ECON4346 28 OCT
... ◦ As the amount of Monsters increases, its marginal utility decreases ◦ As the amount of Snickers decreases, its marginal utility increases ...
... ◦ As the amount of Monsters increases, its marginal utility decreases ◦ As the amount of Snickers decreases, its marginal utility increases ...
Spring 2007 14.44-14.444 Problem Set 3 Due March 2, 2007 1. a
... different discount rates from the discount rate of a social planner. Firms will use a discount rate equal to the cost of funds during any one period which is the interest rate. The social discount rate could differ from this for any number of reasons. For instance if there is an externality associat ...
... different discount rates from the discount rate of a social planner. Firms will use a discount rate equal to the cost of funds during any one period which is the interest rate. The social discount rate could differ from this for any number of reasons. For instance if there is an externality associat ...
chocolate chip cookies
... 6. Graph the number of items you would be willing to sell at the various prices. This is the supply curve graph. 7. Based on your graph, answer the following questions: a. At what price were the most people willing to buy the item? ...
... 6. Graph the number of items you would be willing to sell at the various prices. This is the supply curve graph. 7. Based on your graph, answer the following questions: a. At what price were the most people willing to buy the item? ...
Document
... What happens to the equilibrium Price? Price decreases What happens to the equilibrium Quantity? Quantity increases In the market for daycare: the number of children born in the US has steadily decreased since the year 2000 ...
... What happens to the equilibrium Price? Price decreases What happens to the equilibrium Quantity? Quantity increases In the market for daycare: the number of children born in the US has steadily decreased since the year 2000 ...
short-run supply curve - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... total revenue and total cost, where total cost includes all costs—both explicit and implicit—associated with resources used by the firm. • Accounting profit is simply total revenue less all explicit costs incurred. – does not subtract the implicit costs. ...
... total revenue and total cost, where total cost includes all costs—both explicit and implicit—associated with resources used by the firm. • Accounting profit is simply total revenue less all explicit costs incurred. – does not subtract the implicit costs. ...
Exercise 2 Multiple Choice Questions. Choose the best answer. 1. If
... a. gamblers have an inelastic demand for gambling in Clark County. b. gamblers have an elastic demand for gambling in Clark County. c. gamblers have unitary demand for gambling in Clark County. d. Clark County citizens must gamble a lot. e. Tourists must gamble a lot. 3. If the elasticity of supply ...
... a. gamblers have an inelastic demand for gambling in Clark County. b. gamblers have an elastic demand for gambling in Clark County. c. gamblers have unitary demand for gambling in Clark County. d. Clark County citizens must gamble a lot. e. Tourists must gamble a lot. 3. If the elasticity of supply ...
Document
... – If the good is normal and its price rises, both IE and SE will tend to lead to a reduction in the quantity demanded of the good. – If the good is inferior and its price rises, the IE will increase quantity demanded, at the same time, SE decreases the quantity demanded. In general, SE is stronger t ...
... – If the good is normal and its price rises, both IE and SE will tend to lead to a reduction in the quantity demanded of the good. – If the good is inferior and its price rises, the IE will increase quantity demanded, at the same time, SE decreases the quantity demanded. In general, SE is stronger t ...
Parallel Questions
... because as output increases the average total costs falls. There are high fixed costs to producing a newspaper (writing it, including photos and ads, checking copy, and laying out articles). But once the newspaper is written and ready to be printed, these high fixed costs can be spread over a large ...
... because as output increases the average total costs falls. There are high fixed costs to producing a newspaper (writing it, including photos and ads, checking copy, and laying out articles). But once the newspaper is written and ready to be printed, these high fixed costs can be spread over a large ...
Quiz March 26
... » Information is a public good – High exclusion cost – Non-rival consumption » Assists competitive markets by providing information to ...
... » Information is a public good – High exclusion cost – Non-rival consumption » Assists competitive markets by providing information to ...
ECO 2301 Spring 2014 Sec 002 Klaus Becker EXAM 1
... More productive resources will shift the PPC outward. ...
... More productive resources will shift the PPC outward. ...
Answer Monopoly, Regulated Monopoly
... Regulation is necessary because unregulated monopolies produce too little and cause a deadweight loss by using too few resources in this industry compared to others. Regulation of utilities, however, if forcing them to earn only a risk-adjusted normal rate of return on invested capital, results (in ...
... Regulation is necessary because unregulated monopolies produce too little and cause a deadweight loss by using too few resources in this industry compared to others. Regulation of utilities, however, if forcing them to earn only a risk-adjusted normal rate of return on invested capital, results (in ...
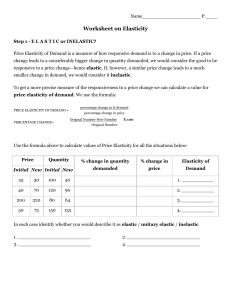
Worksheet on Elasticity
... Judge the products in the table below to decide whether you think they will be elastic or inelastic: ...
... Judge the products in the table below to decide whether you think they will be elastic or inelastic: ...
Are Price Controls Good or Bad?
... #1-Price Controls: Floors and Ceilings #2-Import Quotas #3-Subsidies #4-Excise Taxes ...
... #1-Price Controls: Floors and Ceilings #2-Import Quotas #3-Subsidies #4-Excise Taxes ...
Industrial Organization
... substitutability, to the same potential buyers • Common buyers for sellers • Common sellers for buyers • Relatively homogeneous product ...
... substitutability, to the same potential buyers • Common buyers for sellers • Common sellers for buyers • Relatively homogeneous product ...
Demand
... How much does the person really want to go to China or how big a hassle is it to come back. Number of Individuals going to Chinese Consulate for visa. ...
... How much does the person really want to go to China or how big a hassle is it to come back. Number of Individuals going to Chinese Consulate for visa. ...
cm24e perfect competition
... to this model is not does it correspond to actual industries but rather does it provide a good approximation to how our economic system actually allocates resources. I have argued in T12 and T22 that this model does not do a good job of explaining how the US economy actually operates. 2. A perfectly ...
... to this model is not does it correspond to actual industries but rather does it provide a good approximation to how our economic system actually allocates resources. I have argued in T12 and T22 that this model does not do a good job of explaining how the US economy actually operates. 2. A perfectly ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑