Richter scale - Plain Local Schools
... • FOCUS = place deep within the Earth and along the fault where rupture occurs • EPICENTER = geographic point on surface directly above focus • SEISMIC WAVES produced by the release of energy – move out in circles from the point of rupture (focus) – 2 types: surface & body (travel inside & thro ...
... • FOCUS = place deep within the Earth and along the fault where rupture occurs • EPICENTER = geographic point on surface directly above focus • SEISMIC WAVES produced by the release of energy – move out in circles from the point of rupture (focus) – 2 types: surface & body (travel inside & thro ...
EARTHQUAKE WAVES
... Their speed depend on how easily the material can be compressed, how rigid it is, and its density. They are the fastest waves, and thus the first to arrive, travelling at speeds of 4-7 km/sec in the earth’s crust. They sometimes hit houses with a boom of sound which rattles windows, but they general ...
... Their speed depend on how easily the material can be compressed, how rigid it is, and its density. They are the fastest waves, and thus the first to arrive, travelling at speeds of 4-7 km/sec in the earth’s crust. They sometimes hit houses with a boom of sound which rattles windows, but they general ...
Earthquakes
... • They are vibrations of Earth that occur when the lithosphere is strained. • Focus is the exact source underground where the earthquake occurred. • Epicenter is the same location on the Earth’s surface. • They can be 100 km or less. ...
... • They are vibrations of Earth that occur when the lithosphere is strained. • Focus is the exact source underground where the earthquake occurred. • Epicenter is the same location on the Earth’s surface. • They can be 100 km or less. ...
Guide to Seismic Phases
... Guide to Seismic Phases The change of seismic velocities within Earth, as well as the possibility of conversions between compressional (P) waves and shear (S) waves, results in many possible wave paths. Each path produces a separate seismic phase on seismograms. Seismic phases are described with one ...
... Guide to Seismic Phases The change of seismic velocities within Earth, as well as the possibility of conversions between compressional (P) waves and shear (S) waves, results in many possible wave paths. Each path produces a separate seismic phase on seismograms. Seismic phases are described with one ...
Notes Earthquakes
... SURFACE WAVES: These are restricted to the lithosphere, or surface of the Earth, and are responsible for most of the actual ground-shaking. Most of the kinetic energy of an earthquake is released in the form of surface waves. In fact practically all of the damage done by an earthquake is caused by s ...
... SURFACE WAVES: These are restricted to the lithosphere, or surface of the Earth, and are responsible for most of the actual ground-shaking. Most of the kinetic energy of an earthquake is released in the form of surface waves. In fact practically all of the damage done by an earthquake is caused by s ...
EARTHQUAKES & VOLCANOES
... Seismology is the study of earthquakes and seismic waves that move through and around the earth. A seismologist is a scientist who studies earthquakes and seismic waves. What Are Seismic Waves? • Seismic waves are the waves of energy caused by the sudden breaking of rock within the earth or an explo ...
... Seismology is the study of earthquakes and seismic waves that move through and around the earth. A seismologist is a scientist who studies earthquakes and seismic waves. What Are Seismic Waves? • Seismic waves are the waves of energy caused by the sudden breaking of rock within the earth or an explo ...
Lab 3 - Geologic Structures, Maps, and Block Diagrams
... – Anticlines - Oldest rocks in the middle young ...
... – Anticlines - Oldest rocks in the middle young ...
Elasticity and Anisotropy of Common Crustal Minerals
... Shown above are composition ranging from albite to anorthite on the x-axis and velocity in km/s on the y-axis. Plotted are velocities from previous elasticity data and from my data. The vertical lines are not error bars – they are the maximum and minimum velocity values observed at each respective c ...
... Shown above are composition ranging from albite to anorthite on the x-axis and velocity in km/s on the y-axis. Plotted are velocities from previous elasticity data and from my data. The vertical lines are not error bars – they are the maximum and minimum velocity values observed at each respective c ...
waves & sound study guide
... called a ___________? Medium 17. When part of the Earth’s crust breaks, __________ waves pass through the Earth. Seismic 18. Sound travels the best and fastest through? Solids ...
... called a ___________? Medium 17. When part of the Earth’s crust breaks, __________ waves pass through the Earth. Seismic 18. Sound travels the best and fastest through? Solids ...
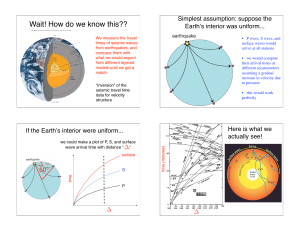
Wait! How do we know this??
... what we would expect from different layered models until we get a match ...
... what we would expect from different layered models until we get a match ...
Integrated Science Chapter 19 Name
... 9. Explain why volcanoes form at both convergent plate boundaries and divergent plate boundaries. ...
... 9. Explain why volcanoes form at both convergent plate boundaries and divergent plate boundaries. ...
Ch. 6.2 Notes
... to be recorded by a seismograph. 1. S-waves can only travel through ______________ material. 2. S-waves are ______________ waves which means that they cause rock particles to move at _____________ angles to the direction in which the waves are traveling. iii. _______________________ waves are create ...
... to be recorded by a seismograph. 1. S-waves can only travel through ______________ material. 2. S-waves are ______________ waves which means that they cause rock particles to move at _____________ angles to the direction in which the waves are traveling. iii. _______________________ waves are create ...
Earthquakes
... First waves to be detected during an earthquake Moves rock back and forth, which stretches and ...
... First waves to be detected during an earthquake Moves rock back and forth, which stretches and ...
Earthquakes Unit STUDY GUIDE
... c. can travel through solids, liquids, and gases. d. cause the Earth's surface to roll up and down. Most earthquakes occur along or near the edges of the Earth's a. oceans. c. rivers. b. tectonic plates. d. continents. ____ motion occurs where two tectonic plates slip past each other. a. Convergent ...
... c. can travel through solids, liquids, and gases. d. cause the Earth's surface to roll up and down. Most earthquakes occur along or near the edges of the Earth's a. oceans. c. rivers. b. tectonic plates. d. continents. ____ motion occurs where two tectonic plates slip past each other. a. Convergent ...
wave - UniMAP Portal
... At any time/point, the combined waveform of two or more interfering waves is given by the sum of the displacements of the individual waves at each point in the medium. ...
... At any time/point, the combined waveform of two or more interfering waves is given by the sum of the displacements of the individual waves at each point in the medium. ...
Seeing Our Universe Through Electromagnetic Radiation
... waves travel at different speeds through different mediums, the students will become a wave. Materials 4 pieces of string 3 meters long, 4 pieces 1.5 meter long, 4 pieces 75 cm long, a stopwatch, data table. Set Up Five (or more) students will be the electromagnetic wave by standing in a line holdin ...
... waves travel at different speeds through different mediums, the students will become a wave. Materials 4 pieces of string 3 meters long, 4 pieces 1.5 meter long, 4 pieces 75 cm long, a stopwatch, data table. Set Up Five (or more) students will be the electromagnetic wave by standing in a line holdin ...
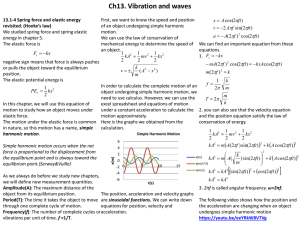
13.1-4 Spring force and elastic energy revisited. (Hooke’s law)
... A wave traveling in the positive x-direction is the maximum speed of the object if the pictured in Figure below. Find the amplitude of the motion is 0.0300m.(b) amplitude, wave length, speed and period What is the velocity of the object when the of the wave if it has a frequency of 8.00 Hz. displace ...
... A wave traveling in the positive x-direction is the maximum speed of the object if the pictured in Figure below. Find the amplitude of the motion is 0.0300m.(b) amplitude, wave length, speed and period What is the velocity of the object when the of the wave if it has a frequency of 8.00 Hz. displace ...
A simple approach to the joint inversion of seismic body and surface
... velocity can be determined from inter-station travel times. The principal drawback is the limited lateral sensitivity inherent in measuring long-period signals over short baselines. The lateral scale of resolved features for surface waves is frequently an order of magnitude greater than the correspo ...
... velocity can be determined from inter-station travel times. The principal drawback is the limited lateral sensitivity inherent in measuring long-period signals over short baselines. The lateral scale of resolved features for surface waves is frequently an order of magnitude greater than the correspo ...
Convergent Boundaries
... expansion and contraction of bedrock. • P-waves also have the ability to travel through solid, liquid, and ...
... expansion and contraction of bedrock. • P-waves also have the ability to travel through solid, liquid, and ...
Well-seismic bandwidth and time-lapse seismic characterization: physical considerations
... Reservoirs are commonly heterogeneous. Injection of CO2 related to enhanced oil recovery operations may cause strong lateral and depth-dependent changes of heterogeneity both within the reservoir and the surrounding formations. A seismic signal propagating through the reservoir and the surrounding f ...
... Reservoirs are commonly heterogeneous. Injection of CO2 related to enhanced oil recovery operations may cause strong lateral and depth-dependent changes of heterogeneity both within the reservoir and the surrounding formations. A seismic signal propagating through the reservoir and the surrounding f ...
Main Seismic Phases: Seismic Phases and 3D Seismic Waves
... Not all phases are easily distinguishable: Below is the result from a 3.5 event in Lethbridge. Only P and surface waves are seen near Claresholm region. Strong decay due to sedimentary cover and attenuation. ...
... Not all phases are easily distinguishable: Below is the result from a 3.5 event in Lethbridge. Only P and surface waves are seen near Claresholm region. Strong decay due to sedimentary cover and attenuation. ...
EGU06-A-10085 - Copernicus Meetings
... Central Alborz is the convergence point of the eastern and the western parts of the Alborz Mountains where great earthquakes have made a lot of fatalities. The central Alborz faults, especially around Tehran, are from mountain bordering type building heights and troughs that are mostly compressive o ...
... Central Alborz is the convergence point of the eastern and the western parts of the Alborz Mountains where great earthquakes have made a lot of fatalities. The central Alborz faults, especially around Tehran, are from mountain bordering type building heights and troughs that are mostly compressive o ...
Earthquake Powerpoint
... • FOCUS = place deep within the Earth and along the fault where rupture occurs • EPICENTER = geographic point on surface directly above focus • SEISMIC WAVES produced by the release of energy – move out in circles from the point of rupture (focus) – 2 types: surface & body (travel inside & through e ...
... • FOCUS = place deep within the Earth and along the fault where rupture occurs • EPICENTER = geographic point on surface directly above focus • SEISMIC WAVES produced by the release of energy – move out in circles from the point of rupture (focus) – 2 types: surface & body (travel inside & through e ...
Earthquake Notes
... energy from rocks that rupture because they have been subjected to stresses beyond their limit. This energy, which takes the form of waves, radiates in all directions from the earthquake's source, called the focus. The movements that produce most earthquakes occur along large fractures, called fault ...
... energy from rocks that rupture because they have been subjected to stresses beyond their limit. This energy, which takes the form of waves, radiates in all directions from the earthquake's source, called the focus. The movements that produce most earthquakes occur along large fractures, called fault ...
The Earth’s structure - Bishopston Comprehensive School
... • Earthquakes are caused when tension is released from inside the crust. • This happens because plates do not move smoothly - sometimes they get stuck. • When this happens a great deal of pressure builds up. • When this pressure is eventually released, an earthquake tends to occur. ...
... • Earthquakes are caused when tension is released from inside the crust. • This happens because plates do not move smoothly - sometimes they get stuck. • When this happens a great deal of pressure builds up. • When this pressure is eventually released, an earthquake tends to occur. ...
Surface wave inversion

Inversion is the set of methods used to infer properties through physical measurements. Surface wave inversion is the method by which elastic properties, density, and thickness of layers in the subsurface are attained through analysis of surface wavedispersion. The entire inversion process requires the gathering of seismic data, the creation of dispersion curves, and finally the inference of subsurface properties.