Test 2
... 6. A _________ is a chart that shows the amount of a good or service that would be produced at various prices in the market. a) Demand curve b) Supply Schedule c) Demand Schedule d) Law of Supply 7. If product A and Product B are substitutes. What will happen to the demand for product A if the price ...
... 6. A _________ is a chart that shows the amount of a good or service that would be produced at various prices in the market. a) Demand curve b) Supply Schedule c) Demand Schedule d) Law of Supply 7. If product A and Product B are substitutes. What will happen to the demand for product A if the price ...
Economics Chapter 6 Bringing Supply and Demand Together
... Unlike central planning, a distribution system based on prices costs nothing to administer. ...
... Unlike central planning, a distribution system based on prices costs nothing to administer. ...
Chapter 6 Equilibrium Surplus Shortage 11-14-11
... 11-14-11 Goal: Discover how market equilibrium is reached. Review: A market based economic system depends on cooperation of consumers and producers -Consumers goal (demand): is to purchase the best products at the lowest prices -Producers goal (supply): is to make profit and provide products at the ...
... 11-14-11 Goal: Discover how market equilibrium is reached. Review: A market based economic system depends on cooperation of consumers and producers -Consumers goal (demand): is to purchase the best products at the lowest prices -Producers goal (supply): is to make profit and provide products at the ...
Homework Quiz 5
... pressure from all the cholesterol!) When the price of a Big Mac increases to $3, his consumption of Big Macs falls to 800 a year. a. Calculate his price elasticity of demand for Big Macs and determine whether his demand is elastic, unit elastic or inelastic. ...
... pressure from all the cholesterol!) When the price of a Big Mac increases to $3, his consumption of Big Macs falls to 800 a year. a. Calculate his price elasticity of demand for Big Macs and determine whether his demand is elastic, unit elastic or inelastic. ...
ECONOMICS FOR MODULE A –CCA BY DR.LUCAS WEBIRO We characterize
... things equal” assumption. In this context, it means that income, wealth, prices of other goods, population, and preferences all remain fixed. Of course, in the real world other things are rarely equal. Lots of things tend to change at once. But that’s not a fault of the model; it’s a virtue. The who ...
... things equal” assumption. In this context, it means that income, wealth, prices of other goods, population, and preferences all remain fixed. Of course, in the real world other things are rarely equal. Lots of things tend to change at once. But that’s not a fault of the model; it’s a virtue. The who ...
practice midterm_ans
... B. demand for the good remains constant. C. demand for the good increases. D. supply of the good remains constant. E. supply of the good increases. ...
... B. demand for the good remains constant. C. demand for the good increases. D. supply of the good remains constant. E. supply of the good increases. ...
supply and demand exercises
... 10. Assuming that wheat and corn can both be grown on the same type of land, a decrease in the price of corn, other things being equal, will cause: a) a rightward shift of the supply curve for corn; b) an upward movement along the supply curve for wheat; c) a decrease in the opportunity cost associa ...
... 10. Assuming that wheat and corn can both be grown on the same type of land, a decrease in the price of corn, other things being equal, will cause: a) a rightward shift of the supply curve for corn; b) an upward movement along the supply curve for wheat; c) a decrease in the opportunity cost associa ...
Chapter 3 - Aufinance
... travel (substitute goods); a decline in the price of DVD players increases the demand for DVD movies (complementary goods). ...
... travel (substitute goods); a decline in the price of DVD players increases the demand for DVD movies (complementary goods). ...
McGraw-Hill - Gordon State College
... of DVD players increases the demand for DVD movies (complementary goods). ...
... of DVD players increases the demand for DVD movies (complementary goods). ...
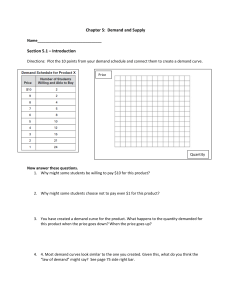
Chapter 5: Demand and Supply Section 5.1 – Introduction
... 3. You have created a demand curve for the product. What happens to the quantity demanded for this product when the price goes down? When the price goes up? ...
... 3. You have created a demand curve for the product. What happens to the quantity demanded for this product when the price goes down? When the price goes up? ...
Principles of Microeconomics
... Principles of Microeconomics Sample Demand Questions On a graph show the change in demand, or quantity demanded that results from the following event. In words, determine whether demand increases or decreases (shifts left or right), or if the quantity demanded increases (a move down the demand curve ...
... Principles of Microeconomics Sample Demand Questions On a graph show the change in demand, or quantity demanded that results from the following event. In words, determine whether demand increases or decreases (shifts left or right), or if the quantity demanded increases (a move down the demand curve ...
Document
... 1. Which of the following will not change the demand for oranges? a. A change in consumers’ incomes b. A change in the price of grapefruits, a substitute for oranges c. A change in the price of oranges d. A change in consumers’ taste for oranges e. An expectation that the price of oranges will chang ...
... 1. Which of the following will not change the demand for oranges? a. A change in consumers’ incomes b. A change in the price of grapefruits, a substitute for oranges c. A change in the price of oranges d. A change in consumers’ taste for oranges e. An expectation that the price of oranges will chang ...
Izmir University of Economics ECON 100 Fall 2013
... a) What is the equilibrium price and quantity? How can you tell? Equilibrium in a market occurs when quantity demanded is equal to quantity supplied. Therefore, the market is in equilibrium at the point where supply curve and demand curve intersect, with the corresponding equilibrium price of 6 pou ...
... a) What is the equilibrium price and quantity? How can you tell? Equilibrium in a market occurs when quantity demanded is equal to quantity supplied. Therefore, the market is in equilibrium at the point where supply curve and demand curve intersect, with the corresponding equilibrium price of 6 pou ...
NAME - Jamestown Public Schools
... _____2. A product that can be used to replace the purchase of similar products when prices rise. _____3. This exists when a small change in a good’s price has a large impact on the quantity demanded. _____4. Examples of these include rent, interest on loans, and salaries _____5. A product that is co ...
... _____2. A product that can be used to replace the purchase of similar products when prices rise. _____3. This exists when a small change in a good’s price has a large impact on the quantity demanded. _____4. Examples of these include rent, interest on loans, and salaries _____5. A product that is co ...
Supply - Images
... Cause for a change in supply= Number of Factors, such as: 1. Change in Technology 2. Change in the Cost of inputs ...
... Cause for a change in supply= Number of Factors, such as: 1. Change in Technology 2. Change in the Cost of inputs ...
Demand and Supply
... • Qown = D(pown,pother,y) • If income goes up and P the demand curve shifts out, the good is a normal good. • If it shifts in, it is an inferior good. ...
... • Qown = D(pown,pother,y) • If income goes up and P the demand curve shifts out, the good is a normal good. • If it shifts in, it is an inferior good. ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑