Population Ecology - Fulton County Schools
... Review… Discuss What is a population? Population – a single species in a single location at the same time ...
... Review… Discuss What is a population? Population – a single species in a single location at the same time ...
AP Biology Reading Guide ... Fred and Theresa Holtzclaw
... graph, add a third line that approximates a population with an exponential value of 1.25. ...
... graph, add a third line that approximates a population with an exponential value of 1.25. ...
Chapter 53 reading guide
... graph, add a third line that approximates a population with an exponential value of 1.25. ...
... graph, add a third line that approximates a population with an exponential value of 1.25. ...
Document
... population? a. number of individuals c. number of species b. color of individuals d. kind of adaptations _____ 7. For a population’s growth rate to be zero a. more deaths than births must occur. b. more births than deaths must occur. c. no births can occur. d. the average number of births and deaths ...
... population? a. number of individuals c. number of species b. color of individuals d. kind of adaptations _____ 7. For a population’s growth rate to be zero a. more deaths than births must occur. b. more births than deaths must occur. c. no births can occur. d. the average number of births and deaths ...
Competition
... 17.6.4 Regulation of Population Size Fecundity is the reproductive capacity of individual females of a species. Birth rate or natality is used to measure fecundity. Death rate or mortality is the number of individuals of a species which die per unit time. Immigration occurs when individuals ...
... 17.6.4 Regulation of Population Size Fecundity is the reproductive capacity of individual females of a species. Birth rate or natality is used to measure fecundity. Death rate or mortality is the number of individuals of a species which die per unit time. Immigration occurs when individuals ...
Organism A Organism B Mutualism
... 1. Exponential growth = J-curve Very fast growth, occurs when resources are very abundant 2. Logistic growth = S-curve Fast growth followed by plateau. This is what population growth tends to look like in nature Carrying Capacity and Limiting Factors Carrying Capacity describes the maximum number of ...
... 1. Exponential growth = J-curve Very fast growth, occurs when resources are very abundant 2. Logistic growth = S-curve Fast growth followed by plateau. This is what population growth tends to look like in nature Carrying Capacity and Limiting Factors Carrying Capacity describes the maximum number of ...
Environmental Science
... Section 1: How Populations Change in Size Read the passage below and answer the questions that follow. Over time, the growth rates of populations change because birth rates and death rates increase or decrease. Growth rates can be positive, negative, or zero. For a population’s growth rate to be zer ...
... Section 1: How Populations Change in Size Read the passage below and answer the questions that follow. Over time, the growth rates of populations change because birth rates and death rates increase or decrease. Growth rates can be positive, negative, or zero. For a population’s growth rate to be zer ...
ORGANISMS AND POPULATIONS
... Growth Models : The two growth models are : (i) Exponential growth model Exponential Growth Equation is Nt = N0ert Where Nt = Population density after time t N0 = Population density at time zero r = intrinsic rate of natural increase e = the base of natural logarithms (2.71828) (ii) ...
... Growth Models : The two growth models are : (i) Exponential growth model Exponential Growth Equation is Nt = N0ert Where Nt = Population density after time t N0 = Population density at time zero r = intrinsic rate of natural increase e = the base of natural logarithms (2.71828) (ii) ...
Biomes Study Guide: Bio Lab H
... Chapter 3 Ch 3 vocab: ammonia, biogeochemical cycle, nitrogen fixation, denitrification, limiting nutrient, ecosystems, keystone species, food chain, ...
... Chapter 3 Ch 3 vocab: ammonia, biogeochemical cycle, nitrogen fixation, denitrification, limiting nutrient, ecosystems, keystone species, food chain, ...
Practice Quiz 6 - Iowa State University
... Ro=E lxmx Lx=age specific survivorship Mx=age specific fertility 22) The maximum number of individuals a certain area can sustain is know as a) the intrinsic rate of growth b) the resource limit c) the carrying capacity d) the logistic equation 23) The amount of land necessary for survival for each ...
... Ro=E lxmx Lx=age specific survivorship Mx=age specific fertility 22) The maximum number of individuals a certain area can sustain is know as a) the intrinsic rate of growth b) the resource limit c) the carrying capacity d) the logistic equation 23) The amount of land necessary for survival for each ...
interactions in the ecosystem
... Darwin – noticed that most organisms produce many more offspring than will Actually survive into adulthood (some babies do die) Abiotic factors like water and land (space) limit population size and reproduction rate ...
... Darwin – noticed that most organisms produce many more offspring than will Actually survive into adulthood (some babies do die) Abiotic factors like water and land (space) limit population size and reproduction rate ...
Module 19 Population Growth Models
... The logistic growth model describes populations that experience a carrying capacity Populations do not typically experience exponential growth indefinitely. They are limited by resources and carrying capacity. • Limiting resource A resource that a population cannot live without and that occurs in q ...
... The logistic growth model describes populations that experience a carrying capacity Populations do not typically experience exponential growth indefinitely. They are limited by resources and carrying capacity. • Limiting resource A resource that a population cannot live without and that occurs in q ...
ecology - Newton County Schools
... • Populations are not limited only by environmental factors, but are also controlled by various interactions among organisms that share a community. • Predation and crowding / stress can also affect ...
... • Populations are not limited only by environmental factors, but are also controlled by various interactions among organisms that share a community. • Predation and crowding / stress can also affect ...
Population Review
... As the number of predators increases, the number of prey decreases, resulting in less food = predators pop decreases, allowing prey pop to increase. Less food available for other organisms = intraspecific & interspecific competition. Humans intervene if a population gets too large by having hu ...
... As the number of predators increases, the number of prey decreases, resulting in less food = predators pop decreases, allowing prey pop to increase. Less food available for other organisms = intraspecific & interspecific competition. Humans intervene if a population gets too large by having hu ...
Population Dynamics and Ecosystems Review What factors must be
... 25. How do our eating habits affect the carrying capacity for humans on the planet? Explain. What should we be eating to maximize global population? 26. In 2010, the population of Upper Fremont is 200,000 and growing at a rate of 2% each year. ...
... 25. How do our eating habits affect the carrying capacity for humans on the planet? Explain. What should we be eating to maximize global population? 26. In 2010, the population of Upper Fremont is 200,000 and growing at a rate of 2% each year. ...
Why can`t we all just get along?
... Exponential growth cannot continue indefinitely; something will run out . . . Environmental resistance – the combination of factors that keeps a population from reaching its maximum growth rate. Carrying capacity – the maximum number of individuals that a particular habitat can support indefinitely. ...
... Exponential growth cannot continue indefinitely; something will run out . . . Environmental resistance – the combination of factors that keeps a population from reaching its maximum growth rate. Carrying capacity – the maximum number of individuals that a particular habitat can support indefinitely. ...
Ecology EOC Review
... –Producers – get energy from sun & use some for own metabolism –Primary Consumers – get 10% of original energy from producers and use some for own metabolism –Secondary Consumers – get 10% of energy from primary consumers and use some for own metabolism –Tertiary Consumers – get 10% of energy from s ...
... –Producers – get energy from sun & use some for own metabolism –Primary Consumers – get 10% of original energy from producers and use some for own metabolism –Secondary Consumers – get 10% of energy from primary consumers and use some for own metabolism –Tertiary Consumers – get 10% of energy from s ...
07_PopBio
... Hares – when high pop density, increased competition for food and increased predation = low birth rate & high death rate = sharp pop ...
... Hares – when high pop density, increased competition for food and increased predation = low birth rate & high death rate = sharp pop ...
Chapter 52 - Canyon ISD
... effect of population density on the per capita of increase, allowing this rate to vary from maximum at low population size to zero as carrying capacity is reached – When they are well below K, population increases drastically and slows down when it reaches K ...
... effect of population density on the per capita of increase, allowing this rate to vary from maximum at low population size to zero as carrying capacity is reached – When they are well below K, population increases drastically and slows down when it reaches K ...
SBI4U Population Dynamics
... 5. What are THREE different patterns in “survivorship” that species exhibit? For each pattern a) use a graph/figure to illustrate the pattern, b) describe characteristics of species that show that pattern, and c) provide an example of a species that exhibits that pattern 6. How does the number of of ...
... 5. What are THREE different patterns in “survivorship” that species exhibit? For each pattern a) use a graph/figure to illustrate the pattern, b) describe characteristics of species that show that pattern, and c) provide an example of a species that exhibits that pattern 6. How does the number of of ...
Populations and Communities Study Guide Populations
... What is a habitat? What basic needs are provided by an organism’s habitat? Why do different organisms live in different habitats? What might happen to an organism if its habitat could not meet one of its needs? What are biotic factors? What are abiotic factors? Why are water and sunlight important t ...
... What is a habitat? What basic needs are provided by an organism’s habitat? Why do different organisms live in different habitats? What might happen to an organism if its habitat could not meet one of its needs? What are biotic factors? What are abiotic factors? Why are water and sunlight important t ...
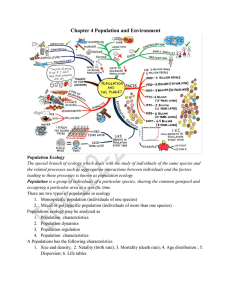
Chapter 4 Population and Environment
... • Under favourable condition population density increases • k-selected population have a relatively constant density at or near optimum limit Drawbacks of Logistic theory (assumptions made) 1. Environment is assumed to be constant 2. No time lag occurs in response of the population to the change in ...
... • Under favourable condition population density increases • k-selected population have a relatively constant density at or near optimum limit Drawbacks of Logistic theory (assumptions made) 1. Environment is assumed to be constant 2. No time lag occurs in response of the population to the change in ...