Degenerate PCR - Yale School of Medicine
... doesn't fit quite correctly in double stranded DNA, so there may be an energetic penalty to pay when the helix bulges out at this purine:purine pairing). Recently, most people have been using inosine in their primers at positions where any of the four bases might be required. Each use of inosine thu ...
... doesn't fit quite correctly in double stranded DNA, so there may be an energetic penalty to pay when the helix bulges out at this purine:purine pairing). Recently, most people have been using inosine in their primers at positions where any of the four bases might be required. Each use of inosine thu ...
Nucleic Acids - Structure and Replication
... For more awesome GCSE and A level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ ...
... For more awesome GCSE and A level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ ...
lecture 6 genetic languages and mutations_RECAP
... An error in transcription does NOT result in a change to the DNA. An error in translation does NOT result in a change to the DNA. Only an error in DNA replication will lead to a change in DNA. ...
... An error in transcription does NOT result in a change to the DNA. An error in translation does NOT result in a change to the DNA. Only an error in DNA replication will lead to a change in DNA. ...
Agilent 101: An Introduction to Microarrays and Genomics
... the G’s line up with the C’s. This complementary bonding gives DNA a number of remarkable properties, including the ability to make RNA copies of genes and to reproduce the entire molecule. It is also the basis for Agilent’s genomic measurement products. From DNA to microarrays A DNA microarray is s ...
... the G’s line up with the C’s. This complementary bonding gives DNA a number of remarkable properties, including the ability to make RNA copies of genes and to reproduce the entire molecule. It is also the basis for Agilent’s genomic measurement products. From DNA to microarrays A DNA microarray is s ...
DNA 1. Evidence for DNA as the genetic material.
... placed. The strands separate because shorter segments travel through the gel faster than longer segments. These fragments are then stained so that we can see them. The unique DNA sequences of each person produce a unique collection of fragments of various lengths, which results in a unique pattern o ...
... placed. The strands separate because shorter segments travel through the gel faster than longer segments. These fragments are then stained so that we can see them. The unique DNA sequences of each person produce a unique collection of fragments of various lengths, which results in a unique pattern o ...
notes
... mRNA can now leave the nucleus (through nuclear pore) and enter the cytoplasm cut out introns and splice exons together ...
... mRNA can now leave the nucleus (through nuclear pore) and enter the cytoplasm cut out introns and splice exons together ...
MAPPING GENES TO TRAITS IN DOGS USING SNPs
... DNA of many dogs to find variations that are common in one group compared to another. A variation is not a useful marker if it only occurs in one or a few dogs. Students may also mention that researchers need to look at many dogs to find SNPs associated with one trait and not another. 5. Do humans ...
... DNA of many dogs to find variations that are common in one group compared to another. A variation is not a useful marker if it only occurs in one or a few dogs. Students may also mention that researchers need to look at many dogs to find SNPs associated with one trait and not another. 5. Do humans ...
1 Introduction 2 Central Dogma of molecular biology 3 DNA
... the process by which some organisms survive to successfully have offsprings while those who don’t stand the test of evolution eventually perish in time. The reasons why some organisms survive and have progeny that will carry their genetic information while others don’t is complex. In particular, it ...
... the process by which some organisms survive to successfully have offsprings while those who don’t stand the test of evolution eventually perish in time. The reasons why some organisms survive and have progeny that will carry their genetic information while others don’t is complex. In particular, it ...
Nuclear Architecture, Chromosome Territories, Chromatin Dynamics
... cells to 2xSSC. In case that the cover slip cannot be striped off easily, incubate briefly in 2xSSC and try again. All following washing steps should be performed e.g. in 6-or 12 well plates with marked slots. In order to avoid drying up of cells, cover slips should quickly transferred from one well ...
... cells to 2xSSC. In case that the cover slip cannot be striped off easily, incubate briefly in 2xSSC and try again. All following washing steps should be performed e.g. in 6-or 12 well plates with marked slots. In order to avoid drying up of cells, cover slips should quickly transferred from one well ...
Lab 8
... 5. Discard the alcohol/detergent solution remaining in the beaker into specially labeled waste jars (do not pour down the sink). Confirming the DNA 1. Remove the rod and the spooled DNA from the test tube. Dry the DNA with a clean filter paper. Describe the appearance of the crude DNA. 2. Dissolve t ...
... 5. Discard the alcohol/detergent solution remaining in the beaker into specially labeled waste jars (do not pour down the sink). Confirming the DNA 1. Remove the rod and the spooled DNA from the test tube. Dry the DNA with a clean filter paper. Describe the appearance of the crude DNA. 2. Dissolve t ...
The amount if DNA in each human cell nucleus is
... This, and the next step serve to wash the DNA. Since these wash solutions contain ethanol, the DNA remains precipitated and unable to pass through the filter in the spin column. Discard the tube containing the filtrate, and insert the spin column into a new 2 ml microfuge tube. 8. Add 500 l of Qiag ...
... This, and the next step serve to wash the DNA. Since these wash solutions contain ethanol, the DNA remains precipitated and unable to pass through the filter in the spin column. Discard the tube containing the filtrate, and insert the spin column into a new 2 ml microfuge tube. 8. Add 500 l of Qiag ...
Title - Iowa State University
... What is a character and a trait? How would this be related to a gene and an allele? character - heritable feature, trait a specific variant of a character gene - allele two or more forms of a gene What is phenotype and genotype? pheno - physical, geno- DNA ‘phenotype is not genotype!’ Describe Medel ...
... What is a character and a trait? How would this be related to a gene and an allele? character - heritable feature, trait a specific variant of a character gene - allele two or more forms of a gene What is phenotype and genotype? pheno - physical, geno- DNA ‘phenotype is not genotype!’ Describe Medel ...
Document
... 9.1 Manipulating DNA Scientists use several techniques to manipulate DNA. • Chemicals, computers, and bacteria are used to work with DNA. • Scientists use these tools in genetics research and biotechnology. ...
... 9.1 Manipulating DNA Scientists use several techniques to manipulate DNA. • Chemicals, computers, and bacteria are used to work with DNA. • Scientists use these tools in genetics research and biotechnology. ...
Genetic Test Review Packet What is a Punnet square and what is it
... There is a 0% probability that there will be a rat with black fur, 100% of them will have white fur. Define the following terms: 7. Allele- one of a pair of genes that determine a specific trait. 8. Phenotype- the physical appearance of an organism. 9. Genotype- the set of genes carried by an organi ...
... There is a 0% probability that there will be a rat with black fur, 100% of them will have white fur. Define the following terms: 7. Allele- one of a pair of genes that determine a specific trait. 8. Phenotype- the physical appearance of an organism. 9. Genotype- the set of genes carried by an organi ...
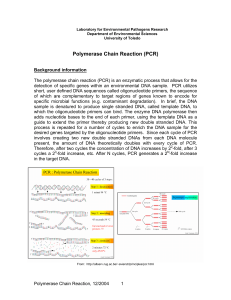
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) - Department of Environmental
... master mix is made in which enough of each reagent to satisfy all reactions is combined into one tube, and then dispensed among the individual reaction tubes. Template DNA is then added to each tube. This limits pipetting errors as well as the potential for contamination, as the reagent tubes are op ...
... master mix is made in which enough of each reagent to satisfy all reactions is combined into one tube, and then dispensed among the individual reaction tubes. Template DNA is then added to each tube. This limits pipetting errors as well as the potential for contamination, as the reagent tubes are op ...
Name: 1) Which statement best describes the relationship between
... What will most likely happen if there is a change in the first three subunits on the up per strand of molecule 1? A) A portion of molecule 2 may be different. B) M olecule 1 will split apart, triggering an immune response. ...
... What will most likely happen if there is a change in the first three subunits on the up per strand of molecule 1? A) A portion of molecule 2 may be different. B) M olecule 1 will split apart, triggering an immune response. ...
Tutorial - Faster Better Media
... Four rules govern the optimal size-range of most conventional conductive media in continuous voltage gel electrophoresis. 1) Tris ions cause small DNA (50-500 bp) to form fuzzy bands. Acetate buffers also tend to produce fuzzy bands in the smaller size range. In contrast, borate ions allow sharp ba ...
... Four rules govern the optimal size-range of most conventional conductive media in continuous voltage gel electrophoresis. 1) Tris ions cause small DNA (50-500 bp) to form fuzzy bands. Acetate buffers also tend to produce fuzzy bands in the smaller size range. In contrast, borate ions allow sharp ba ...
SNP genotyping

SNP genotyping is the measurement of genetic variations of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) between members of a species. It is a form of genotyping, which is the measurement of more general genetic variation. SNPs are one of the most common types of genetic variation. An SNP is a single base pair mutation at a specific locus, usually consisting of two alleles (where the rare allele frequency is >1%). SNPs are found to be involved in the etiology of many human diseases and are becoming of particular interest in pharmacogenetics. Because SNPs are conserved during evolution, they have been proposed as markers for use in quantitative trait loci (QTL) analysis and in association studies in place of microsatellites. The use of SNPs is being extended in the HapMap project, which aims to provide the minimal set of SNPs needed to genotype the human genome. SNPs can also provide a genetic fingerprint for use in identity testing. The increase in interest in SNPs has been reflected by the furious development of a diverse range of SNP genotyping methods.