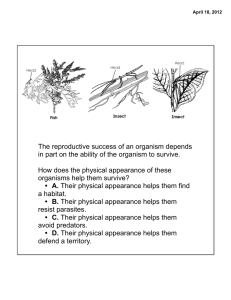
How functional is functional? Ecological groupings in terrestrial
... capacity of focal organisms to provide a specific ecosystem service (Tilman et al. 1997). EGs have been applied in several fields of ecology, e.g. to clarify general relationships between EGs and ecosystem functioning (e.g. Du Toit and Cumming 1999; Diaz and Cabido 2001; Brodie et al. 2009), to clas ...
... capacity of focal organisms to provide a specific ecosystem service (Tilman et al. 1997). EGs have been applied in several fields of ecology, e.g. to clarify general relationships between EGs and ecosystem functioning (e.g. Du Toit and Cumming 1999; Diaz and Cabido 2001; Brodie et al. 2009), to clas ...
Traveling wave solutions of a reaction diffusion model for competing
... has been paid to the interaction of the pioneer-climax populations with the spatial environment. If we are to consider the next step in modeling the pioneer-climax populations interaction then space is a natural way to go. This move toward including the spatial environment in population models is be ...
... has been paid to the interaction of the pioneer-climax populations with the spatial environment. If we are to consider the next step in modeling the pioneer-climax populations interaction then space is a natural way to go. This move toward including the spatial environment in population models is be ...
Page 1 662 Trophic ecology The study of the structure of feeding
... scattered remnant populations by hunting. The reduction of sea otters likely resulted in dramatic changes in prey population dynamics in ecosystems previously occupied by sea otters. For example, in rocky subtidal habitats the abundance of sea urchins, a preferred prey item of otters, was much highe ...
... scattered remnant populations by hunting. The reduction of sea otters likely resulted in dramatic changes in prey population dynamics in ecosystems previously occupied by sea otters. For example, in rocky subtidal habitats the abundance of sea urchins, a preferred prey item of otters, was much highe ...
Landscape dynamics and conservation decisions Applied
... Applied conservation is about deciding what to do where and when. We have a suite of excellent tools and theories for deciding what to do where, traditional conservation planning, however we do not have easy to use tools for deciding when to take those actions. In this talk I define the dynamic prio ...
... Applied conservation is about deciding what to do where and when. We have a suite of excellent tools and theories for deciding what to do where, traditional conservation planning, however we do not have easy to use tools for deciding when to take those actions. In this talk I define the dynamic prio ...
bYTEBoss Conservation Ecology PPT
... regions • Without their native predators, parasites, and pathogens, introduced species may spread rapidly ...
... regions • Without their native predators, parasites, and pathogens, introduced species may spread rapidly ...
chapter 6 interplay between scale, resolution, life history and food
... change is a function of proximity to the source perturbation. Some have questioned the spiderweb model of food webs on the basis many or perhaps most species appear to be influenced by only a few species (Berryman 1993). Their second model, the Christmas tree, views communities as having structural ...
... change is a function of proximity to the source perturbation. Some have questioned the spiderweb model of food webs on the basis many or perhaps most species appear to be influenced by only a few species (Berryman 1993). Their second model, the Christmas tree, views communities as having structural ...
Guidance note on biodiversity for use by Hydro when entering into
... important in areas where biodiversity is in an undisturbed, pristine state, is unique or threatened, or have a specific value for local societies affected. In cases where the ecosystems and species composition are already degraded or destroyed, the policy needs to be adjusted. Going back to an alrea ...
... important in areas where biodiversity is in an undisturbed, pristine state, is unique or threatened, or have a specific value for local societies affected. In cases where the ecosystems and species composition are already degraded or destroyed, the policy needs to be adjusted. Going back to an alrea ...
Scaling of ecological dominance and resilience in kelp communities
... environmental forcing functions. In addition, it also depends upon cascading patterns of predation on the kelps, their epiphytes, and sea urchins. Our understanding of this resilience depends upon synthesis of both ecological succession and resistance to invasion. What of the future? The natural dis ...
... environmental forcing functions. In addition, it also depends upon cascading patterns of predation on the kelps, their epiphytes, and sea urchins. Our understanding of this resilience depends upon synthesis of both ecological succession and resistance to invasion. What of the future? The natural dis ...
Adaptive Radiation - Princeton University Press
... the way they exploit the environment. When the differentiation has proceeded rapidly, the evolutionary transitions from one state to another can readily be characterized and strongly interpreted. Angiosperm plants, dinosaurs, and marsupial mammals are typical examples at high taxonomic levels. Typic ...
... the way they exploit the environment. When the differentiation has proceeded rapidly, the evolutionary transitions from one state to another can readily be characterized and strongly interpreted. Angiosperm plants, dinosaurs, and marsupial mammals are typical examples at high taxonomic levels. Typic ...
Species Interactions and Community Ecology
... - Who eats whom? • Matter and energy move through the community • Trophic levels = rank in the feeding hierarchy ...
... - Who eats whom? • Matter and energy move through the community • Trophic levels = rank in the feeding hierarchy ...
Existence and construction of large stable food webs
... Conditions for stability —A sufficient criterion for dynamical stability is the existence of a Lyapunov function [24, 30]. Assume ...
... Conditions for stability —A sufficient criterion for dynamical stability is the existence of a Lyapunov function [24, 30]. Assume ...
Estimating cost functions for the four large carnivores in Sweden
... different goals, namely to exterminate the carnivore populations. For this, bounties were paid to those who killed any of the four large carnivores. The aim of this paper is to estimate social cost functions for the four large carnivores in Sweden based on regression models of cost and population nu ...
... different goals, namely to exterminate the carnivore populations. For this, bounties were paid to those who killed any of the four large carnivores. The aim of this paper is to estimate social cost functions for the four large carnivores in Sweden based on regression models of cost and population nu ...
Biogeography and ecology: towards the integration of two disciplines
... out choices between using phylogenetic and functional diversity, whether to weight species abundance, and the relevance of species versus landscape diversity. In a very practical sense, quantifying biodiversity in a way that is useful for conservation and management depends on the goals of biodivers ...
... out choices between using phylogenetic and functional diversity, whether to weight species abundance, and the relevance of species versus landscape diversity. In a very practical sense, quantifying biodiversity in a way that is useful for conservation and management depends on the goals of biodivers ...
Valuation 2: Environmental Demand Theory
... this may reflect a higher truth, but is not handy for a decision analytic tool • What to make of an assessment that praises Iceland and Indonesia, while condemning Bangladesh and Singapore? • Part of this comes from using world average productivity figures ...
... this may reflect a higher truth, but is not handy for a decision analytic tool • What to make of an assessment that praises Iceland and Indonesia, while condemning Bangladesh and Singapore? • Part of this comes from using world average productivity figures ...
Lack, Skutch, and Moreau: The Early Development of
... a successionof B/5 would so shorten the reproductive lives of the parents that their total of offspring, produced in smaller, less exacting broods, would be greater.” Concerning the possibility that nest predation could select for smaller brood size, Moreau (1944, p. 309) stated, “Again, a greater a ...
... a successionof B/5 would so shorten the reproductive lives of the parents that their total of offspring, produced in smaller, less exacting broods, would be greater.” Concerning the possibility that nest predation could select for smaller brood size, Moreau (1944, p. 309) stated, “Again, a greater a ...
Invaders - Lesson Corner
... Interactions and Relationships among Organisms. Explain to students that interspecific competition can occur between other species besides animals. Provide students with a Focus FOR MEDIA INTERACTION by asking students to watch the next video sequence for what organisms are competing in a meadow. PL ...
... Interactions and Relationships among Organisms. Explain to students that interspecific competition can occur between other species besides animals. Provide students with a Focus FOR MEDIA INTERACTION by asking students to watch the next video sequence for what organisms are competing in a meadow. PL ...
3.1 Section Objectives – page 65
... • The colonization of organisms in a completely barren land is called primary succession. ...
... • The colonization of organisms in a completely barren land is called primary succession. ...
Power Point Notes 4.3 Succession
... Secondary succession proceeds __________________________ than primary succession, in part because _________________ survives the disturbance. As a result, new and surviving _________________________ can regrow rapidly. ...
... Secondary succession proceeds __________________________ than primary succession, in part because _________________ survives the disturbance. As a result, new and surviving _________________________ can regrow rapidly. ...
Theoretical ecology

Theoretical ecology is the scientific discipline devoted to the study of ecological systems using theoretical methods such as simple conceptual models, mathematical models, computational simulations, and advanced data analysis. Effective models improve understanding of the natural world by revealing how the dynamics of species populations are often based on fundamental biological conditions and processes. Further, the field aims to unify a diverse range of empirical observations by assuming that common, mechanistic processes generate observable phenomena across species and ecological environments. Based on biologically realistic assumptions, theoretical ecologists are able to uncover novel, non-intuitive insights about natural processes. Theoretical results are often verified by empirical and observational studies, revealing the power of theoretical methods in both predicting and understanding the noisy, diverse biological world.The field is broad and includes foundations in applied mathematics, computer science, biology, statistical physics, genetics, chemistry, evolution, and conservation biology. Theoretical ecology aims to explain a diverse range of phenomena in the life sciences, such as population growth and dynamics, fisheries, competition, evolutionary theory, epidemiology, animal behavior and group dynamics, food webs, ecosystems, spatial ecology, and the effects of climate change.Theoretical ecology has further benefited from the advent of fast computing power, allowing the analysis and visualization of large-scale computational simulations of ecological phenomena. Importantly, these modern tools provide quantitative predictions about the effects of human induced environmental change on a diverse variety of ecological phenomena, such as: species invasions, climate change, the effect of fishing and hunting on food network stability, and the global carbon cycle.