MATHEMATICAL METHODS SOLUTION OF LINEAR SYSTEMS I
... Equivalent matrices: Two mxn matrices are called equivalent if one can be obtained from the other by a sequence of elementary operations. Equivalent matrices have the same order and the same rank. Normal form (or) canonical form: Any matrix of rank r > 0 can be reduced by elementary row and column o ...
... Equivalent matrices: Two mxn matrices are called equivalent if one can be obtained from the other by a sequence of elementary operations. Equivalent matrices have the same order and the same rank. Normal form (or) canonical form: Any matrix of rank r > 0 can be reduced by elementary row and column o ...
3.5 Perform Basic Matrix Operations
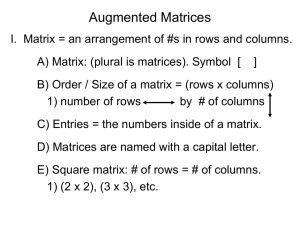
... II..Augment = to enhance, to make something bigger. A) Augmented matrix = a linear system written as a single matrix. 1) ax + by = # a b # a b # cx + dy = # ...
... II..Augment = to enhance, to make something bigger. A) Augmented matrix = a linear system written as a single matrix. 1) ax + by = # a b # a b # cx + dy = # ...
21-241 (Fall 15) Problems for Review Session (Sep 27, 2015) 1.
... (b) To prove that R2 restricted to x ≥ y is not a vector space, we want to show that the closure property does not hold. It suffices to show that there is a v = (xv , yv ) with xv ≥ yv , and its inverse −v = (−xv , −yv ) is not in the space since −xv ≤ −yv . (c) Given A and B are matrices, and AB is ...
... (b) To prove that R2 restricted to x ≥ y is not a vector space, we want to show that the closure property does not hold. It suffices to show that there is a v = (xv , yv ) with xv ≥ yv , and its inverse −v = (−xv , −yv ) is not in the space since −xv ≤ −yv . (c) Given A and B are matrices, and AB is ...
The calculation of the degree of an approximate greatest common
... The calculation of the degree of an approximate greatest common divisor (AGCD) of two inexact polynomials f (y) and g(y) is a non-trivial computation because it reduces to the estimation of the rank loss of a resultant matrix R(f, g). This computation is usually performed by placing a threshold on t ...
... The calculation of the degree of an approximate greatest common divisor (AGCD) of two inexact polynomials f (y) and g(y) is a non-trivial computation because it reduces to the estimation of the rank loss of a resultant matrix R(f, g). This computation is usually performed by placing a threshold on t ...