MICROECONOMICS A Lecture Outline and its Detail Coverage
... Consumer choice and the demand function: maximizing utility subject to income (diagram and the mathematical form) The derivation of a demand curve – proving the law of demand Income and substitution effects due to a price change PRODUCTION Production function as a function of four wheels Production ...
... Consumer choice and the demand function: maximizing utility subject to income (diagram and the mathematical form) The derivation of a demand curve – proving the law of demand Income and substitution effects due to a price change PRODUCTION Production function as a function of four wheels Production ...
Assignment 2
... Answer all questions. While you are encouraged to discuss with your classmates, you must write up your own script. (The answer to each question should not exceed one page.) Please hand in your script to your TA (Miss Titi Hung) on or before the deadline via her pageon box on the 9th floor of K.K. Le ...
... Answer all questions. While you are encouraged to discuss with your classmates, you must write up your own script. (The answer to each question should not exceed one page.) Please hand in your script to your TA (Miss Titi Hung) on or before the deadline via her pageon box on the 9th floor of K.K. Le ...
BUAD 200: Classnotes Week 5 S08
... 1. Surplus: A surplus exists if (at a given price) the quantity supplied is greater than the quantity demanded. If a surplus exists, some sellers are dissatisfied, and competition between sellers will cause the price to fall. 2. Shortage: A Shortage exists if (at a given price) the quantity demanded ...
... 1. Surplus: A surplus exists if (at a given price) the quantity supplied is greater than the quantity demanded. If a surplus exists, some sellers are dissatisfied, and competition between sellers will cause the price to fall. 2. Shortage: A Shortage exists if (at a given price) the quantity demanded ...
ECO1 REV1 – Answers
... for profits, then supply in the textile industry will flourish. More profits not only encourage existing firms to produce more, but they also attract new sellers, which reinforces the increase in supply. b. Capital becomes readily available for grain growers. The increase availability and access to ...
... for profits, then supply in the textile industry will flourish. More profits not only encourage existing firms to produce more, but they also attract new sellers, which reinforces the increase in supply. b. Capital becomes readily available for grain growers. The increase availability and access to ...
Lesson 14: Supply and Demand
... When supply is limited and customer demand is high, prices are high (ie: Kinect) When customer demand is limited and supply is high, prices are low (ie: cookies) When supply and customer demand are at the same level, prices remain constant (ie: toilet paper and other necessities) ...
... When supply is limited and customer demand is high, prices are high (ie: Kinect) When customer demand is limited and supply is high, prices are low (ie: cookies) When supply and customer demand are at the same level, prices remain constant (ie: toilet paper and other necessities) ...
topic 4 - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... is cold. The world’s largest soft drink maker, Coca-Cola, is trialling machines which can automatically raise or lower prices based on demand. The company has been testing the technology in America for about three years. Australian-based coke bottler, Coca-Cola Amatil, confirmed yesterday the so-cal ...
... is cold. The world’s largest soft drink maker, Coca-Cola, is trialling machines which can automatically raise or lower prices based on demand. The company has been testing the technology in America for about three years. Australian-based coke bottler, Coca-Cola Amatil, confirmed yesterday the so-cal ...
Chap002
... One of the most significant factors that appears on both lists is the price of the product being considered. This makes it convenient to relate on the same graph the amount demanded and supplied. The relationship of price and consumer’s quantity demanded is inverse, as shown in Figure 2-1, while sup ...
... One of the most significant factors that appears on both lists is the price of the product being considered. This makes it convenient to relate on the same graph the amount demanded and supplied. The relationship of price and consumer’s quantity demanded is inverse, as shown in Figure 2-1, while sup ...
N. Gregory Mankiw – Principles of Economics Chapter 17
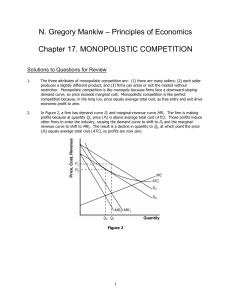
... Figure 3 shows the long-run equilibrium in a monopolistically competitive market. Price equals average total cost. Price is above marginal cost. ...
... Figure 3 shows the long-run equilibrium in a monopolistically competitive market. Price equals average total cost. Price is above marginal cost. ...
Understanding supply
... sell at all prices. Producers control supply-side of our economy. What is the difference between a supply schedule & a supply curve? Which way does the supply curve always slope? Why? The Law of Supply says as prices increase the quantity supplied increases. Do Supply Graphing Exercises, p. 73. ...
... sell at all prices. Producers control supply-side of our economy. What is the difference between a supply schedule & a supply curve? Which way does the supply curve always slope? Why? The Law of Supply says as prices increase the quantity supplied increases. Do Supply Graphing Exercises, p. 73. ...
Micro Lesson 2 - Effingham County Schools
... Demand vs. Quantity Demanded “Demand” is the whole picture…all of the quantities demanded at every price. ...
... Demand vs. Quantity Demanded “Demand” is the whole picture…all of the quantities demanded at every price. ...
SalestaxOct19
... The effect of a sales tax collected from sellers is to A) Shift the demand curve up. B) Shift the supply curve down. C) Shift the demand curve down. D) Shift the supply curve up. E) Shift both the demand and the supply curve. ...
... The effect of a sales tax collected from sellers is to A) Shift the demand curve up. B) Shift the supply curve down. C) Shift the demand curve down. D) Shift the supply curve up. E) Shift both the demand and the supply curve. ...
MicroPreS_Part 1
... •Used to explain or predict economic phenomena. • Abstractions of reality • Proceed by making simplifying assumptions. • Can be judged according to how successful they are in explaining and predicting phenomena. ...
... •Used to explain or predict economic phenomena. • Abstractions of reality • Proceed by making simplifying assumptions. • Can be judged according to how successful they are in explaining and predicting phenomena. ...
Industrial Economics
... c=5 and no fixed costs. She can charge different prices in the two markets. What is the profit maximazing combination of quantities for this monopolist? Q2. Suppose that a monopoly can produce any level of output it wishes at a constant marginal cost of $5 per unit. Assume that the monopoly sells it ...
... c=5 and no fixed costs. She can charge different prices in the two markets. What is the profit maximazing combination of quantities for this monopolist? Q2. Suppose that a monopoly can produce any level of output it wishes at a constant marginal cost of $5 per unit. Assume that the monopoly sells it ...
Print › Quiz 2 Material | Quizlet | Quizlet
... because people have unlimited wants but resources are limited various economic decisions must be made to allocate resources efficiently actions or activities that are done for ...
... because people have unlimited wants but resources are limited various economic decisions must be made to allocate resources efficiently actions or activities that are done for ...
Study Guide 2015
... 2) Rational people make a decision to do or buy something when the MB (marginal benefit) is ____________ than the MC (marginal cost) a. If people make decisions at the margin, explain why it makes sense for producers to provide an incentive (a cost savings) to consumers to as they increase the quant ...
... 2) Rational people make a decision to do or buy something when the MB (marginal benefit) is ____________ than the MC (marginal cost) a. If people make decisions at the margin, explain why it makes sense for producers to provide an incentive (a cost savings) to consumers to as they increase the quant ...
LAMC ECON 1 W03
... 1. Surplus: A surplus exists if (at a given price) the quantity supplied is greater than the quantity demanded. If a surplus exists, some sellers are dissatisfied, and competition between sellers will cause the price to fall. 2. Shortage: A Shortage exists if (at a given price) the quantity demanded ...
... 1. Surplus: A surplus exists if (at a given price) the quantity supplied is greater than the quantity demanded. If a surplus exists, some sellers are dissatisfied, and competition between sellers will cause the price to fall. 2. Shortage: A Shortage exists if (at a given price) the quantity demanded ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑