, for example, can sum to give a relatively constant plant community as long as not all species increase or decrease together. These researchers, in a sense, changed the stability question by embracing population level ...
... atively constant competitive communities. Variation at the plant population level, for example, can sum to give a relatively constant plant community as long as not all species increase or decrease together. These researchers, in a sense, changed the stability question by embracing population level ...
Community Structure and Biodiversity
... Competitors may have equal access to a resource; compete to exploit resource more effectively ...
... Competitors may have equal access to a resource; compete to exploit resource more effectively ...
Theoretical ecology

Theoretical ecology is the scientific discipline devoted to the study of ecological systems using theoretical methods such as simple conceptual models, mathematical models, computational simulations, and advanced data analysis. Effective models improve understanding of the natural world by revealing how the dynamics of species populations are often based on fundamental biological conditions and processes. Further, the field aims to unify a diverse range of empirical observations by assuming that common, mechanistic processes generate observable phenomena across species and ecological environments. Based on biologically realistic assumptions, theoretical ecologists are able to uncover novel, non-intuitive insights about natural processes. Theoretical results are often verified by empirical and observational studies, revealing the power of theoretical methods in both predicting and understanding the noisy, diverse biological world.The field is broad and includes foundations in applied mathematics, computer science, biology, statistical physics, genetics, chemistry, evolution, and conservation biology. Theoretical ecology aims to explain a diverse range of phenomena in the life sciences, such as population growth and dynamics, fisheries, competition, evolutionary theory, epidemiology, animal behavior and group dynamics, food webs, ecosystems, spatial ecology, and the effects of climate change.Theoretical ecology has further benefited from the advent of fast computing power, allowing the analysis and visualization of large-scale computational simulations of ecological phenomena. Importantly, these modern tools provide quantitative predictions about the effects of human induced environmental change on a diverse variety of ecological phenomena, such as: species invasions, climate change, the effect of fishing and hunting on food network stability, and the global carbon cycle.