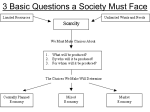
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Spring 2009 Test 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Econ 2113 – Test #1A Name________________________________ Dr. Rupp – Spring 2009 Pledge: “I have neither given or received aid on this exam” Signature_____________________________________ Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Turn cell phones off (if your phone rings during the test you will be ineligible to answer the extra credit question). ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ ____ 1. The opportunity cost of an item is a. the number of hours needed to earn money to buy the item. b. what you give up to get that item. c. usually less than the dollar value of the item. d. the dollar value of the item. 2. If the United States decides to trade with Mexico, we know that a. Mexico will benefit, but trade with a less developed country could not benefit the United States. b. it will not benefit Mexico because workers in the United States are more productive. c. Mexico and the United States can both benefit. d. it will not benefit either country because their cultural differences are too vast. 3. The "invisible hand" directs economic activity through a. advertising. b. prices. c. central planning. d. government regulations. 4. With respect to the attainment of an efficient allocation of resources, which of the following statements is correct? a. Markets are always a good way to organize economic activity. b. Markets are often a good way to organize economic activity. c. Markets are seldom a good way to organize economic activity. d. Markets are never a good way to organize economic activity. 5. The term "market failure" a. means the same thing as "market power." b. refers to the dissolution of a market when firms decide to quit producing a certain product. c. refers to the failure of a market to produce an efficient allocation of resources. d. refers to government's failure to enforce the property rights of households or firms that participate in a certain market. 6. If a copper refinery does not bear the entire cost of the smoke it emits, it will a. not emit any smoke so as to avoid the entire cost of the smoke. b. emit lower levels of smoke. c. emit an acceptable level of smoke. d. emit too much smoke. 7. Market power refers to the a. power of a single person or small group to influence market prices. b. ability of a person or small group to successfully market new products. c. power of the government to regulate a market. d. importance of a certain market in relation to the overall economy. 8. The income of a typical worker in a country is most closely linked to which of the following? a. population b. productivity c. market power d. government policies 9. An increase in the overall level of prices in an economy is referred to as a. economic growth. b. inflation. c. the price effect. d. the demand effect. 10. The short-run tradeoff between inflation and unemployment implies that, in the short run, a. a decrease in the growth rate of the quantity of money will be accompanied by an increase in the unemployment rate. b. an increase in the growth rate of the quantity of money will be accompanied by an increase in the unemployment rate. c. policymakers are able to reduce the inflation rate and, at the same time, reduce the unemployment rate. d. policymakers can influence the inflation rate, but not the unemployment rate. ____ 11. The bowed-out shape of the production possibilities frontier can be explained by the fact that a. scarcity is a fact of life. b. economic growth is always occurring. c. the opportunity cost of one good in terms of the other depends on how much of each good the economy is producing. d. an assumption that is made in constructing a production possibilities frontier is that tradeoffs are unimportant. ____ 12. A certain production possibilities frontier shows production possibilities for two goods: wheat and shirts. Which of the following concepts can not be illustrated in this model? a. the flow of dollars between (i) sellers of wheat and shirts and (ii) buyers of wheat and shirts b. the tradeoff between production of wheat and production of shirts c. the opportunity cost of shirts in terms of wheat d. the effect of economic growth on production possibilities involving wheat and shirts ____ 13. Suppose a nation is currently producing at a point inside its production possibilities frontier. We know that a. the nation is producing beyond its capacity, and inflation will occur. b. the nation is not using all available resources or is using inferior technology or both. c. the nation is producing an efficient combination of goods. d. there will be a large opportunity cost if the nation tries to increase production of any good. Figure 2-6 ____ 14. Refer to Figure 2-6. A movement from point C to point D could be caused by a. unemployment. b. a decrease in society's preference for bananas. c. fewer resources available for production of bananas. d. All of the above are correct. ____ 15. In a certain economy, peanuts and books are produced, and the economy currently operates on its production possibilities frontier. Which of the following events would allow the economy to produce more peanuts and more books, relative to the quantities of those goods that are being produced now? a. Unemployed labor is put to work producing peanuts and books. b. The economy puts its idle capital to work producing peanuts and books. c. The economy experiences economic growth. d. All of the above are correct. Figure 2-7 ____ 16. Refer to Figure 2-7. Which of the following would most likely have caused the production possibilities frontier to shift outward from A to B? a. an increase in the availability of capital-producing resources b. a technological advance in the consumer-goods industries c. a general technological advance d. a decrease in unemployment ____ 17. Microeconomics is the study of a. the causes & consequences of short-run fluctuations in output. b. how individual households and firms make decisions. c. how government affects the economy. d. how the economy as a whole works. ____ 18. A normative statement describes how the world a. was in the past. b. is in the present. c. will be in the future. d. ought to be. ____ 19. Which of the following statements is not correct? a. Trade allows for specialization. b. Trade has the potential to benefit all nations. c. Trade allows nations to consume outside of their production possibilities curves. d. Absolute advantage is the driving force of specialization. These graphs illustrate the production possibilities available to Fred and Ginger with each person working 40 hours. Figure 3-3 ____ 20. Refer to Figure 3-3. The opportunity cost of 1 pair of tap shoes for Fred is a. 1/3 pair of ballet slippers. b. 1/5 pair of ballet slippers. c. 3/5 pair of ballet slippers. d. 5/3 pairs of ballet slippers. ____ 21. Refer to Figure 3-3. The opportunity cost of 1 pair of ballet slippers for Ginger is a. 1/4 pair of tap shoes. b. 1/3 pair of tap shoes. c. 3/4 pair of tap shoes. d. 4/3 pairs of tap shoes. ____ 22. Refer to Figure 3-3. Ginger has an absolute advantage in a. ballet slippers and Fred has an absolute advantage in tap shoes. b. tap shoes and Fred has an absolute advantage in ballet slippers. c. neither good and Fred has an absolute advantage in both goods. d. both goods and Fred has an absolute advantage in neither good. ____ 23. If Shawn can produce more donuts in one day than Sue can produce in one day, then a. Shawn has a comparative advantage in the production of donuts. b. Sue has a comparative advantage in the production of donuts. c. Shawn has an absolute advantage in the production of donuts. d. Shawn should produce donuts and Sue should spend her time on a different activity. Table 3-5 ____ 24. ____ 25. ____ 26. ____ 27. ____ 28. ____ 29. ____ 30. ____ 31. ____ 32. ____ 33. ____ 34. ____ 35. Hours needed to make one: Amount produced in 2400 hours: Car Airplane Cars Airplanes Japan 30 150 80 16 U.S. 50 200 48 12 Refer to Table 3-5. The opportunity cost of 1 car for Japan is a. 5 airplanes. b. 4 airplanes. c. 1/4 airplane. d. 1/5 airplane. Refer to Table 3-5. The opportunity cost of 1 car for the United States is a. 4 airplanes. b. 3 airplanes. c. 1/3 airplane. d. 1/4 airplane. Refer to Table 3-5. The United States has an absolute advantage in a. airplanes and Japan has an absolute advantage in cars. b. cars and Japan has an absolute advantage in airplanes. c. both cars and airplanes. d. neither cars nor airplanes. Refer to Table 3-5. The United States and Japan could benefit by the United States specializing in a. airplanes and Japan specializing in airplanes. b. cars and Japan specializing in airplanes. c. airplanes and Japan specializing in cars. d. neither good and Japan specializing in cars. The term market always refers to a. an arrangement in which buyers and sellers meet at a specific time and place. b. an arrangement in which an auctioneer plays at least a limited role in setting prices. c. a group of buyers and sellers of a particular good or service. d. All of the above are correct. Which of the following is not a characteristic of a perfectly competitive market? a. Different sellers sell identical products. b. There are many sellers. c. Sellers must accept the price the market determines. d. All of the above are characteristics of a perfectly competitive market. Which of the following would not be a determinant of the demand for a particular good? a. prices of related goods b. income c. tastes d. the prices of the inputs used to produce the good The amount of the good buyers are willing and able to purchase is called the a. demand. b. quantity demanded. c. supply. d. quantity supplied. You lose your job and as a result you buy fewer DVD’s. This shows that you consider DVD’s to be a(n) a. luxury good. b. inferior good. c. normal good. d. complementary good. Alyssa rents 5 movies per month when the price is $3.00 per rental and 7 movies per month when the price is $2.50 per rental. Alyssa’s demand demonstrates the law of a. price. b. supply. c. demand. d. expectations. A higher price for hot dogs would result in a(n) a. increase in the demand for hot dog buns. b. decrease in the demand for hot dog buns. c. increase in the demand for hot dogs. d. decrease in the demand for hot dogs. A demand schedule is a table showing the relationship between a. quantity demanded and quantity supplied, and those quantities are usually positively related. b. quantity demanded and quantity supplied, and those quantities are usually negatively related. c. price and quantity demanded, and those quantities are usually positively related. d. price and quantity demanded, and those quantities are usually negatively related. ____ 36. An increase in demand is represented by a. a movement downward and to the right along a demand curve. b. a movement upward and to the left along a demand curve. c. a rightward shift of a demand curve. d. a leftward shift of a demand curve. ____ 37. Which of the following events could shift the demand curve for gasoline to the left? a. Income of gasoline buyers rises, and gasoline is a normal good. b. Income of gasoline buyers falls, and gasoline is an inferior good. c. Public service announcements are run on television, encouraging people to walk or ride bicycles instead of driving cars. d. The price of gasoline rises. ____ 38. Suppose you make jewelry. If the price of gold falls, we would expect you to a. be willing and able to produce less jewelry than before at each possible price. b. be willing and able to produce more jewelry than before at each possible price. c. face a greater demand for your jewelry. d. face a weaker demand for your jewelry. True/False Indicate whether the sentence or statement is true or false. Figure 2-11 ____ 39. Refer to Figure 2-11. The opportunity cost of more doghouses increases as more doghouses are produced. a) True b) False ____ 40. Trade is based on comparative advantage. a) True b) False Extra Credit Question: To be eligible to answer this extra credit question, you must satisfy both criteria below: • Your cell phone has not rung in class • You are taking this test in class at the regularly scheduled time: (Tuesday, February 3rd) ____ 41. Workers at a bicycle assembly plant currently earn the mandatory minimum wage. If the federal government increases the minimum wage by $1.00 an hour it is likely that the a. demand for bicycle assembly workers will increase. b. supply of bicycles will shift to the right. c. supply of bicycles will shift to the left. d. firm must increase output to maintain profit levels.