Chapter 15 - Powerpoint
... characterize the case of monopoly: – There is a single seller of a product having no close substitutes; there is only one source of supply. – There is complete information regarding price and product availability. – There are barriers to new firms entering the market. ...
... characterize the case of monopoly: – There is a single seller of a product having no close substitutes; there is only one source of supply. – There is complete information regarding price and product availability. – There are barriers to new firms entering the market. ...
Profit maximization in different market structures In the cappuccino
... - The firm in question is large (takes up a large portion of the market); - The firm produces a good that consumers perceive as different from the others; - Searching for the best deal is costly for consumers; ...
... - The firm in question is large (takes up a large portion of the market); - The firm produces a good that consumers perceive as different from the others; - Searching for the best deal is costly for consumers; ...
330Handout Supply and+
... An increase in the price of land (e.g. rent/lease/mortgage), labor (wages, benefits), and/or capital (higher equipment costs/financing of equipment, materials) will increase the firm’s costs, lower their profitability at the current market price, and thus provide an incentive for the firm to reduce ...
... An increase in the price of land (e.g. rent/lease/mortgage), labor (wages, benefits), and/or capital (higher equipment costs/financing of equipment, materials) will increase the firm’s costs, lower their profitability at the current market price, and thus provide an incentive for the firm to reduce ...
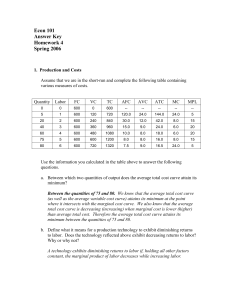
Answers to Homework #4
... competition. Firms and consumers are price takers and there is free entry and exit. Assume this industry is a constant cost industry. The total cost and marginal cost functions for an individual firm are given by the following equations (assume all firms are identical in terms of their technologies, ...
... competition. Firms and consumers are price takers and there is free entry and exit. Assume this industry is a constant cost industry. The total cost and marginal cost functions for an individual firm are given by the following equations (assume all firms are identical in terms of their technologies, ...
MIDTERM EXAMINATION 1
... The demand for Marijuana is given by QD = 100 - 1P + I, where QD is quantity demanded, P is price and I is income. The supply of Marijuana is given by QS = P ½E, where QS is quantity supplied and E represents the dollar amount spent by the government to eradicate Marijuana fields. a) Derive an expre ...
... The demand for Marijuana is given by QD = 100 - 1P + I, where QD is quantity demanded, P is price and I is income. The supply of Marijuana is given by QS = P ½E, where QS is quantity supplied and E represents the dollar amount spent by the government to eradicate Marijuana fields. a) Derive an expre ...
multiple choice answers
... AVC = q2 – 8q + 20 and dAVC/dq = 2q – 8. We can set this derivative= 0 to find the output level at which AVC reaches its minimum. So, 2q – 8 =0, or q=4. Substituting this value into the AVC function gives us (4)2 – 8(4) + 20 = $4. The correct answer is (C). 20. In a perfectly competitive constant co ...
... AVC = q2 – 8q + 20 and dAVC/dq = 2q – 8. We can set this derivative= 0 to find the output level at which AVC reaches its minimum. So, 2q – 8 =0, or q=4. Substituting this value into the AVC function gives us (4)2 – 8(4) + 20 = $4. The correct answer is (C). 20. In a perfectly competitive constant co ...
Solution
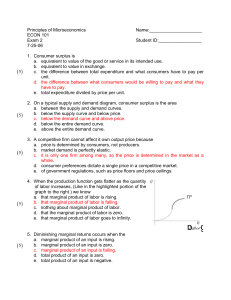
... 5. Diminishing marginal returns occurs when the a. marginal product of an input is rising. b. marginal product of an input is zero. c. marginal product of an input is falling. d. total product of an input is zero. e. total product of an input is negative. ...
... 5. Diminishing marginal returns occurs when the a. marginal product of an input is rising. b. marginal product of an input is zero. c. marginal product of an input is falling. d. total product of an input is zero. e. total product of an input is negative. ...
Perfect competition and suppy
... The conditions of perfect competition imply that producers and consumers are price takers. Price-taking behavior implies that agents make decisions taking the price to be given, that is, believing that their individual actions cannot affect the price. They cannot set the price at which they buy and ...
... The conditions of perfect competition imply that producers and consumers are price takers. Price-taking behavior implies that agents make decisions taking the price to be given, that is, believing that their individual actions cannot affect the price. They cannot set the price at which they buy and ...
PowerPoint
... If a firm can produce a different product that is priced higher, it may change production to capitalize on higher profits. Sometimes it is unfeasible to shift fixed assets to produce different products, i.e. removing an orchard to take advantage of higher corn prices. ...
... If a firm can produce a different product that is priced higher, it may change production to capitalize on higher profits. Sometimes it is unfeasible to shift fixed assets to produce different products, i.e. removing an orchard to take advantage of higher corn prices. ...
Test answers
... AVC = q2 – 8q + 20 and dAVC/dq = 2q – 8. We can set this derivative= 0 to find the output level at which AVC reaches its minimum. So, 2q – 8 =0, or q=4. Substituting this value into the AVC function gives us (4)2 – 8(4) + 20 = $4. The correct answer is (C). 20. In a perfectly competitive constant co ...
... AVC = q2 – 8q + 20 and dAVC/dq = 2q – 8. We can set this derivative= 0 to find the output level at which AVC reaches its minimum. So, 2q – 8 =0, or q=4. Substituting this value into the AVC function gives us (4)2 – 8(4) + 20 = $4. The correct answer is (C). 20. In a perfectly competitive constant co ...
Marginalist Hall of Fame
... • Constrained optimization in the face of diminishing marginal utility (the final degree of utility) relative prices – MU decreases with quantity (Gossen’s First Law) – Equilibrium: MUx/px = MUy/py = MUz/pz (Gossen’s Second Law) ...
... • Constrained optimization in the face of diminishing marginal utility (the final degree of utility) relative prices – MU decreases with quantity (Gossen’s First Law) – Equilibrium: MUx/px = MUy/py = MUz/pz (Gossen’s Second Law) ...
Microeconomics-Advanced Level
... Topic 3. International trade: theory and practice. Interdependence and gains from trade. The Winners and the Losers of trade. Comparative Advantage and it’s application. Arguments for restricting trade. Topic 4. Supply, Demand and Governmental policies Controls on prices: price Ceilings and price Fl ...
... Topic 3. International trade: theory and practice. Interdependence and gains from trade. The Winners and the Losers of trade. Comparative Advantage and it’s application. Arguments for restricting trade. Topic 4. Supply, Demand and Governmental policies Controls on prices: price Ceilings and price Fl ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑