Tutorial
... transit system, this is evidence that demand is a. price elastic. b. price inelastic c. unitary elastic d. perfectly elastic. A. When price increases and the total revenue decreases, by definition, this represents an elastic demand curve. The revenue lost from selling fewer units is not offset by th ...
... transit system, this is evidence that demand is a. price elastic. b. price inelastic c. unitary elastic d. perfectly elastic. A. When price increases and the total revenue decreases, by definition, this represents an elastic demand curve. The revenue lost from selling fewer units is not offset by th ...
Natural Resource Economics
... The market demand curve for aluminum cans is given by the following equation: P = 8 - 0.4 Q. The supply curve of aluminum cans using virgin raw materials is given by: P = 2, and the supply curve from recycled aluminum cans is given by: P = (4/10) Q. 1. In the space below, plot the market demand curv ...
... The market demand curve for aluminum cans is given by the following equation: P = 8 - 0.4 Q. The supply curve of aluminum cans using virgin raw materials is given by: P = 2, and the supply curve from recycled aluminum cans is given by: P = (4/10) Q. 1. In the space below, plot the market demand curv ...
Economics 313 - Fall 2004 – FINAL EXAM
... preferences over only two goods: $“all other goods” and Springsteen tickets. Suppose she has $500 to spend. Suppose the ticket prices are $100/ticket and that the price of “all other goods” is $1. Suppose Prof. Wissink determines that the solution to her constrained utility optimization problem is t ...
... preferences over only two goods: $“all other goods” and Springsteen tickets. Suppose she has $500 to spend. Suppose the ticket prices are $100/ticket and that the price of “all other goods” is $1. Suppose Prof. Wissink determines that the solution to her constrained utility optimization problem is t ...
Interest Rate Determination
... Interest Rate Determination This chapter: What makes interest rates move up or down? Do not confuse with: What makes interest rates different, such as secondary market, default risk, etc. Apply Demand and Supply analysis to bond market. ...
... Interest Rate Determination This chapter: What makes interest rates move up or down? Do not confuse with: What makes interest rates different, such as secondary market, default risk, etc. Apply Demand and Supply analysis to bond market. ...
Unit III Review
... good, a price increase will make your demand elastic. If it is a small percentage of your budget, your demand is probably inelastic. Necessities vs. luxuries: people will always buy necessities, even when price increases (inelastic). Luxuries are elastic as they are easy to reduce the quantity deman ...
... good, a price increase will make your demand elastic. If it is a small percentage of your budget, your demand is probably inelastic. Necessities vs. luxuries: people will always buy necessities, even when price increases (inelastic). Luxuries are elastic as they are easy to reduce the quantity deman ...
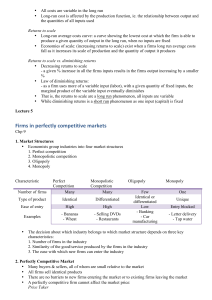
Firms in perfectly competitive markets
... • Long-run average costs curve: a curve showing the lowest cost at which the firm is able to produce a given quantity of output in the long run, when no inputs are fixed • Economies of scale: (increasing returns to scale) exist when a firms long run average costs fall as it increases its scale of pr ...
... • Long-run average costs curve: a curve showing the lowest cost at which the firm is able to produce a given quantity of output in the long run, when no inputs are fixed • Economies of scale: (increasing returns to scale) exist when a firms long run average costs fall as it increases its scale of pr ...
Elasticity of Demand
... • If a curve is more elastic, then small changes in price will cause large changes in quantity ...
... • If a curve is more elastic, then small changes in price will cause large changes in quantity ...
Supply
... Supply is the different quantities of a good that sellers are willing and able to sell (produce) at different prices. What is the Law of Supply? There is a DIRECT (or positive) relationship between price and quantity supplied. •As price increases, the quantity producers make ...
... Supply is the different quantities of a good that sellers are willing and able to sell (produce) at different prices. What is the Law of Supply? There is a DIRECT (or positive) relationship between price and quantity supplied. •As price increases, the quantity producers make ...
Chapter 2 PP - Part 1
... • The total demand for a product or service from all consumers • It is the summation of all individual demand curves • Consumers do not set prices; they react to different prices by altering their quantity demanded ...
... • The total demand for a product or service from all consumers • It is the summation of all individual demand curves • Consumers do not set prices; they react to different prices by altering their quantity demanded ...
Exercises to complete the Equilibrium discussion MULTIPLE
... 11) Consider a market that has many buyers but only one seller. Assume the seller has only one unit of the product to sell. Then the market demand curve will be ________ and the seller's supply curve will be ________. 11) ______ A) downward sloping; vertical B) downward sloping; upward sloping C) ve ...
... 11) Consider a market that has many buyers but only one seller. Assume the seller has only one unit of the product to sell. Then the market demand curve will be ________ and the seller's supply curve will be ________. 11) ______ A) downward sloping; vertical B) downward sloping; upward sloping C) ve ...
Monopolistic Competition Chapter 12
... Monopolistic competition has distinctive behavior which involves product differentiation. ...
... Monopolistic competition has distinctive behavior which involves product differentiation. ...
Lecture 4
... example, if the price of wheat falls, then the quantity of wheat supplied will fall and visa versa. If the price of jellybeans rises, then the quantity of jellybeans will rise and visa versa. Changes in price will be shown as movements along one S-Curve. (See Graph11 above). “Ceteris “Paribus Assump ...
... example, if the price of wheat falls, then the quantity of wheat supplied will fall and visa versa. If the price of jellybeans rises, then the quantity of jellybeans will rise and visa versa. Changes in price will be shown as movements along one S-Curve. (See Graph11 above). “Ceteris “Paribus Assump ...
Name: Date: ______ 1. If resources are “scarce” it means that they
... C) can be increased by decreasing production. D) can be increased by decreasing the price. 55. If a perfectly competitive firm is producing a quantity that generates MC = MR, then profit: A) is maximized. B) can be increased by increasing production. C) can be increased by decreasing production. D) ...
... C) can be increased by decreasing production. D) can be increased by decreasing the price. 55. If a perfectly competitive firm is producing a quantity that generates MC = MR, then profit: A) is maximized. B) can be increased by increasing production. C) can be increased by decreasing production. D) ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑