Chapter 21.1
... supply schedules for all providers of the same good or service. The market supply curve slopes upward, like individual supply curves do. This upward slope shows that all producers in the market would prefer to offer more of the product for sale at higher prices and less at lower prices. ...
... supply schedules for all providers of the same good or service. The market supply curve slopes upward, like individual supply curves do. This upward slope shows that all producers in the market would prefer to offer more of the product for sale at higher prices and less at lower prices. ...
Problem Set 1
... Due Tuesday September 17 at the beginning of lecture Write all answers neatly on the pages given. Draw all graphs and write your answers in the space provided. Show all of your work. You may discuss questions you have with other students, but your answers need to be in your own words. Answers that a ...
... Due Tuesday September 17 at the beginning of lecture Write all answers neatly on the pages given. Draw all graphs and write your answers in the space provided. Show all of your work. You may discuss questions you have with other students, but your answers need to be in your own words. Answers that a ...
Intermediate Microeconomics
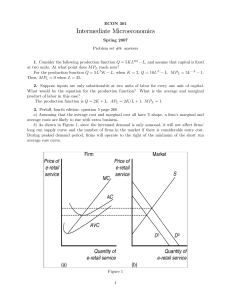
... a) Assuming that the average cost and marginal cost all have U-shape, a firm’s marginal and average costs are likely to rise with extra business. b) As shown in Figure 1, since the increased demand is only seasonal, it will not affect firms’ long run supply curve and the number of firms in the market ...
... a) Assuming that the average cost and marginal cost all have U-shape, a firm’s marginal and average costs are likely to rise with extra business. b) As shown in Figure 1, since the increased demand is only seasonal, it will not affect firms’ long run supply curve and the number of firms in the market ...
Instructions: Fill in the blanks with the correct answers
... 3. Scarce things (that is, things people will buy) are divided into two groups: a. GOODS (commodities or products) b. SERVICES (work done for other people) (p.141) 4. When something is scarce, it has to be rationed, or limited. In our economy, the usual way of determining who gets scarce things is P ...
... 3. Scarce things (that is, things people will buy) are divided into two groups: a. GOODS (commodities or products) b. SERVICES (work done for other people) (p.141) 4. When something is scarce, it has to be rationed, or limited. In our economy, the usual way of determining who gets scarce things is P ...
1 - JustAnswer
... 1. Price elasticity of demand is calculated as (Points: 1) the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price 2. The price elasticity of demand (Points: 1) tells producers what will happen to total revenue if they change product price 3. Along a linear demand curve, ...
... 1. Price elasticity of demand is calculated as (Points: 1) the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price 2. The price elasticity of demand (Points: 1) tells producers what will happen to total revenue if they change product price 3. Along a linear demand curve, ...
Peak Oil Economics - University of Dayton
... Low or zero barriers to entry and exit of buyers and sellers Standardized product or resource Near-perfect information ...
... Low or zero barriers to entry and exit of buyers and sellers Standardized product or resource Near-perfect information ...
Demand
... Market Demand Schedule/Curve • A table or diagram showing the relationship between the price of a good and the total quantity demanded by all consumers. ...
... Market Demand Schedule/Curve • A table or diagram showing the relationship between the price of a good and the total quantity demanded by all consumers. ...
Macroeconomic Principles Problem Set 1.1 Answer Key
... vertical supply curve to the right of S1). With the special tax breaks we observe an additional 300 new homes built, resulting in a new stock of Q+800 homes (vertical supply curve S2). The special tax breaks only affect the home builders, i.e. suppliers, and have no effect on demand. Demand, as usua ...
... vertical supply curve to the right of S1). With the special tax breaks we observe an additional 300 new homes built, resulting in a new stock of Q+800 homes (vertical supply curve S2). The special tax breaks only affect the home builders, i.e. suppliers, and have no effect on demand. Demand, as usua ...
Handout with solution
... the PPF represents the opportunity cost of producing the good on the x-axis in terms of the good on the yaxis; that is, it represents how much of the y-axis good you must give up to produce one more unit of the xaxis good. In many introductory courses, we present the PPF as a linear graph, meaning t ...
... the PPF represents the opportunity cost of producing the good on the x-axis in terms of the good on the yaxis; that is, it represents how much of the y-axis good you must give up to produce one more unit of the xaxis good. In many introductory courses, we present the PPF as a linear graph, meaning t ...
Econ 105 Section 8 Take-home Homework 1 Due Date: Wednesday
... 3. (2 points) Why is entrepreneurship a central part of any business? Chapter 3 4. (5 points) You are given the following individual demand tables for comic books. Price ...
... 3. (2 points) Why is entrepreneurship a central part of any business? Chapter 3 4. (5 points) You are given the following individual demand tables for comic books. Price ...
Practice Questions: Tradeoffs, Opportunity Cost, Supply and Demand
... 12. In recent years, there have been news reports that toys made in China are unsafe. When those news reports show up on CNN and Fox News, what probably happens to the demand for toys made in China? What probably happens to the equilibrium price and quantity of toys made in China? Are Chinese toymak ...
... 12. In recent years, there have been news reports that toys made in China are unsafe. When those news reports show up on CNN and Fox News, what probably happens to the demand for toys made in China? What probably happens to the equilibrium price and quantity of toys made in China? Are Chinese toymak ...
Name: Practice Problems Directions: For each of the scenarios on
... in the table above. Then draw the new demand curve given by this change, and show the new equilibrium price and quantity. 12. Suppose the quantity supplied rises by 20 million pounds per month at each price, while the quantities demanded retain the values shown in the table above. Draw the new suppl ...
... in the table above. Then draw the new demand curve given by this change, and show the new equilibrium price and quantity. 12. Suppose the quantity supplied rises by 20 million pounds per month at each price, while the quantities demanded retain the values shown in the table above. Draw the new suppl ...
public_finance_part1_ch1 (2)
... the ratio of marginal utility per price for particular commodity is equal to the ratio of marginal utility per price of other commodities MU1 ...
... the ratio of marginal utility per price for particular commodity is equal to the ratio of marginal utility per price of other commodities MU1 ...
Economics Final Exam Study Guide
... 13.What does the price elasticity of demand measure? 14.How does price effect goods that are complements to one another? Chapter 4 15.Will the supply curve shift to the left or right if the price of resources needed to make the product increases? 16.What is elasticity of supply? 17.What kind of corr ...
... 13.What does the price elasticity of demand measure? 14.How does price effect goods that are complements to one another? Chapter 4 15.Will the supply curve shift to the left or right if the price of resources needed to make the product increases? 16.What is elasticity of supply? 17.What kind of corr ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑