HANDOUT 2
... As a team, consider your answers to the questions below. Write your answers on your own paper. For each answer, be sure to explain WHY this effect would occur. 1. Explain three arguments of protectionists in your own words. 2. Explain three arguments of free traders in your own words. 3. Define the ...
... As a team, consider your answers to the questions below. Write your answers on your own paper. For each answer, be sure to explain WHY this effect would occur. 1. Explain three arguments of protectionists in your own words. 2. Explain three arguments of free traders in your own words. 3. Define the ...
Markets and Demand
... ¤ As the price of a good increases, the quantity demanded falls ¤ As the price of the good falls, the quantity demanded increases ¤ ceteris paribus Price Quantity Demanded ...
... ¤ As the price of a good increases, the quantity demanded falls ¤ As the price of the good falls, the quantity demanded increases ¤ ceteris paribus Price Quantity Demanded ...
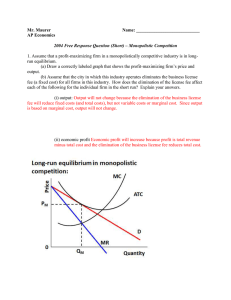
Mr. Maurer Name: AP Economics 2004 Free Response Question
... demand curve be price inelastic? Explain. No, the typical firm’s demand curve would be elastic at the profit-maximizing price because marginal revenue is positive in this portion of the demand curve, so total revenue increases as price decreases. (c) Given the information in part (a), what happens t ...
... demand curve be price inelastic? Explain. No, the typical firm’s demand curve would be elastic at the profit-maximizing price because marginal revenue is positive in this portion of the demand curve, so total revenue increases as price decreases. (c) Given the information in part (a), what happens t ...
Document
... This brief set of sample questions is simply to give you extra practice in preparing for exams. Most of the questions are taken from the testbank and hence, they may not be phrased exactly how I would phrase them in discussion or on your exam. This is NOT a complete test nor does it accurately repre ...
... This brief set of sample questions is simply to give you extra practice in preparing for exams. Most of the questions are taken from the testbank and hence, they may not be phrased exactly how I would phrase them in discussion or on your exam. This is NOT a complete test nor does it accurately repre ...
Solutions 11 - Emilio Cuilty
... Answer: To find the market supply curve we need to horizontally sum the 10 individual supply curves (recall from lecture that the individual firm’s supply curve is equal to its MC curve). Thus, if MC = q + 1 for one firm, then the market supply curve will consist of adding up the 10 individual MC cu ...
... Answer: To find the market supply curve we need to horizontally sum the 10 individual supply curves (recall from lecture that the individual firm’s supply curve is equal to its MC curve). Thus, if MC = q + 1 for one firm, then the market supply curve will consist of adding up the 10 individual MC cu ...
ECON 3070-003 Intermediate Microeconomic Theory
... ECON 3070 Prof. Kruse-Homework #I-due January 13, 1995 Part I For demand represented by the function, Q= 1000-5P, and supply represented by the function, Q=P-200, a) Solve for competitive equilibrium price and quantity. b) Plot the demand and supply curves, noting all horizontal and vertical interc ...
... ECON 3070 Prof. Kruse-Homework #I-due January 13, 1995 Part I For demand represented by the function, Q= 1000-5P, and supply represented by the function, Q=P-200, a) Solve for competitive equilibrium price and quantity. b) Plot the demand and supply curves, noting all horizontal and vertical interc ...
Document
... 9. Whether the following statements are true or false? Give reasons. (i) Two indifference curves never intersects each other. (ii) Income effect of inferior good is positive. (iii) Change in quantity demanded is the explanations of law of demand. 10. Explain the concept of marginal rate of substitut ...
... 9. Whether the following statements are true or false? Give reasons. (i) Two indifference curves never intersects each other. (ii) Income effect of inferior good is positive. (iii) Change in quantity demanded is the explanations of law of demand. 10. Explain the concept of marginal rate of substitut ...
S9 Practice Test
... is equal to the price elasticity of demand for segment BC. is greater than the price elasticity of demand for segment BC. ...
... is equal to the price elasticity of demand for segment BC. is greater than the price elasticity of demand for segment BC. ...
Lecture Notes VI
... @Y Y : The …rst of these is called the substitution @I e¤ect. The second is called the income e¤ect. – Substitution E¤ect: This considers the impact on demand for good Y of an increase in price Pj holding utility constant. If the price of a good goes up holding utility constant, income must increase ...
... @Y Y : The …rst of these is called the substitution @I e¤ect. The second is called the income e¤ect. – Substitution E¤ect: This considers the impact on demand for good Y of an increase in price Pj holding utility constant. If the price of a good goes up holding utility constant, income must increase ...
Lecture 3 -- Markets and Equilibrium Analysis
... derivation of a Individual Producer Supply curves.– Qs = f[+] (P). As we aggregate among all firms in a related industry we derive the Market Supply curve with a similar relationship between price and quantity. Supply decisions in the market are driven by higher prices that will induce greater quant ...
... derivation of a Individual Producer Supply curves.– Qs = f[+] (P). As we aggregate among all firms in a related industry we derive the Market Supply curve with a similar relationship between price and quantity. Supply decisions in the market are driven by higher prices that will induce greater quant ...
Slide 1
... – Government-created monopolies • Patent and copyright laws • Higher prices; Higher profits ...
... – Government-created monopolies • Patent and copyright laws • Higher prices; Higher profits ...
Role of Economics
... Willingness to Pay (WTP) A buyer’s willingness to pay for a good is the maximum amount the buyer will pay for that good. WTP measures how much the buyer values the good. name ...
... Willingness to Pay (WTP) A buyer’s willingness to pay for a good is the maximum amount the buyer will pay for that good. WTP measures how much the buyer values the good. name ...
Cross-Price Elasticities of Demand
... - A given level of average income in a market will sometimes give rise to different market demands depending on how income is distributed - The dependence of market demands on the distribution of income is important when the government considers policies to redistribute income - Engel curves at the ...
... - A given level of average income in a market will sometimes give rise to different market demands depending on how income is distributed - The dependence of market demands on the distribution of income is important when the government considers policies to redistribute income - Engel curves at the ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑