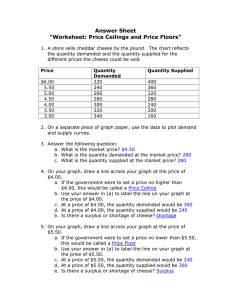
Supply and Demand Section
... Raising minimum wage increases excess labor supply (unemployment). ...
... Raising minimum wage increases excess labor supply (unemployment). ...
unit seven
... of existing firms shift to the left, pushing MR with them. • In the long run, profits are eliminated. This occurs for a firm when its demand curve is just tangent to its average cost curve. ...
... of existing firms shift to the left, pushing MR with them. • In the long run, profits are eliminated. This occurs for a firm when its demand curve is just tangent to its average cost curve. ...
Ecn 100 - UC Davis economics
... right graph, draw a short-run supply curve that would generate positive profit, and the long-run supply curve that would result. Answer: ...
... right graph, draw a short-run supply curve that would generate positive profit, and the long-run supply curve that would result. Answer: ...
tb1_ch04study guide - Mater Academy Lakes High School
... Foundations of Economics, 3e (Bade/Parkin) - Testbank 1 Chapter 4 Demand and Supply 1) A market is defined as ...
... Foundations of Economics, 3e (Bade/Parkin) - Testbank 1 Chapter 4 Demand and Supply 1) A market is defined as ...
assignment 2
... A. there is a perfectly inelastic demand for the good. B. supply exceeds demand. C. demand exceeds supply. D. a surplus exists. 24 If the “regulated-market” price is below the equilibrium (or “free-market” price) price, A. the quantity demanded will be greater than quantity supplied. B. demand will ...
... A. there is a perfectly inelastic demand for the good. B. supply exceeds demand. C. demand exceeds supply. D. a surplus exists. 24 If the “regulated-market” price is below the equilibrium (or “free-market” price) price, A. the quantity demanded will be greater than quantity supplied. B. demand will ...
chapter5 - FBE Moodle
... • List of prices & quantities consumers are willing & able to purchase at each price, all else constant • Derived by horizontally summing demand curves for all individuals in market • Because prices along market demand measure the economic value of each unit of the good, it can be interpreted as the ...
... • List of prices & quantities consumers are willing & able to purchase at each price, all else constant • Derived by horizontally summing demand curves for all individuals in market • Because prices along market demand measure the economic value of each unit of the good, it can be interpreted as the ...
Chapter 9 - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... demand curve; reduces revenue earned from the original (Q-DQ) units of output, the price reduction effect Price-taking firm faces a horizontal demand curve and is not subject to the price reduction effect ...
... demand curve; reduces revenue earned from the original (Q-DQ) units of output, the price reduction effect Price-taking firm faces a horizontal demand curve and is not subject to the price reduction effect ...
6-MarketStructu res
... * A monopoly can be said to exist when the substitutes are: not available at the time required or not price-attainable by consumers or sufficiently different in their attributes to be regarded as unsatisfactory in meeting consumer demand objectives. * A monopolist has the opportunity to set pr ...
... * A monopoly can be said to exist when the substitutes are: not available at the time required or not price-attainable by consumers or sufficiently different in their attributes to be regarded as unsatisfactory in meeting consumer demand objectives. * A monopolist has the opportunity to set pr ...
do not change - St. Clair Schools
... New technology makes the production of I-pods more efficient and less expensive. How will this affect the supply of I-pods: A) Supply will remain the same B) Supply will increase C) Supply will fall D) Supply will fluctuate ...
... New technology makes the production of I-pods more efficient and less expensive. How will this affect the supply of I-pods: A) Supply will remain the same B) Supply will increase C) Supply will fall D) Supply will fluctuate ...
Active Learning in Calculus: ConcepTests
... month, and they get $200 worth of coupons every month regardless of how much food they actually buy. WIC coupons can only be spent on food. (a) Draw this family’s budget line with expenditure on food on the horizontal axis and all other expenses on the vertical axis. (b) Draw a set of indifference c ...
... month, and they get $200 worth of coupons every month regardless of how much food they actually buy. WIC coupons can only be spent on food. (a) Draw this family’s budget line with expenditure on food on the horizontal axis and all other expenses on the vertical axis. (b) Draw a set of indifference c ...
Equilibrium World Price A country will wish to export any
... Consider a world with just two countries, A and B. In country A, domestic demand and supply of a commodity are given by DA = fA(P) and SA = gA(P), respectively. To find whether A will wish to import or export this commodity, we will construct the “excess demand,” EDA(P), for this commodity. Excess d ...
... Consider a world with just two countries, A and B. In country A, domestic demand and supply of a commodity are given by DA = fA(P) and SA = gA(P), respectively. To find whether A will wish to import or export this commodity, we will construct the “excess demand,” EDA(P), for this commodity. Excess d ...
Advantages - Effingham County Schools
... Increase Productivity: Specialization- doing what you have an advantage in Division of labor- splitting big jobs up Investing in human capital. More education = more income. ...
... Increase Productivity: Specialization- doing what you have an advantage in Division of labor- splitting big jobs up Investing in human capital. More education = more income. ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑