Oxidative folding in mitochondria
... -United Mitochondrial Disease foundation: a child born every 15 min suffers or will develop a mito disease by the age of 5 ...
... -United Mitochondrial Disease foundation: a child born every 15 min suffers or will develop a mito disease by the age of 5 ...
r i+5
... Additional rules: No hydrogen bonds between pairs assigned as (HE) and (HH for |i-j|>3) The Ca-based model of hydrogen bonds correlates very well with the real hydrogen bonds. When “translating” the indices need to be properly shifted (by +/- 1) depending on type of secondary structure ...
... Additional rules: No hydrogen bonds between pairs assigned as (HE) and (HH for |i-j|>3) The Ca-based model of hydrogen bonds correlates very well with the real hydrogen bonds. When “translating” the indices need to be properly shifted (by +/- 1) depending on type of secondary structure ...
membrane structure n function
... To make use of this barrier, however, cells have had to evolve ways of transferring specific water-soluble molecules across their membranes in order to ingest essential nutrients, excrete metabolic waste products, and regulate intracellular ion concentrations. The transport of inorganic ions and sma ...
... To make use of this barrier, however, cells have had to evolve ways of transferring specific water-soluble molecules across their membranes in order to ingest essential nutrients, excrete metabolic waste products, and regulate intracellular ion concentrations. The transport of inorganic ions and sma ...
biomolecules (introduction, structure
... leucine, isoleucine, valine and proline), two with aromatic rings (phenylalanine and tryptophan), and one containing sulfur (methionine) as shown in Fig. 6. These are less soluble in water as compared to polar R group containing amino acids. Moreover, glycine is also a non-polar amino acid, which ha ...
... leucine, isoleucine, valine and proline), two with aromatic rings (phenylalanine and tryptophan), and one containing sulfur (methionine) as shown in Fig. 6. These are less soluble in water as compared to polar R group containing amino acids. Moreover, glycine is also a non-polar amino acid, which ha ...
Drafting Patent Claims for Filing in the United States
... requires more than a mere statement that it is part of the invention and reference to a potential method for isolating it; what is required is a description of the DNA itself. Fiers v. Revel • For inventions in an unpredictable art, adequate written description of a genus which embraces widely varia ...
... requires more than a mere statement that it is part of the invention and reference to a potential method for isolating it; what is required is a description of the DNA itself. Fiers v. Revel • For inventions in an unpredictable art, adequate written description of a genus which embraces widely varia ...
in Peptide Synthesis, Molecular Recognition
... proteins of defined three-dimensional structure. Due to these unique conformational properties, Pro residues do not occur in regular {X-helices or ~-sheet structures. Rather, they playa specific structural role as N-terminal caps to {X-helices[4], as helix termination signals [5] or as comer residue ...
... proteins of defined three-dimensional structure. Due to these unique conformational properties, Pro residues do not occur in regular {X-helices or ~-sheet structures. Rather, they playa specific structural role as N-terminal caps to {X-helices[4], as helix termination signals [5] or as comer residue ...
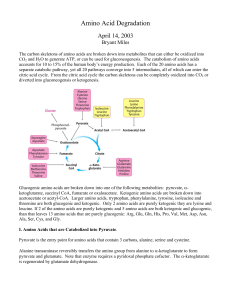
Amino Acid Degradation
... Branched chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase is phosphorylated by a kinase which inactivates the enzyme in a similar manner that pyruvate dehydrogenase is phosphorylated and inactivated. The intake of dietary branched amino acids activates a phosphatase which activates this enzyme. A genetic deficiency i ...
... Branched chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase is phosphorylated by a kinase which inactivates the enzyme in a similar manner that pyruvate dehydrogenase is phosphorylated and inactivated. The intake of dietary branched amino acids activates a phosphatase which activates this enzyme. A genetic deficiency i ...
Homework # 8 Energetics, Electron Transport
... reactions to produce CO2 and H2O? (Hint: do glycolyis and CAC) ...
... reactions to produce CO2 and H2O? (Hint: do glycolyis and CAC) ...
4.1 & 4.2 LDP and R.A.M
... -Now, Dalton used hydrogen first because it was the lightest element and gave it a mass of 1. -he compared all the other element to this value For ex. : when Dalton looked at water, he saw thta 1 g of hydrogen combined with 8 g oxygen -so he gave oxygen a mass of 8 -this was a mistake since 2 atoms ...
... -Now, Dalton used hydrogen first because it was the lightest element and gave it a mass of 1. -he compared all the other element to this value For ex. : when Dalton looked at water, he saw thta 1 g of hydrogen combined with 8 g oxygen -so he gave oxygen a mass of 8 -this was a mistake since 2 atoms ...
Chapter 6
... energy to drive many of their metabolic reactions, such as building protein molecules from amino acids, or making copies of DNA molecules. Energy is used to move chromosomes around during mitosis and meiosis. Most animals also have specialised muscle cells, which use energy to make themselves contra ...
... energy to drive many of their metabolic reactions, such as building protein molecules from amino acids, or making copies of DNA molecules. Energy is used to move chromosomes around during mitosis and meiosis. Most animals also have specialised muscle cells, which use energy to make themselves contra ...
Chapter 1 – name - Nutrition Gardener
... b. protein synthesis requires messenger RNA and transfer RNA. c. most of the body’s thousands of proteins have been studied and characterized. d. the synthesis of a protein by following the genetic code is known as gene expression. ...
... b. protein synthesis requires messenger RNA and transfer RNA. c. most of the body’s thousands of proteins have been studied and characterized. d. the synthesis of a protein by following the genetic code is known as gene expression. ...
Modulator of Diabetes and MetabolicSyndrome: Silent Proteins
... Insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes are traditionally understood to result from a mismatch between insulin requirement and insulin supply [1]. Although essentially the concept still holds true, recent advances in biochemistry including bioinformatics are bringing to the fore newer players in the ...
... Insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes are traditionally understood to result from a mismatch between insulin requirement and insulin supply [1]. Although essentially the concept still holds true, recent advances in biochemistry including bioinformatics are bringing to the fore newer players in the ...
Respiration: Occurs in two places in the cell Cytoplasm and
... The RXNs of Respiration: Electron Transport Chain Chemiosmosis and the proton (H+) motive force Linking e- transport and H+ shuttling to ATP synthesis NADH + H+ ...
... The RXNs of Respiration: Electron Transport Chain Chemiosmosis and the proton (H+) motive force Linking e- transport and H+ shuttling to ATP synthesis NADH + H+ ...
Limits of aerobic metabolism in cancer cells
... lines). The catabolism of isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, tryptophan, and valine requires one or more dehydrogenase steps generating NADH. Alanine, cysteine, glycine, threonine and serine can be converted to pyruvate, which still requires pyruvate dehydrogenase to produce AcCoa (Fig. 1). As ...
... lines). The catabolism of isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, tryptophan, and valine requires one or more dehydrogenase steps generating NADH. Alanine, cysteine, glycine, threonine and serine can be converted to pyruvate, which still requires pyruvate dehydrogenase to produce AcCoa (Fig. 1). As ...
A Review of the Methods available for the Determination of the
... agents tending to break electrovalent bonds. For instance, the number of electrovalent bonds holding the structure together is increased by tanning collagen with vegetable tannins. Tanned collagen is no longer soluble in hot water and swells to a much smaller extent in dilute acids, alkalis, etc. An ...
... agents tending to break electrovalent bonds. For instance, the number of electrovalent bonds holding the structure together is increased by tanning collagen with vegetable tannins. Tanned collagen is no longer soluble in hot water and swells to a much smaller extent in dilute acids, alkalis, etc. An ...
Biomolecular chemistry 3. Translating the genetic code
... as opposed to RNA, level) which may or may not be in the correct frame. • If the next ATG encodes an in frame methionine, the translated protein will be missing the N-terminal sequence between its first two methionine residues. • If the next ATG is out of frame (see +2 translation) then a nonsensica ...
... as opposed to RNA, level) which may or may not be in the correct frame. • If the next ATG encodes an in frame methionine, the translated protein will be missing the N-terminal sequence between its first two methionine residues. • If the next ATG is out of frame (see +2 translation) then a nonsensica ...
Health Canada - Isomer Design
... and is not mentioned anywhere on the DEA website. United Nations: The substance is not listed on the Yellow List - List of Narcotic Drugs under International Control, the Green List - List of Psychotropic Substances under International Control, nor the Red List - List of Precursors and Chemicals Fre ...
... and is not mentioned anywhere on the DEA website. United Nations: The substance is not listed on the Yellow List - List of Narcotic Drugs under International Control, the Green List - List of Psychotropic Substances under International Control, nor the Red List - List of Precursors and Chemicals Fre ...
Types of RNA: mRNA, rRNA and tRNA - Progetto e
... Types of RNA In both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, there are three main types of RNA – messenger RNA or mRNA, ribosomal or rRNA, and transfer RNA or tRNA. These 3 types of RNA are discussed below. Messenger RNA (mRNA) mRNA accounts for just 5% of the total RNA in the cell. mRNA is the most heterogeneo ...
... Types of RNA In both prokaryotes and eukaryotes, there are three main types of RNA – messenger RNA or mRNA, ribosomal or rRNA, and transfer RNA or tRNA. These 3 types of RNA are discussed below. Messenger RNA (mRNA) mRNA accounts for just 5% of the total RNA in the cell. mRNA is the most heterogeneo ...
Food to chew on
... The local purple- or orange-coloured sweet potato is an excellent substitute for the starchy potato or chips or fries. It is rich in alpha- and beta-carotene, which is a provitamin A. Carotene is an oil-soluble antioxidant and should be consumed with some dietary fats to enhance its absorption. Unli ...
... The local purple- or orange-coloured sweet potato is an excellent substitute for the starchy potato or chips or fries. It is rich in alpha- and beta-carotene, which is a provitamin A. Carotene is an oil-soluble antioxidant and should be consumed with some dietary fats to enhance its absorption. Unli ...
- Pacific Biomarkers
... including neuropeptide Y and pancreatic polypeptide (PP). The peptides of this family mediate their effects through several G protein-coupled receptors. PYY is primarily released from endocrine cells of the distal digestive tract and plays an important role in regulating food intake and energy balan ...
... including neuropeptide Y and pancreatic polypeptide (PP). The peptides of this family mediate their effects through several G protein-coupled receptors. PYY is primarily released from endocrine cells of the distal digestive tract and plays an important role in regulating food intake and energy balan ...
Ch6
... • Energy harvested in stepwise process • Electrons transferred to electron carriers, which represent reducing power (easily transfer electrons to molecules) – Raise energy level of recipient molecule • NAD+/NADH, NADP+/NADPH, and FAD/FADH2 ...
... • Energy harvested in stepwise process • Electrons transferred to electron carriers, which represent reducing power (easily transfer electrons to molecules) – Raise energy level of recipient molecule • NAD+/NADH, NADP+/NADPH, and FAD/FADH2 ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.