ECN 104 Notes: Week of March 24 Chapter 9: Pure Competition
... Equilibrium (no more entry/exit) occurs at the price that equals min ATC. ...
... Equilibrium (no more entry/exit) occurs at the price that equals min ATC. ...
File - Edexcel A level Business
... We now consider the basic theories of how the market mechanism works. In this chapter we consider the economics of the law of demand. This is important background to understanding the determination of prices in competitive markets. Demand Demand is defined as the quantity of a good or service that c ...
... We now consider the basic theories of how the market mechanism works. In this chapter we consider the economics of the law of demand. This is important background to understanding the determination of prices in competitive markets. Demand Demand is defined as the quantity of a good or service that c ...
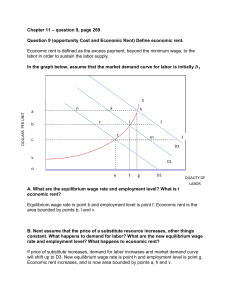
Chapter 11 – question 9, page 269 Question 9 (opportunity Cost and
... Supply labor curve over this range of wages would be vertical, because the quantity of labor supply would not change if substitution effect exactly offsets the income effect. ...
... Supply labor curve over this range of wages would be vertical, because the quantity of labor supply would not change if substitution effect exactly offsets the income effect. ...
An Important Relationship Between Elasticity and Total Revenue
... week at a price of $20 each. His total revenue (price × quanity) per week is $2,000. Suppose Javier raises the price of his basketballs to $22 each, a 10 percent increase in price. As a result, the quantity demanded falls from 100 to 75, a 25 percent reduction. The demand is elastic because the chan ...
... week at a price of $20 each. His total revenue (price × quanity) per week is $2,000. Suppose Javier raises the price of his basketballs to $22 each, a 10 percent increase in price. As a result, the quantity demanded falls from 100 to 75, a 25 percent reduction. The demand is elastic because the chan ...
homework 1998
... market structures? Explain why price can be substituted for marginal revenue in the MR = MC rule when an industry is purely competitive. ANS. To maximize profit, every firm regardless of market structure should produce every unit that adds more to revenue than it does to cost. In this way the firm m ...
... market structures? Explain why price can be substituted for marginal revenue in the MR = MC rule when an industry is purely competitive. ANS. To maximize profit, every firm regardless of market structure should produce every unit that adds more to revenue than it does to cost. In this way the firm m ...
Professor`s Name
... Suppose rainfall was increased from 10 to 20 inches. Assuming that this increase was not so big it damaged the crop, this change would increase the production of wheat given the same inputs or other resources. Because the sellers have more wheat to sell, the supply curve would shift to the right, an ...
... Suppose rainfall was increased from 10 to 20 inches. Assuming that this increase was not so big it damaged the crop, this change would increase the production of wheat given the same inputs or other resources. Because the sellers have more wheat to sell, the supply curve would shift to the right, an ...
The demand for labor is a firm`s MRP curve. The graph shows the
... effect predicts that as wage rates increase, households supply more labor, substituting more labor for leisure. The income effect predicts that as wage rates increase above a certain point, households may want to forgo more income for more leisure time. This would create the backward-bending part of ...
... effect predicts that as wage rates increase, households supply more labor, substituting more labor for leisure. The income effect predicts that as wage rates increase above a certain point, households may want to forgo more income for more leisure time. This would create the backward-bending part of ...
Part F: Supply: Alternative Strategies
... would be profitable to do so, then the firm is effectively saying that the marginal revenue (gained) of the price change exceeds the marginal cost (incurred) (or the marginal revenue lost is less than the marginal cost saved). If the firm is a profit satisficer, however, then any price adjustment in ...
... would be profitable to do so, then the firm is effectively saying that the marginal revenue (gained) of the price change exceeds the marginal cost (incurred) (or the marginal revenue lost is less than the marginal cost saved). If the firm is a profit satisficer, however, then any price adjustment in ...
ECON 2010-100 Principles of Microeconomics
... The course discusses behaviors of households and firms, how do they make choices to maximize their objectives from limited amount of resources available to them. The course has three major parts: consumer theory, producer theory, and market's successes and failures in efficient allocation of resourc ...
... The course discusses behaviors of households and firms, how do they make choices to maximize their objectives from limited amount of resources available to them. The course has three major parts: consumer theory, producer theory, and market's successes and failures in efficient allocation of resourc ...
Monopolistic Competition
... products would be overwhelming. Another way in which monopolistic competition may be socially inefficient is that the number of firms in the market may not be the “ideal” one. There may be too much or too little entry. ...
... products would be overwhelming. Another way in which monopolistic competition may be socially inefficient is that the number of firms in the market may not be the “ideal” one. There may be too much or too little entry. ...
Assessment Schedule – 2011
... Assessment Schedule – 2011 Economics: Demonstrate understanding of how consumer, producer and / or government choices affect society, using market equilibrium (90986) Evidence Statement Question ONE ...
... Assessment Schedule – 2011 Economics: Demonstrate understanding of how consumer, producer and / or government choices affect society, using market equilibrium (90986) Evidence Statement Question ONE ...
Chapter 2
... supply each unit of the product and the actual market price that is paid, summed over all units that are produced and sold. The lowest price at which someone is willing to supply the unit just covers the extra (marginal) cost of producing that unit. To measure producer surplus for a product using re ...
... supply each unit of the product and the actual market price that is paid, summed over all units that are produced and sold. The lowest price at which someone is willing to supply the unit just covers the extra (marginal) cost of producing that unit. To measure producer surplus for a product using re ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑