Exam No. 01 (Fall 2013) PHYS 520A: Electromagnetic Theory I
... where the closed surface encloses the volume between z = za − δ and z = za + δ for infinitely small δ > 0. Choose the plane wave to be incident on the side z = z − δ of the plate, and assuming E = 0 and B = 0 on the side z = z + δ, conclude that F = ẑ · T|z=za −δ , A ...
... where the closed surface encloses the volume between z = za − δ and z = za + δ for infinitely small δ > 0. Choose the plane wave to be incident on the side z = z − δ of the plate, and assuming E = 0 and B = 0 on the side z = z + δ, conclude that F = ẑ · T|z=za −δ , A ...
Ch. 14 Notes - BAschools.org
... through a point in one second. The larger the wavelength, the fewer times it will pass through a point in one second. ...
... through a point in one second. The larger the wavelength, the fewer times it will pass through a point in one second. ...
Seismic velocity and crustal thickness inversions: Moon and Mars
... impact sites. A full 3-D model of the lunar crustal thickness is then obtained using the GRAIL gravimetric data, anchored by the crustal thicknesses under each Apollo station and impact site. To avoid the use of any seismic reference model, a Bayesian inversion technique is implemented. The advantag ...
... impact sites. A full 3-D model of the lunar crustal thickness is then obtained using the GRAIL gravimetric data, anchored by the crustal thicknesses under each Apollo station and impact site. To avoid the use of any seismic reference model, a Bayesian inversion technique is implemented. The advantag ...
Chapter 2: Acoustic Wave Propagation
... Basics of Acoustic Waves • A medium is required for a sound wave. • Physical quantities to describe a sound wave: displacement, strain and pressure. ...
... Basics of Acoustic Waves • A medium is required for a sound wave. • Physical quantities to describe a sound wave: displacement, strain and pressure. ...
Earthquakes and the Interior
... living in earthquake regions, but the seismic waves generated by earthquakes are invaluable for studying the interior of Earth. Earthquake waves indicate several things about Earth’s Interior: 1) Earth appears to be layered, according to composition and physical properties. 2) Density increases wi ...
... living in earthquake regions, but the seismic waves generated by earthquakes are invaluable for studying the interior of Earth. Earthquake waves indicate several things about Earth’s Interior: 1) Earth appears to be layered, according to composition and physical properties. 2) Density increases wi ...
Earth`s interior volc eq2
... • Magnitude - a measure of the strength / energy of an earthquake – Each unit on the Richter scale represents motion that is 10 times larger than the previous unit. • A magnitude of 5 is ten times stronger than a 4. • A magnitude of 6 is 100 times stronger than a 4. ...
... • Magnitude - a measure of the strength / energy of an earthquake – Each unit on the Richter scale represents motion that is 10 times larger than the previous unit. • A magnitude of 5 is ten times stronger than a 4. • A magnitude of 6 is 100 times stronger than a 4. ...
Earthquakes
... • There are two general types of seismic waves: body waves and surface waves. • Surface waves travel just beneath the Earth's surface. • Body waves travel through the Earth's interior. • There are two types of body waves, P waves and S waves. • S waves have much higher amplitude than P waves, travel ...
... • There are two general types of seismic waves: body waves and surface waves. • Surface waves travel just beneath the Earth's surface. • Body waves travel through the Earth's interior. • There are two types of body waves, P waves and S waves. • S waves have much higher amplitude than P waves, travel ...
Earthquake Text Worksheet
... 3c. What type of plate movement causes anticlines and synclines to form? 3d. What type of plate movement causes ‘fault-block’ mountains to form? ...
... 3c. What type of plate movement causes anticlines and synclines to form? 3d. What type of plate movement causes ‘fault-block’ mountains to form? ...
Sample Final Exam Physics 131 Spring 2009
... 20) Consider a large truck carrying a heavy load, such as steel beams. A significant hazard for the driver is that the load may slide forward, crushing the cab, if the truck stops suddenly in an accident or even in braking. Assume, for example, that a 12000 kg load sits on the flat bed of a 20000 kg ...
... 20) Consider a large truck carrying a heavy load, such as steel beams. A significant hazard for the driver is that the load may slide forward, crushing the cab, if the truck stops suddenly in an accident or even in braking. Assume, for example, that a 12000 kg load sits on the flat bed of a 20000 kg ...
Faults - cloudfront.net
... VII. Damage negligible in buildings of good design and construction; slight to moderate in well-built ordinary structures; considerable damage in poorly built or badly designed structures; some chimneys broken. ...
... VII. Damage negligible in buildings of good design and construction; slight to moderate in well-built ordinary structures; considerable damage in poorly built or badly designed structures; some chimneys broken. ...
Particle-wave duality - Sierra College Astronomy Home Page
... mechanics” as, essentially, particles do not have inherent attributes like position or energy, until the moment of measurement collapses the wave function. Einstein, who believed in determinism in physics, despised this notion, saying instead that Quantum was simply incomplete, and missed “hidden va ...
... mechanics” as, essentially, particles do not have inherent attributes like position or energy, until the moment of measurement collapses the wave function. Einstein, who believed in determinism in physics, despised this notion, saying instead that Quantum was simply incomplete, and missed “hidden va ...
Slide 1 - Mr Lundy`s Room
... particular string are called resonant frequencies. They are also referred to as the fundamental and harmonics. ...
... particular string are called resonant frequencies. They are also referred to as the fundamental and harmonics. ...
Earthquake Recording Station
... 4. Explore: Click Reset, and drag the recording station closer to the epicenter. Click Play. A. How does this seismogram differ from the one you first investigated? ____________ ...
... 4. Explore: Click Reset, and drag the recording station closer to the epicenter. Click Play. A. How does this seismogram differ from the one you first investigated? ____________ ...
Student Exploration: Earthquake – Recording Station
... 4. Explore: Click Reset, and drag the recording station closer to the epicenter. Click Play. A. How does this seismogram differ from the one you first investigated? ____________ ...
... 4. Explore: Click Reset, and drag the recording station closer to the epicenter. Click Play. A. How does this seismogram differ from the one you first investigated? ____________ ...
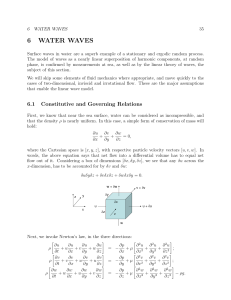
6 WATER WAVES - MIT OpenCourseWare
... of many years, intense storms are increasingly likely to occur, and these create short-term extreme seas that may not be well characterized at all in the sense of a spectrum. For the purpose of describing such processes, the Weibull distribution affords some freedom in shaping the ”tail.” The Weibull ...
... of many years, intense storms are increasingly likely to occur, and these create short-term extreme seas that may not be well characterized at all in the sense of a spectrum. For the purpose of describing such processes, the Weibull distribution affords some freedom in shaping the ”tail.” The Weibull ...
Notes - Earthquakes 2 - Seismic Waves / HW Questions
... • This spot experiences the ___________________ during the earthquake. • After an earthquake, the earthquakes ___________ is given by the _______________ location. Seismic Waves • When there is movement at a fault, energy is released in the form of __________________________: • The shaking occurs as ...
... • This spot experiences the ___________________ during the earthquake. • After an earthquake, the earthquakes ___________ is given by the _______________ location. Seismic Waves • When there is movement at a fault, energy is released in the form of __________________________: • The shaking occurs as ...
Seismic Waves Activity
... order to support the theory of plate tectonics. The evidence proves that there is a distinct relationship between seismic activity, volcanic activity, and the lithospheric plate boundaries. Seismic Data and Plate Tectonics: The interaction along ___________ boundaries results in an increased frequen ...
... order to support the theory of plate tectonics. The evidence proves that there is a distinct relationship between seismic activity, volcanic activity, and the lithospheric plate boundaries. Seismic Data and Plate Tectonics: The interaction along ___________ boundaries results in an increased frequen ...
19.1 Earthquakes
... a jump rope in one hand and raising and lowering it 3) Surface Waves (Love and Rayleigh): the most destructive, cause the ground to move sideways and up and down like an ocean wave Because they happen INSIDE the earth, P-waves and S-waves are also called body waves ...
... a jump rope in one hand and raising and lowering it 3) Surface Waves (Love and Rayleigh): the most destructive, cause the ground to move sideways and up and down like an ocean wave Because they happen INSIDE the earth, P-waves and S-waves are also called body waves ...
SG Earth Layers
... -how the temperature changes as you go from the surface toward the center of Earth -how pressure changes as you go from the surface toward the center of Earth -how deep we have drilled into the earth, relative to its size -how evidence from seismic waves help scientists learn about Earth’s interior ...
... -how the temperature changes as you go from the surface toward the center of Earth -how pressure changes as you go from the surface toward the center of Earth -how deep we have drilled into the earth, relative to its size -how evidence from seismic waves help scientists learn about Earth’s interior ...
19.1 Earthquakes
... a jump rope in one hand and raising and lowering it 3) Surface Waves (Love and Rayleigh): the most destructive, cause the ground to move sideways and up and down like an ocean wave Because they happen INSIDE the earth, P-waves and S-waves are also called body waves ...
... a jump rope in one hand and raising and lowering it 3) Surface Waves (Love and Rayleigh): the most destructive, cause the ground to move sideways and up and down like an ocean wave Because they happen INSIDE the earth, P-waves and S-waves are also called body waves ...
Lab 10: Reverse Time Depth Migration
... However, deviations from horizontal stratigraphy and wave effects both distort the sections and volumes. In unmigrated seismic data, dipping reflections appear displaced down dip and at shallower dip angles than the actual reflectors. Sharp bends and truncations in reflectors produce non-physical di ...
... However, deviations from horizontal stratigraphy and wave effects both distort the sections and volumes. In unmigrated seismic data, dipping reflections appear displaced down dip and at shallower dip angles than the actual reflectors. Sharp bends and truncations in reflectors produce non-physical di ...
3-Component Seismograph
... Earthquake—shaking or trembling of the earth that accompanies rock movements extending anywhere from the crust to 680 km below the Earth’s surface. It is the release of stored elastic energy caused by sudden fracture and movement of rocks inside the Earth. Part of the energy released produces seismi ...
... Earthquake—shaking or trembling of the earth that accompanies rock movements extending anywhere from the crust to 680 km below the Earth’s surface. It is the release of stored elastic energy caused by sudden fracture and movement of rocks inside the Earth. Part of the energy released produces seismi ...
Earthquakes
... of the Earth. As the waves propagate, the rocks are elastically deformed by change in either volume or shape. ...
... of the Earth. As the waves propagate, the rocks are elastically deformed by change in either volume or shape. ...
Surface wave inversion

Inversion is the set of methods used to infer properties through physical measurements. Surface wave inversion is the method by which elastic properties, density, and thickness of layers in the subsurface are attained through analysis of surface wavedispersion. The entire inversion process requires the gathering of seismic data, the creation of dispersion curves, and finally the inference of subsurface properties.