30 - Edgemead High School
... Describe and apply simple rules to deduce bond formation, viz. o different atoms, each with an unpaired valence electron can share these electrons to form a chemical bond o different atoms with paired valence electrons called lone pairs of electrons, cannot share these four electrons and cannot form ...
... Describe and apply simple rules to deduce bond formation, viz. o different atoms, each with an unpaired valence electron can share these electrons to form a chemical bond o different atoms with paired valence electrons called lone pairs of electrons, cannot share these four electrons and cannot form ...
Lecture Presentation to accompany Principles of Life
... Fatty acids can be converted to acetyl CoA. Proteins are hydrolyzed to amino acids that can feed into glycolysis or the citric acid cycle. ...
... Fatty acids can be converted to acetyl CoA. Proteins are hydrolyzed to amino acids that can feed into glycolysis or the citric acid cycle. ...
Enzymes in Food Technology
... • Casein (from Latin caseus, "cheese") is the name for a family of related phosphoprotein proteins (αS1, αS2, β, κ). • These proteins are commonly found in mammalian milk, making up 80% of the proteins in cow milk and between 60% and 65% of the proteins in human milk. • Casein has a wide variety of ...
... • Casein (from Latin caseus, "cheese") is the name for a family of related phosphoprotein proteins (αS1, αS2, β, κ). • These proteins are commonly found in mammalian milk, making up 80% of the proteins in cow milk and between 60% and 65% of the proteins in human milk. • Casein has a wide variety of ...
Department of Biological Sciences
... The course is designed to provide an understanding of the physical, structural and functional properties of the chemical components of living matter. The course will cover the three major classes of biological molecules: proteins, carbohydrates and lipids. Emphasis will be on the chemical properties ...
... The course is designed to provide an understanding of the physical, structural and functional properties of the chemical components of living matter. The course will cover the three major classes of biological molecules: proteins, carbohydrates and lipids. Emphasis will be on the chemical properties ...
P site - Industrial ISD
... RNA plays multiple roles in the cell: a review • The cellular machinery of protein synthesis and ER targeting is dominated by various kinds of RNA. • The diverse functions of RNA are based, in part, on its ability to form hydrogen bonds with other nucleic acid molecules (DNA or RNA). • It can also ...
... RNA plays multiple roles in the cell: a review • The cellular machinery of protein synthesis and ER targeting is dominated by various kinds of RNA. • The diverse functions of RNA are based, in part, on its ability to form hydrogen bonds with other nucleic acid molecules (DNA or RNA). • It can also ...
Chapter 6 Cellular Energy
... Fatty acids can be converted to acetyl CoA. Proteins are hydrolyzed to amino acids that can feed into glycolysis or the citric acid cycle. ...
... Fatty acids can be converted to acetyl CoA. Proteins are hydrolyzed to amino acids that can feed into glycolysis or the citric acid cycle. ...
Trans-Tonoplast Transport of the Sulfur Containing
... the cellular sulfur, mainly in the form of sulfate (cf. RENNENBERG 1984). They also contain some glutathione and methionine (Table 1). Vacuolar cysteine-levels were usually below or close to the detection limit of analysis. In order, to understand the pattern of compartmentation of sulfur-containing ...
... the cellular sulfur, mainly in the form of sulfate (cf. RENNENBERG 1984). They also contain some glutathione and methionine (Table 1). Vacuolar cysteine-levels were usually below or close to the detection limit of analysis. In order, to understand the pattern of compartmentation of sulfur-containing ...
Chemistry of the Non
... • H is a special case. Electronegativity is important when determining whether an element is a metal. Nonmetals tend to have higher electronegativities than metals. • Thus, reactions of metals and nonmetals often yield ionic compounds. • Compounds formed between nonmetals tend to be molecular. As we ...
... • H is a special case. Electronegativity is important when determining whether an element is a metal. Nonmetals tend to have higher electronegativities than metals. • Thus, reactions of metals and nonmetals often yield ionic compounds. • Compounds formed between nonmetals tend to be molecular. As we ...
Codon Dictionary Worksheet
... instance, the codon UUU attracts the anticodon of the tRNA that carries the amino acid “phe” (phenylalanine), and the codon CAA attracts the anticodon of the tRNA that carries the amino acid “gln” (glutamine). Which codon attracts the tRNA that carries the amino acid “pro” (proline)? (Answer #9 belo ...
... instance, the codon UUU attracts the anticodon of the tRNA that carries the amino acid “phe” (phenylalanine), and the codon CAA attracts the anticodon of the tRNA that carries the amino acid “gln” (glutamine). Which codon attracts the tRNA that carries the amino acid “pro” (proline)? (Answer #9 belo ...
Chapter 17 - cloudfront.net
... 20. Describe the structure of a ribosome and explain how this structure relates to function. ...
... 20. Describe the structure of a ribosome and explain how this structure relates to function. ...
synthase is regulated by mRNA splicing
... described (1). Briefly, the cDNA'was isolated from CEF infected with tsNY72-4RSV, a temperature-sensitive mutant of Rous sarcoma virus. The CEF-147 cDNA detected rare 3.0-kb and -5.0-kb mRNAs in nontransformed CEF. When pp60v-src in tsNY72-4RSV-infected cells was activated by temperature shift, cell ...
... described (1). Briefly, the cDNA'was isolated from CEF infected with tsNY72-4RSV, a temperature-sensitive mutant of Rous sarcoma virus. The CEF-147 cDNA detected rare 3.0-kb and -5.0-kb mRNAs in nontransformed CEF. When pp60v-src in tsNY72-4RSV-infected cells was activated by temperature shift, cell ...
The end products of aerobic respiration are?
... Respiration includes inhalation, expiration processes during inspiration the volume of the chest cavity is increased as the diaphragm contracts dome flattens out, its internal pressure decreases and the air from the outside rushes into the lungs. Respiration is not essentially a process of combustio ...
... Respiration includes inhalation, expiration processes during inspiration the volume of the chest cavity is increased as the diaphragm contracts dome flattens out, its internal pressure decreases and the air from the outside rushes into the lungs. Respiration is not essentially a process of combustio ...
DNA, RNA, and Protein Synthesis
... • X-Ray Evidence – Rosalind Franklin used X-ray diffraction to get information about the structure of DNA. – She aimed an X-ray beam at concentrated DNA samples and recorded the scattering pattern of the X-rays on film. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall ...
... • X-Ray Evidence – Rosalind Franklin used X-ray diffraction to get information about the structure of DNA. – She aimed an X-ray beam at concentrated DNA samples and recorded the scattering pattern of the X-rays on film. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall ...
Nucleoside Phosphoramidate Monoesters: Potential
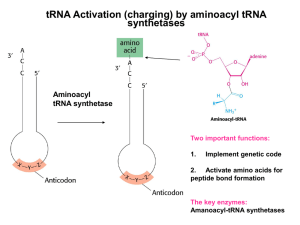
... The accuracy of protein synthesis depends on correct charging of tRNAs with amino acids 1. tRNA synthetases must link tRNAs with their correct amino acids. 2. tRNA synthetases recognize correct amino acids by specific binding to the active site and proofreading. 3. tRNA synthetases recognize correc ...
... The accuracy of protein synthesis depends on correct charging of tRNAs with amino acids 1. tRNA synthetases must link tRNAs with their correct amino acids. 2. tRNA synthetases recognize correct amino acids by specific binding to the active site and proofreading. 3. tRNA synthetases recognize correc ...
21:120:202 Foundations of Biology: Cell and Molecular Biology Lab
... the ability to describe the general structure of biomolecules as well as their role in cellular metabolism and the flow of genetic information; information and concepts on bioenergetics and the use of energy by cells; the information on the principles of membrane transport mechanisms and their role ...
... the ability to describe the general structure of biomolecules as well as their role in cellular metabolism and the flow of genetic information; information and concepts on bioenergetics and the use of energy by cells; the information on the principles of membrane transport mechanisms and their role ...
NADH - Cloudfront.net
... • Summary: 10 NADH, 2 FADH, 4 ATP, 4 CO2. The 10 NADH and 2 FADH (both energy molecules) will drive the next stage of cellular respiration in the Electron Transport Chain. ...
... • Summary: 10 NADH, 2 FADH, 4 ATP, 4 CO2. The 10 NADH and 2 FADH (both energy molecules) will drive the next stage of cellular respiration in the Electron Transport Chain. ...
Fatty Acid Synthesis
... The conversion of stearoyl-CoA to oleoyl-CoA in eukaryotes is catalyzed by stearoyl-CoA desaturase in a reaction sequence that also involves cytochrome b5 and cytochrome b5 reductase. Two electrons are passed from NADH through the chain of reactions as shown, and two electrons are also derived from ...
... The conversion of stearoyl-CoA to oleoyl-CoA in eukaryotes is catalyzed by stearoyl-CoA desaturase in a reaction sequence that also involves cytochrome b5 and cytochrome b5 reductase. Two electrons are passed from NADH through the chain of reactions as shown, and two electrons are also derived from ...
2. The Respiratory System
... Gas exchange can now take place more quickly meaning exercise can be maintained at a higher intensity for longer. 15 of 28 ...
... Gas exchange can now take place more quickly meaning exercise can be maintained at a higher intensity for longer. 15 of 28 ...
Document
... = partial specific volume of the solute (units: cm3/g) One rough estimation of the partial specific volume of a protein, which may be used if the sequence of the protein is not known, is: average partial specific volume of proteins = 0.725 cm^3/g Because the average of experimentally determined p ...
... = partial specific volume of the solute (units: cm3/g) One rough estimation of the partial specific volume of a protein, which may be used if the sequence of the protein is not known, is: average partial specific volume of proteins = 0.725 cm^3/g Because the average of experimentally determined p ...
S.O.L. Review
... B. It has the same number of protons and two more electrons than C-12 C. It has the same number of protons but two more neutrons than C-12 D. It has a different number of protons and two more neutrons than C-12 ...
... B. It has the same number of protons and two more electrons than C-12 C. It has the same number of protons but two more neutrons than C-12 D. It has a different number of protons and two more neutrons than C-12 ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.