Trophic polymorphism in a terrestrial salamander John C. Maerz,
... where morphs are easily distinguished, and readily accept that those polymorphisms are adaptive (Skúlason and Smith, 1995; Smith and Skúlason, 1996). Less appreciated but potentially more common are cases of trophic polymorphism where phenotypes cannot easily be distinguished and show a continuous, ...
... where morphs are easily distinguished, and readily accept that those polymorphisms are adaptive (Skúlason and Smith, 1995; Smith and Skúlason, 1996). Less appreciated but potentially more common are cases of trophic polymorphism where phenotypes cannot easily be distinguished and show a continuous, ...
Towards a trait-based quantification of species
... In principle, fundamental and realized species niches can be quantified by the changes in abundance, or simply occurrence, of a population over environmental gradients. Although niche determination is relatively straightforward for some organisms, such as microorganisms that can be readily cultured, ...
... In principle, fundamental and realized species niches can be quantified by the changes in abundance, or simply occurrence, of a population over environmental gradients. Although niche determination is relatively straightforward for some organisms, such as microorganisms that can be readily cultured, ...
Habitat filtering and niche differentiation jointly explain
... competition models postulates that long-term species coexistence is possible if the strength of inter-specific interactions is lower than that of intra-specific interactions (Chesson, 2000; Murrell, 2010). A signature of this process stabilizing species diversity is that species’ per capita growth r ...
... competition models postulates that long-term species coexistence is possible if the strength of inter-specific interactions is lower than that of intra-specific interactions (Chesson, 2000; Murrell, 2010). A signature of this process stabilizing species diversity is that species’ per capita growth r ...
Saxidomus giganteus - Scholars` Bank
... broadcast spawning through a ciliated trochophore stage to a veliger larva. Bivalve veligers are characterized by a ciliated velum that is used for swimming, feeding and respiration. The veliger larva is also found in many gastropod larvae, but the larvae in the two groups can be recognized by shell ...
... broadcast spawning through a ciliated trochophore stage to a veliger larva. Bivalve veligers are characterized by a ciliated velum that is used for swimming, feeding and respiration. The veliger larva is also found in many gastropod larvae, but the larvae in the two groups can be recognized by shell ...
predation risk affects relative strength of top-down
... a series of three multinomial logistic regressions were performed to determine if one or more behaviors occurred significantly more frequently than others (SAS 2001). For each regression, a different behavior was used as the reference to which the other three behaviors were contrasted (Allison 1999) ...
... a series of three multinomial logistic regressions were performed to determine if one or more behaviors occurred significantly more frequently than others (SAS 2001). For each regression, a different behavior was used as the reference to which the other three behaviors were contrasted (Allison 1999) ...
Species Abundance, Not Diet Breadth, Drives the Persistence of the
... necessary for New Jersey only. Many pollinator species are not positively associated with the native forest habitat type but instead are more abundant in human-disturbed habitats. This is true in forested biomes generally (Winfree et al. 2011), in our previous work in this region (Winfree and Kremen ...
... necessary for New Jersey only. Many pollinator species are not positively associated with the native forest habitat type but instead are more abundant in human-disturbed habitats. This is true in forested biomes generally (Winfree et al. 2011), in our previous work in this region (Winfree and Kremen ...
Plant Attribute Diversity, Resilience, and Ecosystem Function: The
... functional groupings, one of which (their third type) concerns the functions that plants perform. However, this type is defined in relation to ‘‘either the contribution of species to ecosystem processes or to the response of species to changes in environmental variables.’’ The species within such fu ...
... functional groupings, one of which (their third type) concerns the functions that plants perform. However, this type is defined in relation to ‘‘either the contribution of species to ecosystem processes or to the response of species to changes in environmental variables.’’ The species within such fu ...
How will biotic interactions influence climate change–induced range
... but few studies assess how and whether these interactions will impede or accelerate climate change–induced range shifts. In this paper, we explore how ecologists might move forward on this question. We first outline the conditions under which biotic interactions can result in range shifts that proce ...
... but few studies assess how and whether these interactions will impede or accelerate climate change–induced range shifts. In this paper, we explore how ecologists might move forward on this question. We first outline the conditions under which biotic interactions can result in range shifts that proce ...
Aquatic Insects for Biomonitoring Freshwater Ecosystems: A Report
... source of food for fish. Trichoptera larvae, pupae and adults also form an important link in the food chain and they have also been used extensively by trout fishing enthusiasts as models for “flies”. ...
... source of food for fish. Trichoptera larvae, pupae and adults also form an important link in the food chain and they have also been used extensively by trout fishing enthusiasts as models for “flies”. ...
ABSTRACTS - POPBIO is a conference
... to climate change and may change the competitive balance within a community. we studied twelve herbaceous species along two altitudinal gradients ranging from 700 to 1800 m, a.s.l. in the Bavarian alps, covering a difference of 6.6 k in mean annual temperature. we monitored flowering phenology at we ...
... to climate change and may change the competitive balance within a community. we studied twelve herbaceous species along two altitudinal gradients ranging from 700 to 1800 m, a.s.l. in the Bavarian alps, covering a difference of 6.6 k in mean annual temperature. we monitored flowering phenology at we ...
Hostplant genotype mediates supply and demand of animal food in
... 1999; Gadd & Raubenheimer, 2000), we hypothesise that these two groups have different nutritional and reproductive requirements, and different natural enemies and thus respond differently to specific host-plant genotypes. If so, some plants may harbour herbivorous prey in large numbers, while provid ...
... 1999; Gadd & Raubenheimer, 2000), we hypothesise that these two groups have different nutritional and reproductive requirements, and different natural enemies and thus respond differently to specific host-plant genotypes. If so, some plants may harbour herbivorous prey in large numbers, while provid ...
Long-term dynamics of biotic and abiotic resistance to exotic species
... and restoration of native plant and animal populations and communities are critical aspects of vernal pool conservation within the region. In previous research, we compared patterns and mechanisms of plant community development and exotic species invasions in naturally occurring and restored vernal ...
... and restoration of native plant and animal populations and communities are critical aspects of vernal pool conservation within the region. In previous research, we compared patterns and mechanisms of plant community development and exotic species invasions in naturally occurring and restored vernal ...
Society for Conservation Biology
... mortality that woodrats apparently cannot persist where raccoons are common (LoGiudice 2000). of Exotic species invasions occur as a consequence these become sucand travel. When trade global species cessfully established in new habitats, they may affect native species through the processes of predat ...
... mortality that woodrats apparently cannot persist where raccoons are common (LoGiudice 2000). of Exotic species invasions occur as a consequence these become sucand travel. When trade global species cessfully established in new habitats, they may affect native species through the processes of predat ...
Physiological Ecology of Rocky Intertidal Organisms: A Synergy of Concepts L T *
... Thus, these studies strongly suggest that there are substantial physiological costs for a marine invertebrate to cope with the thermal stress experienced in the rocky intertidal zone (also see Dahlhoff et al., 2001; Tomanek and Somero, 2002). Recent work has also emphasized that we still have much t ...
... Thus, these studies strongly suggest that there are substantial physiological costs for a marine invertebrate to cope with the thermal stress experienced in the rocky intertidal zone (also see Dahlhoff et al., 2001; Tomanek and Somero, 2002). Recent work has also emphasized that we still have much t ...
Pelagic Biogeography - Scientific Committee on Oceanic Research
... of pelagic biogeographic regions or provinces as used by various authors. To have done so would have greatly increased the size of the Glossary, we believe to the detriment of its usefulness. Every term we list can be found in use in the literature and defined elsewhere. We have invented nothing, sa ...
... of pelagic biogeographic regions or provinces as used by various authors. To have done so would have greatly increased the size of the Glossary, we believe to the detriment of its usefulness. Every term we list can be found in use in the literature and defined elsewhere. We have invented nothing, sa ...
2007-2008 - Illinois Natural History Survey
... Long before the term “outreach” was coined, Forbes had it right when he wrote in 1878,”It is . . . of great importance to the public welfare that the methods of work and habits of thought by which achievements of modern science have been made, should be brought to bear as far as possible upon the da ...
... Long before the term “outreach” was coined, Forbes had it right when he wrote in 1878,”It is . . . of great importance to the public welfare that the methods of work and habits of thought by which achievements of modern science have been made, should be brought to bear as far as possible upon the da ...
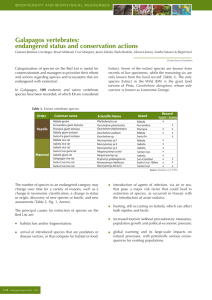
Galapagos vertebrates: endangered status and conservation actions
... habitat loss and/or fragmentation; arrival of introduced species that are predators or disease vectors, or that compete for habitat or food; ...
... habitat loss and/or fragmentation; arrival of introduced species that are predators or disease vectors, or that compete for habitat or food; ...
Animal cooperation among unrelated individuals | SpringerLink
... A second path to the evolution of cooperation has been dubbed “byproduct mutualism” (Brown 1983; Connor 1995; also see West-Eberhard 1975; Rothstein and Pirotti 1987). My colleagues and I have argued that for byproduct mutualism to operate, a boomerang effect – any uncertainty that increases the pro ...
... A second path to the evolution of cooperation has been dubbed “byproduct mutualism” (Brown 1983; Connor 1995; also see West-Eberhard 1975; Rothstein and Pirotti 1987). My colleagues and I have argued that for byproduct mutualism to operate, a boomerang effect – any uncertainty that increases the pro ...
pdf
... of predator and seed species as within-block effects. The following design was repeated in the four study sites. Four blocks (replicates) were randomly selected within each microhabitat, each block consisting of an individual plant (in the case of shrub microhabitats) or a square 2 × 2 m in an open ...
... of predator and seed species as within-block effects. The following design was repeated in the four study sites. Four blocks (replicates) were randomly selected within each microhabitat, each block consisting of an individual plant (in the case of shrub microhabitats) or a square 2 × 2 m in an open ...
Aquatic biomes
... The most extreme effects of the new species can be a disruption of the balance between the different species of organisms that were originally living in the ecosystem ...
... The most extreme effects of the new species can be a disruption of the balance between the different species of organisms that were originally living in the ecosystem ...
Pesticide effects on freshwater zooplankton: an ecological perspective
... is a positive relationship between body size and sensitivity to lindane in cladocerans. This was considered to be due to the fact that cladocerans are most sensitive to chemicals just after molting, and that large-sized animals molt more times than smaller ones prior to reproduction. Size-related re ...
... is a positive relationship between body size and sensitivity to lindane in cladocerans. This was considered to be due to the fact that cladocerans are most sensitive to chemicals just after molting, and that large-sized animals molt more times than smaller ones prior to reproduction. Size-related re ...
Theoretical ecology

Theoretical ecology is the scientific discipline devoted to the study of ecological systems using theoretical methods such as simple conceptual models, mathematical models, computational simulations, and advanced data analysis. Effective models improve understanding of the natural world by revealing how the dynamics of species populations are often based on fundamental biological conditions and processes. Further, the field aims to unify a diverse range of empirical observations by assuming that common, mechanistic processes generate observable phenomena across species and ecological environments. Based on biologically realistic assumptions, theoretical ecologists are able to uncover novel, non-intuitive insights about natural processes. Theoretical results are often verified by empirical and observational studies, revealing the power of theoretical methods in both predicting and understanding the noisy, diverse biological world.The field is broad and includes foundations in applied mathematics, computer science, biology, statistical physics, genetics, chemistry, evolution, and conservation biology. Theoretical ecology aims to explain a diverse range of phenomena in the life sciences, such as population growth and dynamics, fisheries, competition, evolutionary theory, epidemiology, animal behavior and group dynamics, food webs, ecosystems, spatial ecology, and the effects of climate change.Theoretical ecology has further benefited from the advent of fast computing power, allowing the analysis and visualization of large-scale computational simulations of ecological phenomena. Importantly, these modern tools provide quantitative predictions about the effects of human induced environmental change on a diverse variety of ecological phenomena, such as: species invasions, climate change, the effect of fishing and hunting on food network stability, and the global carbon cycle.