Mole Equation Homework Hint: Start equations with the numbers
... Hint: Start equations with the numbers given, and pay close attention to what the question is asking you to find. Usually, the first step in most stoichiometry problems (calculation of quantities in chemical equations) is to convert the given numbers to moles. SHOW YOUR WORK!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ...
... Hint: Start equations with the numbers given, and pay close attention to what the question is asking you to find. Usually, the first step in most stoichiometry problems (calculation of quantities in chemical equations) is to convert the given numbers to moles. SHOW YOUR WORK!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! ...
I. Arabidopsis Is a Model Organism
... B. She discovered that “controlling elements,” later called transposons, could undergo transposition and move from one location to another on the chromosome. 1. If a transposon lands in the middle of another gene, it prevents the expression of that gene. 2. This is responsible for the expression of ...
... B. She discovered that “controlling elements,” later called transposons, could undergo transposition and move from one location to another on the chromosome. 1. If a transposon lands in the middle of another gene, it prevents the expression of that gene. 2. This is responsible for the expression of ...
Kretsu Anna PFUR
... These enzymes are synthesized by a variety of microorganisms. * For their cultivation optimum conditions (temperature, composition and pH, oxygen concentration, etc.) is required. ...
... These enzymes are synthesized by a variety of microorganisms. * For their cultivation optimum conditions (temperature, composition and pH, oxygen concentration, etc.) is required. ...
Sterilization & Disinfection
... Heat is usually applied at temperatures above boiling (121°C) to kill spores, but heat-sensitive materials such as milk are exposed to temperatures below boiling (pasteurization) that kills the pathogens in milk but does not sterilize it. ...
... Heat is usually applied at temperatures above boiling (121°C) to kill spores, but heat-sensitive materials such as milk are exposed to temperatures below boiling (pasteurization) that kills the pathogens in milk but does not sterilize it. ...
The O 2
... sequences as well as the relative positions of AAs in space. • Proteins need well defined structures to function properly. Their structures are organized in a hierarchy format, that is, primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure. ...
... sequences as well as the relative positions of AAs in space. • Proteins need well defined structures to function properly. Their structures are organized in a hierarchy format, that is, primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure. ...
solute - Life Science Academy
... ◦ Cellular work can be sustained: ◦ “ATM Machine” ◦ ATP is a renewable resource that cells regenerate ATP ...
... ◦ Cellular work can be sustained: ◦ “ATM Machine” ◦ ATP is a renewable resource that cells regenerate ATP ...
Understanding Cells: The Basic Units of Life Cells make up the
... What exactly are cells? Cells are sacs of fluid surrounded by membranes. Inside the fluid float chemicals and organelles. An organism contains parts that are smaller than a cell, but the cell is the smallest part of the organism that retains characteristics of the entire organism. For example, a cel ...
... What exactly are cells? Cells are sacs of fluid surrounded by membranes. Inside the fluid float chemicals and organelles. An organism contains parts that are smaller than a cell, but the cell is the smallest part of the organism that retains characteristics of the entire organism. For example, a cel ...
Energy, Catalysis, and Biosynthesis
... unequal sharing of electrons across a covalent bond (d) equal sharing of electrons across a covalent bond ...
... unequal sharing of electrons across a covalent bond (d) equal sharing of electrons across a covalent bond ...
Document
... Lipids are energy rich and provides 9 kcal/gm dietary lipids 90% triacylglycerols (TAGs) also include cholesterol esters, phospholipids, essential unsaturated fatty acids; fat-soluble vitamins most dietary fat transported to adipose for storage dietary TAGs hydrolyzed in the intestine by pancreatic ...
... Lipids are energy rich and provides 9 kcal/gm dietary lipids 90% triacylglycerols (TAGs) also include cholesterol esters, phospholipids, essential unsaturated fatty acids; fat-soluble vitamins most dietary fat transported to adipose for storage dietary TAGs hydrolyzed in the intestine by pancreatic ...
Dark Reactions
... carbohydrates and fats of the plant. The capacity to accumulate carbon atoms from carbon dioxide for the net synthesis of carbohydrate distinguishes the photoautotrophic from the heterotrophic. The Calvin Cycle takes place in the stroma of the chloroplast. The Calvin cycle is named after Melvin Calv ...
... carbohydrates and fats of the plant. The capacity to accumulate carbon atoms from carbon dioxide for the net synthesis of carbohydrate distinguishes the photoautotrophic from the heterotrophic. The Calvin Cycle takes place in the stroma of the chloroplast. The Calvin cycle is named after Melvin Calv ...
energy
... such as cereal, pulses and potatoes and foods and drinks containing sugars such as milk, fruits and vegetables, jam, confectionery, table sugar and some soft drinks. Sugars are called simple carbohydrates. They are called simple because your body digests them quickly and easily. Starchy Carbohydrate ...
... such as cereal, pulses and potatoes and foods and drinks containing sugars such as milk, fruits and vegetables, jam, confectionery, table sugar and some soft drinks. Sugars are called simple carbohydrates. They are called simple because your body digests them quickly and easily. Starchy Carbohydrate ...
STUDY OF MOLECULAR CRYSTAL OF HYDROXY
... effects. The most used drugs are paracetamol and phenacetin. Paracetamol, as metabolite of phenacetin, has similar medicamental property but does not share phenacetin’s carcirogenic side effects. Therefore it is one of the most popular analgesic and antipyretic drug today. As a rule, the majority of ...
... effects. The most used drugs are paracetamol and phenacetin. Paracetamol, as metabolite of phenacetin, has similar medicamental property but does not share phenacetin’s carcirogenic side effects. Therefore it is one of the most popular analgesic and antipyretic drug today. As a rule, the majority of ...
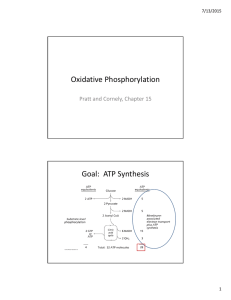
Oxidative Phosphorylation Goal: ATP Synthesis
... Through Q cycle Problem 10: An iron‐ sulfur protein in Complex III donates an electron to cytochrome c. Use the half reactions below to calculate the standard free energy change. How can you account for the fact that this process is spontaneous in the cell? ...
... Through Q cycle Problem 10: An iron‐ sulfur protein in Complex III donates an electron to cytochrome c. Use the half reactions below to calculate the standard free energy change. How can you account for the fact that this process is spontaneous in the cell? ...
The Cell, 5e
... a. Increase in 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate synthesis by rbc b. Decrease in 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate synthesis by rbc c. Increase in hemoglobin synthesis by rbc d. Decrease in hemoglobin synthesis by rbc ...
... a. Increase in 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate synthesis by rbc b. Decrease in 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate synthesis by rbc c. Increase in hemoglobin synthesis by rbc d. Decrease in hemoglobin synthesis by rbc ...
Describe the structure/ function of blood cell types
... • Explain the metabolism of the red blood cell • Explain basics of hematopoiesis from bone marrow • Describe some errors of hemoglobin function, anemias, hemoglobin switching • Describe the structure/ function of blood group ...
... • Explain the metabolism of the red blood cell • Explain basics of hematopoiesis from bone marrow • Describe some errors of hemoglobin function, anemias, hemoglobin switching • Describe the structure/ function of blood group ...
Datasheet - LifeSensors
... Interferon stimulated gene 15 (ISG15) is a member of the ubiquitin-like protein family whose expression is increased following stimulation with type 1 Interferons. ISG15-VME is synthesized by the conjugation of 4-amino-but-2-enoic acid methyl ester to the C-terminus of ISG15G156. Binding of ISG15-V ...
... Interferon stimulated gene 15 (ISG15) is a member of the ubiquitin-like protein family whose expression is increased following stimulation with type 1 Interferons. ISG15-VME is synthesized by the conjugation of 4-amino-but-2-enoic acid methyl ester to the C-terminus of ISG15G156. Binding of ISG15-V ...
Red Blood Cell Metabolism: Objectives
... 5. How is 2,3-DPG synthesized and how does its concentration change in response to hypoxia in erythrocytes? a. 2,3-DPG is synthesized by: i. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate 1,3-diphosphoglycerate 2,3-DPG 1. Enzyme to 2,3-DPG: Diphosphoglycerate mutase 2. It can go back into the glycolysis pathway with ...
... 5. How is 2,3-DPG synthesized and how does its concentration change in response to hypoxia in erythrocytes? a. 2,3-DPG is synthesized by: i. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate 1,3-diphosphoglycerate 2,3-DPG 1. Enzyme to 2,3-DPG: Diphosphoglycerate mutase 2. It can go back into the glycolysis pathway with ...
role of molecular modelling in drug design
... Drug design is the inventive process of finding new medications based on the knowledge of a biological target. The drug is most commonly an organic small molecule that activates or inhibits the function of a biomolecule such as a protein, which inturn results in a therapeutic benefit to the patient. ...
... Drug design is the inventive process of finding new medications based on the knowledge of a biological target. The drug is most commonly an organic small molecule that activates or inhibits the function of a biomolecule such as a protein, which inturn results in a therapeutic benefit to the patient. ...
class10-science-notes
... (ii) Walls are one cell thick only for easy exchange of blood. Platelets- Plug the leaks of arteries and veins by clotting the blood. Lymph- Extracellular fluid similar to plasma but colourless with lesser protein. Function of lymph- (i) Transportation of digested & absorbed fats from the smal ...
... (ii) Walls are one cell thick only for easy exchange of blood. Platelets- Plug the leaks of arteries and veins by clotting the blood. Lymph- Extracellular fluid similar to plasma but colourless with lesser protein. Function of lymph- (i) Transportation of digested & absorbed fats from the smal ...
Biochemistry - Textbooks Online
... Biochemistry (Study of Biomolecules and their functions). Along with these branches certain other specialities have also come up such as Agricultural Biochemistry, Pharmacological Biochemistry etc. ...
... Biochemistry (Study of Biomolecules and their functions). Along with these branches certain other specialities have also come up such as Agricultural Biochemistry, Pharmacological Biochemistry etc. ...
Drafting Patent Claims for Filing in the United States
... requires more than a mere statement that it is part of the invention and reference to a potential method for isolating it; what is required is a description of the DNA itself. Fiers v. Revel • For inventions in an unpredictable art, adequate written description of a genus which embraces widely varia ...
... requires more than a mere statement that it is part of the invention and reference to a potential method for isolating it; what is required is a description of the DNA itself. Fiers v. Revel • For inventions in an unpredictable art, adequate written description of a genus which embraces widely varia ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.