Steps of Translation
... 2. A tRNA carrying an amino acid approaches 3. The Anticodon on the tRNA pairs with codon 4. The tRNA drops off it’s amino acid 5. An enzyme forms a peptide bond between amino acids 6. This process continues to form a protein until a STOP codon is reached and then the new protein is released. ...
... 2. A tRNA carrying an amino acid approaches 3. The Anticodon on the tRNA pairs with codon 4. The tRNA drops off it’s amino acid 5. An enzyme forms a peptide bond between amino acids 6. This process continues to form a protein until a STOP codon is reached and then the new protein is released. ...
DO NOW
... Why does the leading strand form continuously while the lagging strand is formed in fragments? ...
... Why does the leading strand form continuously while the lagging strand is formed in fragments? ...
1 Name Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Chemical Level of
... 25. The basic make-up of an organic compound are the carbons making the ___________________________. When hydrogens are attached to this, you can refer to that compound as a _________________________. Attached to these basic units are _______________________________ which confers characteristic chem ...
... 25. The basic make-up of an organic compound are the carbons making the ___________________________. When hydrogens are attached to this, you can refer to that compound as a _________________________. Attached to these basic units are _______________________________ which confers characteristic chem ...
Computational Prediction of Beta Structure from Amino Acid
... Our algorithm outperformed its predecessors in sensitivity to beta strands and in the false positive rate of beta strand discovery, showing approximately a two-and-a-half times improvement. Conclusions/Discussion Our algorithm improved beta structure prediction substantially by considering close as ...
... Our algorithm outperformed its predecessors in sensitivity to beta strands and in the false positive rate of beta strand discovery, showing approximately a two-and-a-half times improvement. Conclusions/Discussion Our algorithm improved beta structure prediction substantially by considering close as ...
Cell Respiration Practice Packet
... Define the words in the boxes. On the line across each arrow, write a phrase that describes how the words in the boxes are related to one another. ...
... Define the words in the boxes. On the line across each arrow, write a phrase that describes how the words in the boxes are related to one another. ...
Cellular Respiration Chapter 9
... Just like glycolysis!! Fermentation A series of reactions that convert NADH (from glycolysis) back into NAD allowing glycolysis to keep producing a small amount of ATP ...
... Just like glycolysis!! Fermentation A series of reactions that convert NADH (from glycolysis) back into NAD allowing glycolysis to keep producing a small amount of ATP ...
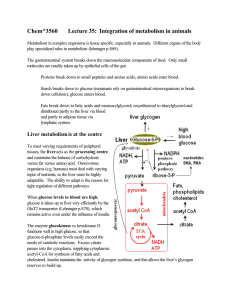
Chem*3560 Lecture 35: Integration of metabolism in animals
... the pentose phosphate pathway is relatively inactive. ...
... the pentose phosphate pathway is relatively inactive. ...
hwk- pg-331 - WordPress.com
... association an initiator methionine-tRNA with the small ribosomal subunit. The complex binds the mRNA at the 5' cap and scans for the AUG start codon. The large ribosomal subunit then binds, completing the ribosome, and translation proceeds. 2. The role of tRNA in translation is to shuttle the appro ...
... association an initiator methionine-tRNA with the small ribosomal subunit. The complex binds the mRNA at the 5' cap and scans for the AUG start codon. The large ribosomal subunit then binds, completing the ribosome, and translation proceeds. 2. The role of tRNA in translation is to shuttle the appro ...
6 Review of Molecular Biology
... DNA consists of a pair of molecules, organized as strands running start-to-end and joined by hydrogen bonds along their lengths.[ Each strand is a chain of chemical "building blocks", called nucleotides, of which there are four types: adenine (abbreviated A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T ...
... DNA consists of a pair of molecules, organized as strands running start-to-end and joined by hydrogen bonds along their lengths.[ Each strand is a chain of chemical "building blocks", called nucleotides, of which there are four types: adenine (abbreviated A), cytosine (C), guanine (G) and thymine (T ...
Lab #7 Exoenzymes, Differential and Selective Media
... Consequently, they are capable of degrading a variety of organic molecules. These molecules can be categorized by their structure and size. Some commonly utilized organic molecules are either macromolecules or constituents of macromolecules. The classes of organic macromolecules include proteins, ca ...
... Consequently, they are capable of degrading a variety of organic molecules. These molecules can be categorized by their structure and size. Some commonly utilized organic molecules are either macromolecules or constituents of macromolecules. The classes of organic macromolecules include proteins, ca ...
A plant has stunted growth and yellowing leaves because it is
... This answer suggests the student understands that this is a dehydration synthesis reaction because a hydrogen atom is removed from one amino acid and a hydroxyl group is removed from the other, and that the hydrogen and hydroxyl group form a water molecule, which is released to the environment. ...
... This answer suggests the student understands that this is a dehydration synthesis reaction because a hydrogen atom is removed from one amino acid and a hydroxyl group is removed from the other, and that the hydrogen and hydroxyl group form a water molecule, which is released to the environment. ...
Topic 3 MCQs revision
... The rate of reaction decreases continuously with increase in substrate concentration. ...
... The rate of reaction decreases continuously with increase in substrate concentration. ...
Slide 1
... Food enters the small intestine from the stomach. It passes along the small intestine where the soluble food is taken into the blood through the walls. ...
... Food enters the small intestine from the stomach. It passes along the small intestine where the soluble food is taken into the blood through the walls. ...
Microbial Metabolism
... • Hydrolysis reactions yield little energy & mostly lost as heat. • Simple sugars (e.g. glucose) enter catabolic reactions early at Glycolysis, PPP, E-DP, or used to biosynthesize other ...
... • Hydrolysis reactions yield little energy & mostly lost as heat. • Simple sugars (e.g. glucose) enter catabolic reactions early at Glycolysis, PPP, E-DP, or used to biosynthesize other ...
Citric Acid Cycle
... acids, ATP, etc K, Mg, Ca, Fe are required in relatively high levels Function as cofactors in enzyme reactions and as cations they act as buffers within the cells ...
... acids, ATP, etc K, Mg, Ca, Fe are required in relatively high levels Function as cofactors in enzyme reactions and as cations they act as buffers within the cells ...
Lecture 5: Basic Plant Biochemistry: Carbohydrates, Proteins
... that decomposes after the wound or incision heals ...
... that decomposes after the wound or incision heals ...
here - Crossfit Snohomish
... DIRECTIONS: Mix one scoop in 8-12 ounces of water or desired beverage and consume 15 minutes before workouts. May be used as pre workout for performance, post workout for recovery, general energy support or as directed by your healthcare practitioner. Elite Fuel: represents an extraordinary step for ...
... DIRECTIONS: Mix one scoop in 8-12 ounces of water or desired beverage and consume 15 minutes before workouts. May be used as pre workout for performance, post workout for recovery, general energy support or as directed by your healthcare practitioner. Elite Fuel: represents an extraordinary step for ...
File
... • The group OH can also substitute for hydrogen atoms in a hydrocarbon. • Each OH is made of an oxygen atom and a hydrogen atom and is called a hydroxyl group. • An alcohol is a substituted hydrocarbon that contains one or more hydroxyl groups. • When a hydroxyl group is substituted for one hydrogen ...
... • The group OH can also substitute for hydrogen atoms in a hydrocarbon. • Each OH is made of an oxygen atom and a hydrogen atom and is called a hydroxyl group. • An alcohol is a substituted hydrocarbon that contains one or more hydroxyl groups. • When a hydroxyl group is substituted for one hydrogen ...
4.2.1 Liver MS - Mrs Miller`s Blog
... long loop of Henlé or/ deep / wide, medulla ; very low water potential in medulla / AW ; A higher concentration of salts collecting duct more permeable to water ; large number of, water permeable channels / aquaporins, in collecting duct ; more sensitive to ADH / more ADH produced ; AVP ; e.g. other ...
... long loop of Henlé or/ deep / wide, medulla ; very low water potential in medulla / AW ; A higher concentration of salts collecting duct more permeable to water ; large number of, water permeable channels / aquaporins, in collecting duct ; more sensitive to ADH / more ADH produced ; AVP ; e.g. other ...
Visualizing Biological Pathways
... • Experiment 1: Used dissected livers of warm blooded animals and learned of the synthesis of sugar from lactic acid (from reduction of acid), and oxidative deanimation as a way to break down amino acids. Conclusion: Liver is the most important metabolic organ of the body. • Experiment 2: Pressing o ...
... • Experiment 1: Used dissected livers of warm blooded animals and learned of the synthesis of sugar from lactic acid (from reduction of acid), and oxidative deanimation as a way to break down amino acids. Conclusion: Liver is the most important metabolic organ of the body. • Experiment 2: Pressing o ...
Metabolic Pathways and Energy Production
... • Mitochondria are where energy-producing reactions occur ...
... • Mitochondria are where energy-producing reactions occur ...
Biochemistry
_and_Carl_Ferdinand_Cori.jpg?width=300)
Biochemistry, sometimes called biological chemistry, is the study of chemical processes within and relating to living organisms. By controlling information flow through biochemical signaling and the flow of chemical energy through metabolism, biochemical processes give rise to the complexity of life. Over the last decades of the 20th century, biochemistry has become so successful at explaining living processes that now almost all areas of the life sciences from botany to medicine to genetics are engaged in biochemical research. Today, the main focus of pure biochemistry is in understanding how biological molecules give rise to the processes that occur within living cells, which in turn relates greatly to the study and understanding of whole organisms.Biochemistry is closely related to molecular biology, the study of the molecular mechanisms by which genetic information encoded in DNA is able to result in the processes of life. Depending on the exact definition of the terms used, molecular biology can be thought of as a branch of biochemistry, or biochemistry as a tool with which to investigate and study molecular biology.Much of biochemistry deals with the structures, functions and interactions of biological macromolecules, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates and lipids, which provide the structure of cells and perform many of the functions associated with life. The chemistry of the cell also depends on the reactions of smaller molecules and ions. These can be inorganic, for example water and metal ions, or organic, for example the amino acids which are used to synthesize proteins. The mechanisms by which cells harness energy from their environment via chemical reactions are known as metabolism. The findings of biochemistry are applied primarily in medicine, nutrition, and agriculture. In medicine, biochemists investigate the causes and cures of disease. In nutrition, they study how to maintain health and study the effects of nutritional deficiencies. In agriculture, biochemists investigate soil and fertilizers, and try to discover ways to improve crop cultivation, crop storage and pest control.