Lecture 6: Supply and Demand
... A market is in equilibrium when the price is such that the quantity supplied is equal to quantity demanded. A market is in equilibrium when the price is such that excess supply equals excess demand equals zero. ...
... A market is in equilibrium when the price is such that the quantity supplied is equal to quantity demanded. A market is in equilibrium when the price is such that excess supply equals excess demand equals zero. ...
The monopolist`s firm demand curve is:
... average total cost equals marginal cost. At the point where the marginal revenue equals zero for a monopolist facing a straight-line demand curve, total revenue is: a. greater than 1. b. maximum. c. less than 1. d. equal to zero. At any point where a monopolist's marginal revenue is positive, the do ...
... average total cost equals marginal cost. At the point where the marginal revenue equals zero for a monopolist facing a straight-line demand curve, total revenue is: a. greater than 1. b. maximum. c. less than 1. d. equal to zero. At any point where a monopolist's marginal revenue is positive, the do ...
Chapter 6-4 The Elasticity of Supply PPT
... The shape of the supply curve depends primarily on the length of time being considered. In the short run, at least one of the resources used in production cannot be changed. In the long run, the firm has long enough to change any aspect of production, and therefore can more fully ...
... The shape of the supply curve depends primarily on the length of time being considered. In the short run, at least one of the resources used in production cannot be changed. In the long run, the firm has long enough to change any aspect of production, and therefore can more fully ...
In-class Workseet 4
... Overhead for the factor is fixed at $30,000 per week. If more than 5000 units are produced each week, and labor is $45 per unit for those units in excess of 5000, what level of production will minimize average cost? ...
... Overhead for the factor is fixed at $30,000 per week. If more than 5000 units are produced each week, and labor is $45 per unit for those units in excess of 5000, what level of production will minimize average cost? ...
Chapter 5 Notes - Cloudfront.net
... As producers change prices and the quantity of goods supplied, this adjustment period works to eliminate surpluses and shortages In turn, the producers will find an equilibrium point where there are limited shortages and surpluses ...
... As producers change prices and the quantity of goods supplied, this adjustment period works to eliminate surpluses and shortages In turn, the producers will find an equilibrium point where there are limited shortages and surpluses ...
Happy New Year and welcome back for the final semester of your
... graphs and illustrations presented within the course. This understanding is important due to the fact that: “Since 1996, students have been required to draw and label their own graphs for some parts of the free-response questions on the AP Microeconomics Examination. Drawing graphs is not just the k ...
... graphs and illustrations presented within the course. This understanding is important due to the fact that: “Since 1996, students have been required to draw and label their own graphs for some parts of the free-response questions on the AP Microeconomics Examination. Drawing graphs is not just the k ...
Monopolistic Competition
... HW: Activity 3-16 No Current Event this week! Check Class Website for helpful videos on all Unit 3 Material! ...
... HW: Activity 3-16 No Current Event this week! Check Class Website for helpful videos on all Unit 3 Material! ...
Name: Date: ______ 1. An economy is efficient if it is: A) possible to
... A) When the income elasticity of demand is positive, the good is an inferior good. B) When the income elasticity of demand is negative, the good is a normal good. C) Income elasticity of demand measures how much the demand for a good is affected by changes in consumers' incomes. D) Income elasticity ...
... A) When the income elasticity of demand is positive, the good is an inferior good. B) When the income elasticity of demand is negative, the good is a normal good. C) Income elasticity of demand measures how much the demand for a good is affected by changes in consumers' incomes. D) Income elasticity ...
Lecture 2 The Law of Demand
... ■ Also difficult to measure — but important ■ When measurable, include in the analysis. But experience shows—measures are very poor predictors of actions. ■ Like tastes, these can be used to “explain” ...
... ■ Also difficult to measure — but important ■ When measurable, include in the analysis. But experience shows—measures are very poor predictors of actions. ■ Like tastes, these can be used to “explain” ...
ECON 102
... ____ 11. Opportunity costs is a consequence of a. selfish consumers. b. narrow-minded producers. c. greed. d. scarcity. e. inefficiencies. ____ 12. All of the following, except one, will increase the quantity of coffee demanded at each price. Which will not? a. an increase in the price of tea bags ...
... ____ 11. Opportunity costs is a consequence of a. selfish consumers. b. narrow-minded producers. c. greed. d. scarcity. e. inefficiencies. ____ 12. All of the following, except one, will increase the quantity of coffee demanded at each price. Which will not? a. an increase in the price of tea bags ...
Mathematics for Economics
... Solution 4: This is a quadratic function Revenue is an increasing function up to output q and decreasing thereafter Graph is an ‘inverted parabola’ we know that the quadratic term must be negative The general form is: ...
... Solution 4: This is a quadratic function Revenue is an increasing function up to output q and decreasing thereafter Graph is an ‘inverted parabola’ we know that the quadratic term must be negative The general form is: ...
Shifts of the Demand Curve
... demand for most goods. Most items that are purchased are normal goods- goods that consumers demand more of when their incomes increase. ...
... demand for most goods. Most items that are purchased are normal goods- goods that consumers demand more of when their incomes increase. ...
Econ 370
... If the factor prices are equal to 1, what is the marginal cost of producing y units of output? How many units of output would be supplied at price p? What would be the cost per unit of output? Suppose the producer is in a competitive market where p=48 and factor prices are each 1. How many units of ...
... If the factor prices are equal to 1, what is the marginal cost of producing y units of output? How many units of output would be supplied at price p? What would be the cost per unit of output? Suppose the producer is in a competitive market where p=48 and factor prices are each 1. How many units of ...
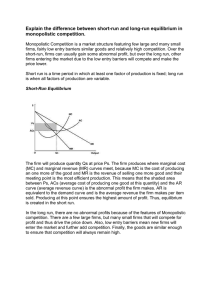
Explain the difference between short-run and long-run
... (MC) and marginal revenue (MR) curves meet, because MC is the cost of producing an one more of the good and MR is the revenue of selling one more good and their meeting point is the most efficient production. This means that the shaded area between Ps, ACs (average cost of producing one good at this ...
... (MC) and marginal revenue (MR) curves meet, because MC is the cost of producing an one more of the good and MR is the revenue of selling one more good and their meeting point is the most efficient production. This means that the shaded area between Ps, ACs (average cost of producing one good at this ...
Sample Test: US Economic System 1. Under which economic
... b. When prices decrease, quantity demanded stays the same c. When prices decrease, quantity demanded decreases d. When prices decrease, quantity demanded causes prices to decrease further 19. Which term is used to describe the extent to which a change in price causes a change in the quantity demande ...
... b. When prices decrease, quantity demanded stays the same c. When prices decrease, quantity demanded decreases d. When prices decrease, quantity demanded causes prices to decrease further 19. Which term is used to describe the extent to which a change in price causes a change in the quantity demande ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑