MCB Lecture 1 – Molecular Diagnostics
... How many cycles must you perform via PCR before you get the first exact sample that you want to amplify? o 4 Cycles If you have a single base difference in sequence that does not affect a restriction site, how do you detect it? o Use PCR and then ASO probes. o The mutation must be known, and it is s ...
... How many cycles must you perform via PCR before you get the first exact sample that you want to amplify? o 4 Cycles If you have a single base difference in sequence that does not affect a restriction site, how do you detect it? o Use PCR and then ASO probes. o The mutation must be known, and it is s ...
Restriction Enzymes
... DAN sequence between them may change. Thus if two DNA molecules differ in sequence, they likely have different lengths for the fragments produced following treatment with restriction enzymes. Typical digestions included a unit of enzyme per microgram of starting DNA, and one enzyme unit usually (dep ...
... DAN sequence between them may change. Thus if two DNA molecules differ in sequence, they likely have different lengths for the fragments produced following treatment with restriction enzymes. Typical digestions included a unit of enzyme per microgram of starting DNA, and one enzyme unit usually (dep ...
(Pulse-field Gel Electrophoresis)
... Why/When: PFGE is performed in the surveillance of retail foods and to monitor for outbreaks. When two or more bacterial isolates match in banding pattern, state epidemiologists are notified and they investigate. The investigation involves interviewing patients to determine if they have a common lin ...
... Why/When: PFGE is performed in the surveillance of retail foods and to monitor for outbreaks. When two or more bacterial isolates match in banding pattern, state epidemiologists are notified and they investigate. The investigation involves interviewing patients to determine if they have a common lin ...
Chapter 16-17 review sheet
... DNA ligase, RNA primase, Okazaki fragments, single-stranded binding proteins, leading strand, lagging strand, 5’, 3’, topoisomerase (gyrase), ATP, GTP, CTP, TTP, template strand, complementary strand, daughter strand, parent strand, RNA primer, and DNA polymerase III, DNA polymerase I. ...
... DNA ligase, RNA primase, Okazaki fragments, single-stranded binding proteins, leading strand, lagging strand, 5’, 3’, topoisomerase (gyrase), ATP, GTP, CTP, TTP, template strand, complementary strand, daughter strand, parent strand, RNA primer, and DNA polymerase III, DNA polymerase I. ...
PCR - churchillcollegebiblio
... forward primer and one is a reverse primer. When they have bound to the complementary sequences on the genomic DNA template strand, they show the Taq polymerase where to start DNA synthesis. The primers are responsible for making sure that only the region of interest is copied. • This is double-stra ...
... forward primer and one is a reverse primer. When they have bound to the complementary sequences on the genomic DNA template strand, they show the Taq polymerase where to start DNA synthesis. The primers are responsible for making sure that only the region of interest is copied. • This is double-stra ...
DNA Paternity Test RFLP analysis (Restriction Fragment Length
... e.g. BamHI XXXXXXXXGGATCCXXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXCCTAGGXXXXXXXXXX -due to spontaneous mutations over time, different people have slightly different base sequences in their DNA -if mutation creates or deletes a restriction site in the DNA, the new DNA will generate more or less fragments/different sized f ...
... e.g. BamHI XXXXXXXXGGATCCXXXXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXCCTAGGXXXXXXXXXX -due to spontaneous mutations over time, different people have slightly different base sequences in their DNA -if mutation creates or deletes a restriction site in the DNA, the new DNA will generate more or less fragments/different sized f ...
LNUC IV.A - UTK-EECS
... ¶1. Denaturation: causes DNA to unwind and separate into its two strands. This occurs by breaking the H-bonds between the bases. ¶2. Thermal denaturing is most common (about 95 C), but there are also chemical denaturing agents. A.3.b ...
... ¶1. Denaturation: causes DNA to unwind and separate into its two strands. This occurs by breaking the H-bonds between the bases. ¶2. Thermal denaturing is most common (about 95 C), but there are also chemical denaturing agents. A.3.b ...
DNA/RNA/Protein Questions
... What are proteins made of? How is the "Genetic Code" read? What is a codon? What is a start codon? Stop codon? What does Translation mean? What organelle makes proteins? What role does tRNA play in making proteins? What is an "anticodon"? What structure is it on? How is mRNA used to make proteins. W ...
... What are proteins made of? How is the "Genetic Code" read? What is a codon? What is a start codon? Stop codon? What does Translation mean? What organelle makes proteins? What role does tRNA play in making proteins? What is an "anticodon"? What structure is it on? How is mRNA used to make proteins. W ...
DNA, Genes, and Chromosome Quiz
... Write the letter on the line of the choice that best answers each question. _____ 4.) How many nitrogenous bases are there in DNA? A.) B.) C.) D.) ...
... Write the letter on the line of the choice that best answers each question. _____ 4.) How many nitrogenous bases are there in DNA? A.) B.) C.) D.) ...
Toxicity of benzo[a]pyrene occurs because of the formation of
... Toxicity of benzo[a]pyrene occurs because of the formation of covalent adducts with DNA guanines. In this work we report the attempt to detect this DNA-adduct using both an electrochemical assay based on gold nanoparticles and a surface plasmon resonance DNA sensor. Detection was achieved via inhibi ...
... Toxicity of benzo[a]pyrene occurs because of the formation of covalent adducts with DNA guanines. In this work we report the attempt to detect this DNA-adduct using both an electrochemical assay based on gold nanoparticles and a surface plasmon resonance DNA sensor. Detection was achieved via inhibi ...
Powerpoint
... They are not subject to natural selection Short repeated segments that are not protein encoding, distributed all over the genome ...
... They are not subject to natural selection Short repeated segments that are not protein encoding, distributed all over the genome ...
Introduction to Psychology
... Subtle chemical signals, or pheromones, have long been known to draw pairs together within the same species, and for a specific reason. In mice, for example, experiments showed that pheromones acted as attractants between males and females who were genetically similar except that they differed in a ...
... Subtle chemical signals, or pheromones, have long been known to draw pairs together within the same species, and for a specific reason. In mice, for example, experiments showed that pheromones acted as attractants between males and females who were genetically similar except that they differed in a ...
BIOL08012 2016 May
... Usually expressed but can be switched off. Always expressed at a constant level. Usually off but can be switched on. ...
... Usually expressed but can be switched off. Always expressed at a constant level. Usually off but can be switched on. ...
DNA
... Spontaneous reactions do NOT just go forward immediately to produce products. This is because the reactants must overcome an activation energy, EA. ...
... Spontaneous reactions do NOT just go forward immediately to produce products. This is because the reactants must overcome an activation energy, EA. ...
Lecture 3 Human Genetics
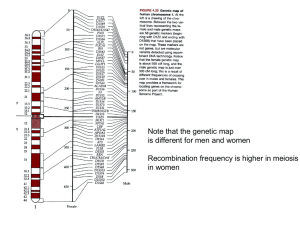
... Many human disorders, conditions and predispositions are multigenic Twin studies where identical twins are raised together or raised apart Look at complex behaviors and ask if they are genetic or environment Answer: For almost every single behavior…..it’s a little of both “Heritability” or the frac ...
... Many human disorders, conditions and predispositions are multigenic Twin studies where identical twins are raised together or raised apart Look at complex behaviors and ask if they are genetic or environment Answer: For almost every single behavior…..it’s a little of both “Heritability” or the frac ...
DNA Fingerprinting and Its Application in Paternity Testing
... probability of paternity is 99.99% or greater when an alleged father’s DNA profile matches that of the child for all the genetic markers. • On the other hand, an alleged father is 100% excluded from paternity if there is a mismatch for three or more genetic markers between the profiles of the child ...
... probability of paternity is 99.99% or greater when an alleged father’s DNA profile matches that of the child for all the genetic markers. • On the other hand, an alleged father is 100% excluded from paternity if there is a mismatch for three or more genetic markers between the profiles of the child ...
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) 分析與應用
... between two individuals at many points throughout the genome – genome variation. • Most commonly, sequence variation occurs at discrete, single‐nucleotide positions referred to as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), which are estimated to occur at a frequency of approximately one per 1000 nucleo ...
... between two individuals at many points throughout the genome – genome variation. • Most commonly, sequence variation occurs at discrete, single‐nucleotide positions referred to as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), which are estimated to occur at a frequency of approximately one per 1000 nucleo ...
DNA Authorization - Donahue Funeral Home
... 2. Please visit the DNA Memorial website. 3. Notify us if you wish to consider DNA banking. Would you like an email reminder? ...
... 2. Please visit the DNA Memorial website. 3. Notify us if you wish to consider DNA banking. Would you like an email reminder? ...
evaluation of a one-step dna extraction method for “touch”
... Due to advances in DNA typing technologies, it is possible to generate a DNA profile from touched objects or trace amounts of biological material (< 100pg). Therefore, it is important to ensure that sample collection and DNA purification methods recover the maximal amount of DNA from each sample. Th ...
... Due to advances in DNA typing technologies, it is possible to generate a DNA profile from touched objects or trace amounts of biological material (< 100pg). Therefore, it is important to ensure that sample collection and DNA purification methods recover the maximal amount of DNA from each sample. Th ...
centromere
... Unique and repeated DNA • If eukaryotic DNA is melted and allowed to re-anneal, it does so in 3 distinct phases • The explanation is that there is highly repetitive DNA (which re-anneals quickly), moderately repetitive DNA (intermediate) and unique or single copy DNA (re-anneals slowly) ...
... Unique and repeated DNA • If eukaryotic DNA is melted and allowed to re-anneal, it does so in 3 distinct phases • The explanation is that there is highly repetitive DNA (which re-anneals quickly), moderately repetitive DNA (intermediate) and unique or single copy DNA (re-anneals slowly) ...
IB Biology 11 SL (H) - Anoka
... ● Outline the process of meiosis, including pairing of homologous chromosomes and crossing over, ● About mutations, their types and causes and their role in genetic variation. followed by two divisions, which results in four haploid cells ● How gel electrophoresis is used in DNA profiling ● Explain ...
... ● Outline the process of meiosis, including pairing of homologous chromosomes and crossing over, ● About mutations, their types and causes and their role in genetic variation. followed by two divisions, which results in four haploid cells ● How gel electrophoresis is used in DNA profiling ● Explain ...
1. Which of the following enzymes will untangle DNA? A
... 16. In DNA replication, the leading strand is the strand that has which conformation? A) 5 to 3 B) 3 to 5 C) Both strands are leading 17. Which of the following is a purine? A) Thymine B) Cytosine C) Adenine D) Alanine 18. Which of the following does not play a role in DNA replication? A) RNA prime ...
... 16. In DNA replication, the leading strand is the strand that has which conformation? A) 5 to 3 B) 3 to 5 C) Both strands are leading 17. Which of the following is a purine? A) Thymine B) Cytosine C) Adenine D) Alanine 18. Which of the following does not play a role in DNA replication? A) RNA prime ...
Biotechnology
... DETERMINING GENOTYPE • Test cross is used to determine parental genotype. • Cross the parent with unknown genotype with an organism that is homozygous recessive for the trait. • Observe the offspring. • Numerous test crosses required to be sure you findings are correct. ...
... DETERMINING GENOTYPE • Test cross is used to determine parental genotype. • Cross the parent with unknown genotype with an organism that is homozygous recessive for the trait. • Observe the offspring. • Numerous test crosses required to be sure you findings are correct. ...
SNP genotyping

SNP genotyping is the measurement of genetic variations of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between members of a species. It is a form of genotyping, which is the measurement of more general genetic variation. SNPs are one of the most common types of genetic variation. An SNP is a single base pair mutation at a specific locus, usually consisting of two alleles (where the rare allele frequency is >1%). SNPs are found to be involved in the etiology of many human diseases and are becoming of particular interest in pharmacogenetics. Because SNPs are conserved during evolution, they have been proposed as markers for use in quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis and in association studies in place of microsatellites. The use of SNPs is being extended in the HapMap project, which aims to provide the minimal set of SNPs needed to genotype the human genome. SNPs can also provide a genetic fingerprint for use in identity testing. The increase in interest in SNPs has been reflected by the furious development of a diverse range of SNP genotyping methods.









![Toxicity of benzo[a]pyrene occurs because of the formation of](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/021940064_1-8f197aea7df98d9d2658a5a3ca962b5c-300x300.png)