Eco 212_____Name
... Every year, the money supply starts rising before the intense Christmas shopping season occurs. If one considers the intense activity of Christmas shopping to be similar to a business cycle expansion, the relationship between the growth of the money supply and the increase in economic activity is be ...
... Every year, the money supply starts rising before the intense Christmas shopping season occurs. If one considers the intense activity of Christmas shopping to be similar to a business cycle expansion, the relationship between the growth of the money supply and the increase in economic activity is be ...
Causes of The Great Depression
... The Great Depression was not the country’s first depression, though it proved to be the longest and most severe. ...
... The Great Depression was not the country’s first depression, though it proved to be the longest and most severe. ...
The Long Swings in Economic Understanding
... couple of decades most everyone was pleased to accept the implied contention that Keynesinism was wrong in pure theory but right in policy practice. However, in switching back to the pre-Keynesian preoccupation with sticky wages, American Keynesianism gradually lost sight of the intertemporal coordi ...
... couple of decades most everyone was pleased to accept the implied contention that Keynesinism was wrong in pure theory but right in policy practice. However, in switching back to the pre-Keynesian preoccupation with sticky wages, American Keynesianism gradually lost sight of the intertemporal coordi ...
There is no such thing as a free lunch
... Allows the application of the Taylor rule ◼ Low inflation no acute problem: close to full capacity ◼ … however it will become when a recession hits ◼ Evidence shows higher inflation to be harmful… ◼ … but only above 10% per month (Barro) ...
... Allows the application of the Taylor rule ◼ Low inflation no acute problem: close to full capacity ◼ … however it will become when a recession hits ◼ Evidence shows higher inflation to be harmful… ◼ … but only above 10% per month (Barro) ...
100 years of business cycle analysis at the Kiel Institute 89th Kieler
... for financial market stress which help to explain the cycle. • Our studies show that recoveries after severe crises are less dynamic than after normal recessions. This has been one reason why we have been not very optimistic in our forecasts. • In addition, uncertainty about economic policy can be a ...
... for financial market stress which help to explain the cycle. • Our studies show that recoveries after severe crises are less dynamic than after normal recessions. This has been one reason why we have been not very optimistic in our forecasts. • In addition, uncertainty about economic policy can be a ...
Chapter 14 – Credit and Financial Crises
... multiplier-accelerator would do if it were based only on real factors. We previously developed a model where investment is a function of the accelerator times the increase in real income. Now, however, the availability of credit at low interest rates may have two effects: 1. increase investment beyo ...
... multiplier-accelerator would do if it were based only on real factors. We previously developed a model where investment is a function of the accelerator times the increase in real income. Now, however, the availability of credit at low interest rates may have two effects: 1. increase investment beyo ...
Is Milton Friedman a Keynesian?
... give rise to multiple rounds of increased spending and increased goods, on real as well as financial assets, on consumption real income. The nearly exclusive focus on this particular goods as well as investment goods. Nominal incomes are channel of effects, together with the belief that investment h ...
... give rise to multiple rounds of increased spending and increased goods, on real as well as financial assets, on consumption real income. The nearly exclusive focus on this particular goods as well as investment goods. Nominal incomes are channel of effects, together with the belief that investment h ...
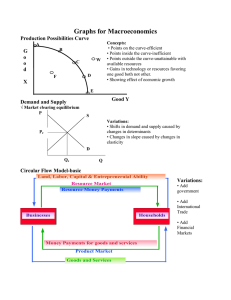
Graphs for Macroeconomics Production Possibilities Curve G o
... • As new demand and supply factors impact this market, changes in interest rate causes changes in investment and interest rate-driven consumption, which affects AD, ASsr, ASlr PL and Real GDP. • When government financing deficit spending, the impact of borrowing increases the demand curve and raises ...
... • As new demand and supply factors impact this market, changes in interest rate causes changes in investment and interest rate-driven consumption, which affects AD, ASsr, ASlr PL and Real GDP. • When government financing deficit spending, the impact of borrowing increases the demand curve and raises ...
History of Economic Thought Pre-Keynesian business
... market rate < natural rate, credit expansion More round about / capital-intensive production processes Rising investment goods prices, delayed increases in wages and consumer goods prices Upper turning point Reserves of the banking system are exhausted: market rate ↑ Recession Bankrupcies, lay-offs, ...
... market rate < natural rate, credit expansion More round about / capital-intensive production processes Rising investment goods prices, delayed increases in wages and consumer goods prices Upper turning point Reserves of the banking system are exhausted: market rate ↑ Recession Bankrupcies, lay-offs, ...
Macro_3.4-_Classical_vs._Keynesian
... a task if in tempestuous seasons they can only tell us that when the storm is past the ocean is flat again” ...
... a task if in tempestuous seasons they can only tell us that when the storm is past the ocean is flat again” ...
Asset Allocation Thoughts: The Global Economy and Asset Returns
... in this document is made on a general basis and is not to be relied on by the reader as advice. Neither the Manager nor any of its employees, associated group companies or agents have given any consideration to nor have they or any of them made any investigation of the investment objectives, financi ...
... in this document is made on a general basis and is not to be relied on by the reader as advice. Neither the Manager nor any of its employees, associated group companies or agents have given any consideration to nor have they or any of them made any investigation of the investment objectives, financi ...
The similarities between the causes of the Great Depression
... to reduce the baneful effects of recession. He introduced his theory to battle the Great Depression. According to the theory of Keynes increasing government spending and reducing tax rates is the most expedient way of stimulating the aggregate demand. He held that the government should spend more fo ...
... to reduce the baneful effects of recession. He introduced his theory to battle the Great Depression. According to the theory of Keynes increasing government spending and reducing tax rates is the most expedient way of stimulating the aggregate demand. He held that the government should spend more fo ...
Long Wave, Globalization and Technological Salvation - Tsang Shu-ki
... deflation and lack of demand at the same time. Now an increasing number of economists, led by Paul Krugman of the MIT, are arguing that the Japanese economy is caught in a liquidity trap, in which saving and investment would only equalize at negative real interest rates.(3) This is a very interestin ...
... deflation and lack of demand at the same time. Now an increasing number of economists, led by Paul Krugman of the MIT, are arguing that the Japanese economy is caught in a liquidity trap, in which saving and investment would only equalize at negative real interest rates.(3) This is a very interestin ...
MV=PQ questions - CHS Commerce Department
... C Concepts must be defined and terms used correctly with depth in answers including the Why, What and How of the situation. ...
... C Concepts must be defined and terms used correctly with depth in answers including the Why, What and How of the situation. ...
Document
... Bad U.S. Monetary Policy Caused the Great Depression “The [1929]recession was an ordinary business cycle. ...
... Bad U.S. Monetary Policy Caused the Great Depression “The [1929]recession was an ordinary business cycle. ...
Lessons of the Great Depression
... I thought the fallacy of identifying tight money with high interest rates and easy money with low interest rates was ...
... I thought the fallacy of identifying tight money with high interest rates and easy money with low interest rates was ...
Business Cycles
... When they believe profits will decline, they reduce production and investment. ...
... When they believe profits will decline, they reduce production and investment. ...
Rational Expectations
... the left). This reduction in output nullifies the expansionary effect of fiscal policy. In accordance with Classical Theory, the rational expectations theory assumes that wages, prices, and interest rates adjust quickly to keep real GDP at the full-employment level. Unemployment is seen as a tempora ...
... the left). This reduction in output nullifies the expansionary effect of fiscal policy. In accordance with Classical Theory, the rational expectations theory assumes that wages, prices, and interest rates adjust quickly to keep real GDP at the full-employment level. Unemployment is seen as a tempora ...
Leijonhufvud paper 2009 KeynesCrisisRev
... 2009). Both Sweden and Finland took some three years to overcome the crisis but have shown what is by European standards strong growth since. The devaluations that aided their export industries were no doubt of great importance for this growth record but it is extremely unlikely that anything like i ...
... 2009). Both Sweden and Finland took some three years to overcome the crisis but have shown what is by European standards strong growth since. The devaluations that aided their export industries were no doubt of great importance for this growth record but it is extremely unlikely that anything like i ...
Slide 1
... emphasis on avoiding excessive credit supply, reveals a diagnosis which interprets bubbles as asset price inflation. Then, the key to macroeconomic stability would lie on fighting not only goods inflation but also asset price inflation. This is clearly stated on the report: “Characteristics of the n ...
... emphasis on avoiding excessive credit supply, reveals a diagnosis which interprets bubbles as asset price inflation. Then, the key to macroeconomic stability would lie on fighting not only goods inflation but also asset price inflation. This is clearly stated on the report: “Characteristics of the n ...
Chapter 5
... Combined monetary and fiscal policy effects Fiscal policy usually has a bigger influence on the demand for loanable funds Monetary policy usually has a bigger influence on the supply of loanable funds ...
... Combined monetary and fiscal policy effects Fiscal policy usually has a bigger influence on the demand for loanable funds Monetary policy usually has a bigger influence on the supply of loanable funds ...
Stages of the Business Cycle
... Identify three likely effects on a business of a downturn in the business cycle a) Higher sales due to rising consumer incomes b) Lower fixed costs due to lower interest rates c) Less risk of the business becoming insolvent d) More difficult to recruit employees e) Lower demand due to business closu ...
... Identify three likely effects on a business of a downturn in the business cycle a) Higher sales due to rising consumer incomes b) Lower fixed costs due to lower interest rates c) Less risk of the business becoming insolvent d) More difficult to recruit employees e) Lower demand due to business closu ...
The New-Keynesian Theory of Aggregate Supply Chapter 8
... • Okun’s Law says that when unemployment increases by 1 percentage point, GDP will fall 3% below trend. ...
... • Okun’s Law says that when unemployment increases by 1 percentage point, GDP will fall 3% below trend. ...