cross price elasticity
... Qb = 2000; Pa = 100, Qa = 1500. (The subscripts a and b refer to “after the storm” and “before the storm”.) a. Assume a linear demand curve for corn, i.e. P = α + β Q. Calculate α, β with the provided information, and draw the demand curve with P on the y-axis and Q on the x-axis. Label the intercep ...
... Qb = 2000; Pa = 100, Qa = 1500. (The subscripts a and b refer to “after the storm” and “before the storm”.) a. Assume a linear demand curve for corn, i.e. P = α + β Q. Calculate α, β with the provided information, and draw the demand curve with P on the y-axis and Q on the x-axis. Label the intercep ...
Chapter 4 - Equilibrium
... the quantity demanded (10 cones) exceeds the quantity supplied (4 cones). With too many buyers chasing too few goods, suppliers can take advantage of the shortage by raising the price. Hence, in both cases, the price adjustment moves the market toward the equilibrium of supply and demand 5 ...
... the quantity demanded (10 cones) exceeds the quantity supplied (4 cones). With too many buyers chasing too few goods, suppliers can take advantage of the shortage by raising the price. Hence, in both cases, the price adjustment moves the market toward the equilibrium of supply and demand 5 ...
Fall 2010 – Test #2
... 9. How much did it cost to produce the output selected in question #8 from the Grimesland plant? a. $30 b. $48.13 c. $16.40 d. $20 e. $28.13 10. What is the total cost of producing 17.5 units of output? a. $26.25 b. $31.25 c. $33.13 d. $48.13 e. $31.72 Complete the following table for the short-run ...
... 9. How much did it cost to produce the output selected in question #8 from the Grimesland plant? a. $30 b. $48.13 c. $16.40 d. $20 e. $28.13 10. What is the total cost of producing 17.5 units of output? a. $26.25 b. $31.25 c. $33.13 d. $48.13 e. $31.72 Complete the following table for the short-run ...
Chapter 9
... The Social Cost of Monopoly Recall: In a competitive market equilibrium, P = MC and there is both productive and allocative efficiency. ...
... The Social Cost of Monopoly Recall: In a competitive market equilibrium, P = MC and there is both productive and allocative efficiency. ...
Chapter 4: Demand
... As the price of your favorite good rises, the purchasing of that good (demand) falls As the price of your favorite good rises, the amount of purchases (demand) of a decent alternative also rises If the price of your favorite good drops, you go back to buying more of your favorite and less of the alt ...
... As the price of your favorite good rises, the purchasing of that good (demand) falls As the price of your favorite good rises, the amount of purchases (demand) of a decent alternative also rises If the price of your favorite good drops, you go back to buying more of your favorite and less of the alt ...
Document
... food have been increasing for most of this century. High productivity in the agriculture sector, relative to income inelasticity for food, has meant that supply has increased by more than demand. As a result, prices have fallen. ...
... food have been increasing for most of this century. High productivity in the agriculture sector, relative to income inelasticity for food, has meant that supply has increased by more than demand. As a result, prices have fallen. ...
Problem Set #8 Key
... b. Show that if utility is separable, neither good can be inferior. In any equilibrium the optimal consumption bundle will be Ux/Px = Uy/Py. If income increases, consumers must consume more of one of the goods. But given Uii<0 increased consumption of one good will yield lower marginal utility for t ...
... b. Show that if utility is separable, neither good can be inferior. In any equilibrium the optimal consumption bundle will be Ux/Px = Uy/Py. If income increases, consumers must consume more of one of the goods. But given Uii<0 increased consumption of one good will yield lower marginal utility for t ...
Lecture Notes: Econ 203 Introductory Microeconomics Lecture 1: 10
... Private goods are rival and excludable and are the kinds of goods markets work best with Public goods are neither excludable nor rival in consumption This promotes the problem of free riders: consumer do not have to pay, so firms will be less willing to provide those goods. Govts tend to provide pub ...
... Private goods are rival and excludable and are the kinds of goods markets work best with Public goods are neither excludable nor rival in consumption This promotes the problem of free riders: consumer do not have to pay, so firms will be less willing to provide those goods. Govts tend to provide pub ...
QUESTIONS FOR DISCUSSION
... sales affect the quantity of kidney transplants or their distribution? The need for kidneys is medically determined and therefore price is not an issue. Anyone who has kidney disease and is in need of a kidney transplant is part of the market demand for kidneys. The demand curve for kidneys would be ...
... sales affect the quantity of kidney transplants or their distribution? The need for kidneys is medically determined and therefore price is not an issue. Anyone who has kidney disease and is in need of a kidney transplant is part of the market demand for kidneys. The demand curve for kidneys would be ...
PART I. Multiple Choice. Choose the best answer.
... 39. If capital and labour are used in rigidly fixed proportions and the price of capital falls, it can be concluded that a. the substitution and output effects will work in the opposite directions so no judgment can be made as to the effect on labour demand. b. the MPP of capital will rise. c. the e ...
... 39. If capital and labour are used in rigidly fixed proportions and the price of capital falls, it can be concluded that a. the substitution and output effects will work in the opposite directions so no judgment can be made as to the effect on labour demand. b. the MPP of capital will rise. c. the e ...
Course Number: ECON 213 - Baton Rouge Community College
... Grading: The College grading policy should be included in the course syllabus. Any special practices should also go here. This should include the instructor’s and/or the department’s policy for make-up work. For example in a speech course, “Speeches not given on due date will receive no grade higher ...
... Grading: The College grading policy should be included in the course syllabus. Any special practices should also go here. This should include the instructor’s and/or the department’s policy for make-up work. For example in a speech course, “Speeches not given on due date will receive no grade higher ...
consumer equilibrium - Indian School Al Wadi Al Kabir
... fallen in the domestic market. What kind of change in terms of the budget line of; given consumer will take place, who spends his entire income on goods X and Y, of which X is diesel? Explain. Derive the law of demand from the single commodity equilibrium – Marginal Utility = Price.(HOTS) ...
... fallen in the domestic market. What kind of change in terms of the budget line of; given consumer will take place, who spends his entire income on goods X and Y, of which X is diesel? Explain. Derive the law of demand from the single commodity equilibrium – Marginal Utility = Price.(HOTS) ...
supply and demand - Lockport Township High School | Haiku
... can affect supply by lowering the cost of production or by increasing productivity • However equipment can break down, or technology might be difficult to obtain. • This would shift to the left (but not usually) ...
... can affect supply by lowering the cost of production or by increasing productivity • However equipment can break down, or technology might be difficult to obtain. • This would shift to the left (but not usually) ...
Chapter 1: The Labor Market
... • Describe re-equilibrating process by changing C.P. factor: – Increase in income causes increase in demand (shift D rightward) – At old P, Qd greater than Qs: so individuals bid up price till reach new ...
... • Describe re-equilibrating process by changing C.P. factor: – Increase in income causes increase in demand (shift D rightward) – At old P, Qd greater than Qs: so individuals bid up price till reach new ...
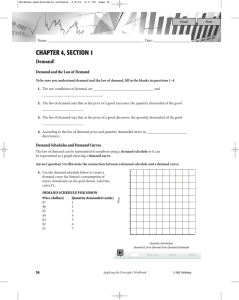
CHAPTER 4, SECTION 1 Demand! Demand and the Law of Demand
... 6. The demand curve shows that at a price of $7, Simon will buy ______ music download(s), and at a price of $1, he will buy ______ music download(s). 7. Simon’s buying behavior demonstrates the law of ______________________. 8. Simon’s change in buying behavior at different prices is a change in ___ ...
... 6. The demand curve shows that at a price of $7, Simon will buy ______ music download(s), and at a price of $1, he will buy ______ music download(s). 7. Simon’s buying behavior demonstrates the law of ______________________. 8. Simon’s change in buying behavior at different prices is a change in ___ ...
How? When? What? The economics of competitive advantage Why?
... 5.8 Producer surplus • Producer surplus is the difference between the revenue obtained by the supplier and its full cost of production. It ...
... 5.8 Producer surplus • Producer surplus is the difference between the revenue obtained by the supplier and its full cost of production. It ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑