Successful Longevity - SENS Research Foundation
... How can a pathway serve as ‘nutrient sensing’? • Should serve as a switch “on” or “off”. • Should be a small pathway that can be amplified by several folds. ...
... How can a pathway serve as ‘nutrient sensing’? • Should serve as a switch “on” or “off”. • Should be a small pathway that can be amplified by several folds. ...
Energetic Effects of Multiple Hydrogen Bonds. Implications for
... contrast to covalent interactions, produces little change in charge distribution.18 Thus, the combined energetic effects of multiple hydrogen bonding and other electrostatic interactions, even if individually modest, can be used by enzymes to achieve significant transition state stabilization. There ...
... contrast to covalent interactions, produces little change in charge distribution.18 Thus, the combined energetic effects of multiple hydrogen bonding and other electrostatic interactions, even if individually modest, can be used by enzymes to achieve significant transition state stabilization. There ...
W+-Retail-summary
... amino acid: soothes. •Anti-age Illuminating agent: Combination of rabdosia Rubescens + Siegesbeckia: Action on collagen synthesis Action on Skin Chromophores(Hemoglob in, Melanin, Collagen) ...
... amino acid: soothes. •Anti-age Illuminating agent: Combination of rabdosia Rubescens + Siegesbeckia: Action on collagen synthesis Action on Skin Chromophores(Hemoglob in, Melanin, Collagen) ...
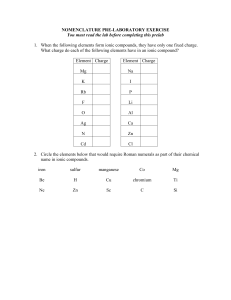
periodic table - Mesa Community College
... DISCUSSION: After the names and symbols of the elements are mastered, we can now move to the second task: assembling these symbols and names and learning how to write formulas and name compounds. Compounds are defined as pure substances that can be broken down to simpler pure substances by a chemica ...
... DISCUSSION: After the names and symbols of the elements are mastered, we can now move to the second task: assembling these symbols and names and learning how to write formulas and name compounds. Compounds are defined as pure substances that can be broken down to simpler pure substances by a chemica ...
How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy Chapter 6 PowerPoint Lectures for
... 6.4 The human body uses energy from ATP for • the body needs a continual • ATP supplies ...
... 6.4 The human body uses energy from ATP for • the body needs a continual • ATP supplies ...
Enzyme Lab
... a chemical reaction without being consumed or transformed by the reaction. The catalyst does not alter the equilibrium constant of the reaction. Only the rate of approach to equilibrium is changed. A catalyst is not required in stoichiometric quantities and is often used in trace amounts. Platinum, ...
... a chemical reaction without being consumed or transformed by the reaction. The catalyst does not alter the equilibrium constant of the reaction. Only the rate of approach to equilibrium is changed. A catalyst is not required in stoichiometric quantities and is often used in trace amounts. Platinum, ...
5. Respiration Booklet TN
... (tri/3) phosphate(s); IGNORE chemical formulae (as Q asks for name) DO NOT CREDIT phosphorus/phosphoryl (PO) Mark the first answer for each letter. If the answer is correct and an additional answer is given that is incorrect or contradicts the correct answer then = 0 marks. (a) (ii) (1) transfers en ...
... (tri/3) phosphate(s); IGNORE chemical formulae (as Q asks for name) DO NOT CREDIT phosphorus/phosphoryl (PO) Mark the first answer for each letter. If the answer is correct and an additional answer is given that is incorrect or contradicts the correct answer then = 0 marks. (a) (ii) (1) transfers en ...
Chapter 3
... • Either way, the VO2 requirement is far greater than any VO2max ever recorded. – Energy is transformed from chemical to mechanical from other ...
... • Either way, the VO2 requirement is far greater than any VO2max ever recorded. – Energy is transformed from chemical to mechanical from other ...
Exercise and Physical Fitness
... Aerobic exercise is powered by chemical reactions that require oxygen, It makes the heart stronger, improves oxygen uptake, and increases endurance Physical fitness increases the body’s flexibility and muscle mass while decreasing the amount of fat ...
... Aerobic exercise is powered by chemical reactions that require oxygen, It makes the heart stronger, improves oxygen uptake, and increases endurance Physical fitness increases the body’s flexibility and muscle mass while decreasing the amount of fat ...
Stoichiometry – Chapter 9
... Stoichiometry ? the name given to the study of quantitative relationships that can be derived from formulas and equations. It is from the Greek words stoicheion, meaning ?element? and metron, meaning ?measure?. There are two types: composition stoichiometry (formulas) and reaction stoichiometry (equ ...
... Stoichiometry ? the name given to the study of quantitative relationships that can be derived from formulas and equations. It is from the Greek words stoicheion, meaning ?element? and metron, meaning ?measure?. There are two types: composition stoichiometry (formulas) and reaction stoichiometry (equ ...
BIOCHEMISTRY Which of the following single
... A. Digestion of dietary polysaccharides takes place to a significant extent in the stomach due to acid hydrolysis. B. Digestion initially takes place in the mouth through the action of - amylase. C. -1,4 glycosidic linkages in cellulose. D. The final end products of digestion are all glucose molecul ...
... A. Digestion of dietary polysaccharides takes place to a significant extent in the stomach due to acid hydrolysis. B. Digestion initially takes place in the mouth through the action of - amylase. C. -1,4 glycosidic linkages in cellulose. D. The final end products of digestion are all glucose molecul ...
Acid – base balance
... All the known low molecular weight and water soluble biosynthetic intermediates possess groups that are almost completely ionised at neutral pH’ ...
... All the known low molecular weight and water soluble biosynthetic intermediates possess groups that are almost completely ionised at neutral pH’ ...
Life 9e - Garvness
... 4. When a molecule loses hydrogen atoms (as opposed to hydrogen ions), it becomes a. reduced. b. oxidized. c. redoxed. d. hydrogenated. e. hydrolyzed. Answer: b Textbook Reference: 9.1 How Does Glucose Oxidation Release Chemical Energy? Page: 169 Bloom’s Category: 1. Remembering 5. ATP is a. a short ...
... 4. When a molecule loses hydrogen atoms (as opposed to hydrogen ions), it becomes a. reduced. b. oxidized. c. redoxed. d. hydrogenated. e. hydrolyzed. Answer: b Textbook Reference: 9.1 How Does Glucose Oxidation Release Chemical Energy? Page: 169 Bloom’s Category: 1. Remembering 5. ATP is a. a short ...
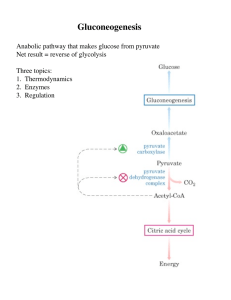
Gluconeogenesis - Creighton Chemistry Webserver
... Formed by phosphorylation of F6-P, catalyzed by PFK-2 Broken down by FBPase-2 PFK-2 and FBPase-2 are two distinct enzyme activities on 1 protein Balance of the 2 activities in the liver, which determines cellular level of F2,6BP, is regulated by glucagon Glucagon - released by pancreas to signal low ...
... Formed by phosphorylation of F6-P, catalyzed by PFK-2 Broken down by FBPase-2 PFK-2 and FBPase-2 are two distinct enzyme activities on 1 protein Balance of the 2 activities in the liver, which determines cellular level of F2,6BP, is regulated by glucagon Glucagon - released by pancreas to signal low ...
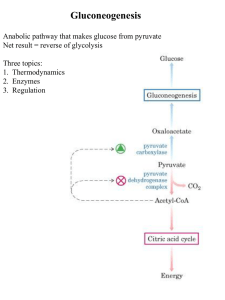
No Slide Title
... Formed by phosphorylation of F6-P, catalyzed by PFK-2 Broken down by FBPase-2 PFK-2 and FBPase-2 are two distinct enzyme activities on 1 protein Balance of the 2 activities in the liver, which determines cellular level of F2,6BP, is regulated by glucagon Glucagon - released by pancreas to signal low ...
... Formed by phosphorylation of F6-P, catalyzed by PFK-2 Broken down by FBPase-2 PFK-2 and FBPase-2 are two distinct enzyme activities on 1 protein Balance of the 2 activities in the liver, which determines cellular level of F2,6BP, is regulated by glucagon Glucagon - released by pancreas to signal low ...
2011
... CH3CH2CH2OH < HOCH2CH(OH)CH2OH < HOCH2CH2OH CH3CH2CH2OH < HOCH2CH2OH < HOCH2CH(OH)CH2OH HOCH2CH2OH < CH3CH2CH2OH < HOCH2CH(OH)CH2OH HOCH2CH2OH < HOCH2CH(OH)CH2OH < CH3CH2CH2OH ...
... CH3CH2CH2OH < HOCH2CH(OH)CH2OH < HOCH2CH2OH CH3CH2CH2OH < HOCH2CH2OH < HOCH2CH(OH)CH2OH HOCH2CH2OH < CH3CH2CH2OH < HOCH2CH(OH)CH2OH HOCH2CH2OH < HOCH2CH(OH)CH2OH < CH3CH2CH2OH ...
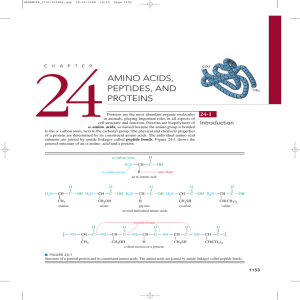
Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins
... those in meat, fish, milk, and eggs. About 50 g of complete protein per day is adequate for adult humans. Proteins that are severely deficient in one or more of the essential amino acids are called incomplete proteins. If the protein in a person’s diet comes mostly from one incomplete source, the am ...
... those in meat, fish, milk, and eggs. About 50 g of complete protein per day is adequate for adult humans. Proteins that are severely deficient in one or more of the essential amino acids are called incomplete proteins. If the protein in a person’s diet comes mostly from one incomplete source, the am ...
AP - 04 - Reactions in Aqueous Solutions
... o Determine the oxidation numbers of everything in H2S, S8, Na2SO3, and SO42(a) When bonded to a nonmetal, hydrogen has an oxidation number of +1 (rule 3b). Because the H2S molecule is neutral, the sum of the oxidation numbers must equal zero (rule 4). Letting x equal the oxidation number of S, we h ...
... o Determine the oxidation numbers of everything in H2S, S8, Na2SO3, and SO42(a) When bonded to a nonmetal, hydrogen has an oxidation number of +1 (rule 3b). Because the H2S molecule is neutral, the sum of the oxidation numbers must equal zero (rule 4). Letting x equal the oxidation number of S, we h ...
Export To Word
... properties. Matter is comprised of atomic, subatomic, and elementary particles. B. Electrons are key to defining chemical and some physical properties, reactivity, and molecular structures. Repeating (periodic) patterns of physical and chemical properties occur among elements that define groups of e ...
... properties. Matter is comprised of atomic, subatomic, and elementary particles. B. Electrons are key to defining chemical and some physical properties, reactivity, and molecular structures. Repeating (periodic) patterns of physical and chemical properties occur among elements that define groups of e ...
STUDY GUIDE
... cotton, and wood are all composed of polymers made by living organisms. Polymers are large molecules—natural or synthetic—made up of many monomers linked together. Homopolymers are polymers made of only a single type of monomer. Copolymers are polymers made of two or more types of monomers. Addition ...
... cotton, and wood are all composed of polymers made by living organisms. Polymers are large molecules—natural or synthetic—made up of many monomers linked together. Homopolymers are polymers made of only a single type of monomer. Copolymers are polymers made of two or more types of monomers. Addition ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.