Predator-Prey Relationships
... differences in food sources are very important. An herbivore usually has an abundance of food readily available, but it has to eat a large amount for sustenance. And while it is eating, it must avoid predators that are looking for their own dinner. In contrast, predators must work much harder to obt ...
... differences in food sources are very important. An herbivore usually has an abundance of food readily available, but it has to eat a large amount for sustenance. And while it is eating, it must avoid predators that are looking for their own dinner. In contrast, predators must work much harder to obt ...
Lesson 5.4 Community Stability
... • Over the course of ecological succession, species diversity increases over time. • Lichens are great pioneer species because they can grow on bare rock. • They are made up of algae that provide food and energy through photosynthesis and fungi that attach to rock and capture moisture. ...
... • Over the course of ecological succession, species diversity increases over time. • Lichens are great pioneer species because they can grow on bare rock. • They are made up of algae that provide food and energy through photosynthesis and fungi that attach to rock and capture moisture. ...
PHYSICAL FEATURES OF THE MARINE ENVIRONMENT:
... Pisaster could now freely enter the area. In contrast, for a similar experiment in Chile, the initial conditions (clear boundary at bottom of the mid-intertidal) were re-established. Why the difference in the two studies? Would you expect the thick beds to persist indefinitely? 8. Be able to list th ...
... Pisaster could now freely enter the area. In contrast, for a similar experiment in Chile, the initial conditions (clear boundary at bottom of the mid-intertidal) were re-established. Why the difference in the two studies? Would you expect the thick beds to persist indefinitely? 8. Be able to list th ...
Eighth Gr BB 1 - Marietta City Schools
... If a healthy ecosystem is one that is home to many different species, mostly native to the area and all interdependent upon one another, what’s an example of an unhealthy ecosystem? Flashback to Florida; let’s take a closer look at the Everglades. The invasive (not original to a specific environment ...
... If a healthy ecosystem is one that is home to many different species, mostly native to the area and all interdependent upon one another, what’s an example of an unhealthy ecosystem? Flashback to Florida; let’s take a closer look at the Everglades. The invasive (not original to a specific environment ...
AP Environmental Science Student Sample Question 1
... describing “if predators” eat small bat populations at the “same rate as when populations were larger, a much larger proportion of the population will be destroyed,” and for considering genetic diversity, as bats with a small population will have “genotypes of individuals in the population” that wil ...
... describing “if predators” eat small bat populations at the “same rate as when populations were larger, a much larger proportion of the population will be destroyed,” and for considering genetic diversity, as bats with a small population will have “genotypes of individuals in the population” that wil ...
PDF - UTK EEB
... • Some pathogens replicate intracellularly within hosts and move between host cells through budding or bursting. How does the rate of intracellular replication affect the rates of immune response clearance by the host? How, in turn, does this lead to changes in the survival of the host and transmiss ...
... • Some pathogens replicate intracellularly within hosts and move between host cells through budding or bursting. How does the rate of intracellular replication affect the rates of immune response clearance by the host? How, in turn, does this lead to changes in the survival of the host and transmiss ...
Restoration of Ecosystems
... – (reclamation, rehabilitation, revegetation) creates unrealistic expectations ...
... – (reclamation, rehabilitation, revegetation) creates unrealistic expectations ...
Emergence of a Discipline
... science that seeks to provide objective answers to questions about how to achieve the goals of biodiversity management set by society? ...
... science that seeks to provide objective answers to questions about how to achieve the goals of biodiversity management set by society? ...
biology_notes_-_module_1_-_version_2 - HSC Guru
... A relationship in which one organism eats another is called predator/prey relationship, or predation. These types of relationships often have a major impact on the abundance of organisms. Populations of predator are dependant on the population of the prey and vice versa. For example, if the populati ...
... A relationship in which one organism eats another is called predator/prey relationship, or predation. These types of relationships often have a major impact on the abundance of organisms. Populations of predator are dependant on the population of the prey and vice versa. For example, if the populati ...
Fish Population abd Fished Population Dynamics
... low population levels then it can be thought of as resilient. If a population naturally varies within a fairly narrow population range then reduceing the population below its lower “boundary” (e.g. by introducing fishing) carries high risk….it takes the population into a state where we have no idea ...
... low population levels then it can be thought of as resilient. If a population naturally varies within a fairly narrow population range then reduceing the population below its lower “boundary” (e.g. by introducing fishing) carries high risk….it takes the population into a state where we have no idea ...
spatial selection and inheritance
... and provides opportunities to borrow from the welldeveloped quantitative framework of quantitative genetics in addressing difficult problems of modeling spatial population dynamics. Most population dynamic models are rooted in the assumption that density-independent population growth is exponential, ...
... and provides opportunities to borrow from the welldeveloped quantitative framework of quantitative genetics in addressing difficult problems of modeling spatial population dynamics. Most population dynamic models are rooted in the assumption that density-independent population growth is exponential, ...
Coastal Conservation Offsets Mortality at Sea: Applying the Bycatch
... buck. It has been difficult for even the best managed fisheries to avoid high levels of nontarget species mortality. New Zealand’s squid fishery and Hawaii’s pelagic longline fishery – generating $122 and $50 million a year, respectively - closed early in the 2005 season due to bycatch of endangere ...
... buck. It has been difficult for even the best managed fisheries to avoid high levels of nontarget species mortality. New Zealand’s squid fishery and Hawaii’s pelagic longline fishery – generating $122 and $50 million a year, respectively - closed early in the 2005 season due to bycatch of endangere ...
A Bug`s Life: Competition Among Species Towards
... consequently derived. By means of a Lotka-Volterra dynamic system we describe the evolution of two populations (bees and locusts) that differently approach the management of those natural resources they contend for, and thus make a simple parable of today’s societies playing the current environmenta ...
... consequently derived. By means of a Lotka-Volterra dynamic system we describe the evolution of two populations (bees and locusts) that differently approach the management of those natural resources they contend for, and thus make a simple parable of today’s societies playing the current environmenta ...
But not selectively
... But be careful some predators can detect alarm calls Vervets have different predators Eagles, leopards and snakes Each predator type needs to evoke a different behavioral response For eagle get low to ground (but that would get you eaten by a ...
... But be careful some predators can detect alarm calls Vervets have different predators Eagles, leopards and snakes Each predator type needs to evoke a different behavioral response For eagle get low to ground (but that would get you eaten by a ...
File
... 16. As some food sources became limited, finches with particular beak characteristics were better suited for the environment and were able to use other food sources. They were able to mate and pass on these favourable beak characteristics to the next generation. This is natural selection. 17. A livi ...
... 16. As some food sources became limited, finches with particular beak characteristics were better suited for the environment and were able to use other food sources. They were able to mate and pass on these favourable beak characteristics to the next generation. This is natural selection. 17. A livi ...
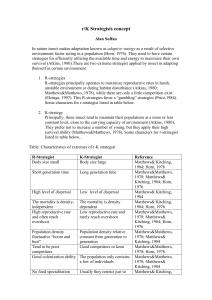
r/K Strategists concept
... with their life strategies to survive in the environment (Denno and Dingle, 1981; Robinson, 1987). In this concept, species are classified as r-strategists and Kstrategists (Zadoks and Schein, 1979; Pedigo, 1989). Insects (species) which have high reproductive rates but with low survival rates are ...
... with their life strategies to survive in the environment (Denno and Dingle, 1981; Robinson, 1987). In this concept, species are classified as r-strategists and Kstrategists (Zadoks and Schein, 1979; Pedigo, 1989). Insects (species) which have high reproductive rates but with low survival rates are ...
FOOD WEBS
... The hypothesis that stability begets complexity corresponds to the naturalist's intuition about the "balance of nature" (Pimm 1991). Perhaps for this reason, the stability-complexity hypothesis was accepted uncritically until the early 1970s, beginning with the publication of a brief, but important, ...
... The hypothesis that stability begets complexity corresponds to the naturalist's intuition about the "balance of nature" (Pimm 1991). Perhaps for this reason, the stability-complexity hypothesis was accepted uncritically until the early 1970s, beginning with the publication of a brief, but important, ...
Impacts of biological invasions: what`s what and - UNIV-TLSE3
... non-native species introduced by acclimatization societies were considered ‘exotic’ curiosities, often viewed as a resource [11]. Today, some still see many introduced populations as assets, because of aesthetic properties, popularity as ornamental plants and pets, or economic value. Certain non-nat ...
... non-native species introduced by acclimatization societies were considered ‘exotic’ curiosities, often viewed as a resource [11]. Today, some still see many introduced populations as assets, because of aesthetic properties, popularity as ornamental plants and pets, or economic value. Certain non-nat ...
Section 2 Models in Science
... Figure 1 This orange is a physical model of Earth. Notice how the shapes of the continents change when the orange peel is flattened. ...
... Figure 1 This orange is a physical model of Earth. Notice how the shapes of the continents change when the orange peel is flattened. ...
TRA-938: A PARKWAY IN A PRAIRIE: THE RT. HON. HERB GRAY
... new crossing of the Detroit River between Windsor, Ontario and Detroit, Michigan. Tallgrass prairie ecosystems are one of the most endangered vegetation communities on Earth and home to many rare species. The Parkway's ecological approach has resulted in an increase of over 100 ha. of Tallgrass Prai ...
... new crossing of the Detroit River between Windsor, Ontario and Detroit, Michigan. Tallgrass prairie ecosystems are one of the most endangered vegetation communities on Earth and home to many rare species. The Parkway's ecological approach has resulted in an increase of over 100 ha. of Tallgrass Prai ...
lecture presentations - Hialeah Senior High School
... classified by whether they help, harm, or have no effect on the species involved • Ecologists call relationships between species in a community interspecific interactions • Examples are competition, predation, herbivory, symbiosis (parasitism, mutualism, and commensalism), and facilitation • Intersp ...
... classified by whether they help, harm, or have no effect on the species involved • Ecologists call relationships between species in a community interspecific interactions • Examples are competition, predation, herbivory, symbiosis (parasitism, mutualism, and commensalism), and facilitation • Intersp ...
File - Ms. Hamadeh`s AP Environmental Science Coral
... of life on earth? What is biological evolution by natural selection, and how can it account for the current diversity of organisms on the earth? How can geologic processes, climate change and catastrophes affect biological evolution? What is an ecological niche, and how does it help a population ...
... of life on earth? What is biological evolution by natural selection, and how can it account for the current diversity of organisms on the earth? How can geologic processes, climate change and catastrophes affect biological evolution? What is an ecological niche, and how does it help a population ...
Theoretical ecology

Theoretical ecology is the scientific discipline devoted to the study of ecological systems using theoretical methods such as simple conceptual models, mathematical models, computational simulations, and advanced data analysis. Effective models improve understanding of the natural world by revealing how the dynamics of species populations are often based on fundamental biological conditions and processes. Further, the field aims to unify a diverse range of empirical observations by assuming that common, mechanistic processes generate observable phenomena across species and ecological environments. Based on biologically realistic assumptions, theoretical ecologists are able to uncover novel, non-intuitive insights about natural processes. Theoretical results are often verified by empirical and observational studies, revealing the power of theoretical methods in both predicting and understanding the noisy, diverse biological world.The field is broad and includes foundations in applied mathematics, computer science, biology, statistical physics, genetics, chemistry, evolution, and conservation biology. Theoretical ecology aims to explain a diverse range of phenomena in the life sciences, such as population growth and dynamics, fisheries, competition, evolutionary theory, epidemiology, animal behavior and group dynamics, food webs, ecosystems, spatial ecology, and the effects of climate change.Theoretical ecology has further benefited from the advent of fast computing power, allowing the analysis and visualization of large-scale computational simulations of ecological phenomena. Importantly, these modern tools provide quantitative predictions about the effects of human induced environmental change on a diverse variety of ecological phenomena, such as: species invasions, climate change, the effect of fishing and hunting on food network stability, and the global carbon cycle.