understanding supply - Bibb County Schools
... If Elasticity is less than one supply is considered ________ If Elasticity is equal to one supply is said to be ___________. ...
... If Elasticity is less than one supply is considered ________ If Elasticity is equal to one supply is said to be ___________. ...
micro2002o
... • For instance, on Cowick street they just opened a new Pharmacy right next to another one. • Why do political parties (at least in the US) seem to have the same agenda? • This can be explained by firms trying to get the most customers. ...
... • For instance, on Cowick street they just opened a new Pharmacy right next to another one. • Why do political parties (at least in the US) seem to have the same agenda? • This can be explained by firms trying to get the most customers. ...
Marginalist Hall of Fame: Austrian School
... [An economist] must be a mathematician, historian, statesman, philosopher – in some degree. He must understand symbols and speak in words. Keynes on Jevons – Marshall priority: [Jevon’s final utility] lives merely in the tenuous world of bright ideas … Jevons saw the kettle boil Alfred Marshall, 184 ...
... [An economist] must be a mathematician, historian, statesman, philosopher – in some degree. He must understand symbols and speak in words. Keynes on Jevons – Marshall priority: [Jevon’s final utility] lives merely in the tenuous world of bright ideas … Jevons saw the kettle boil Alfred Marshall, 184 ...
Demand and Supply
... price of crude petroleum jumped from $21.54 to $30.50 per barrel (almost 42% increase) before any physical reduction in the current amount of oil available for sale. One year later, the price of oil was $21.32 per barrel. • In August 1987, a 386 PC sold at $6,995. In March 1992, the same computer so ...
... price of crude petroleum jumped from $21.54 to $30.50 per barrel (almost 42% increase) before any physical reduction in the current amount of oil available for sale. One year later, the price of oil was $21.32 per barrel. • In August 1987, a 386 PC sold at $6,995. In March 1992, the same computer so ...
File
... Now suppose that textile producers in other countries are willing to sell large quantities of cloth in Canada for only $25 per unit. b. Assuming that Canadian textile producers have large fixed costs, what is the short-run effect of these imports on the quantity produced by an individual producer an ...
... Now suppose that textile producers in other countries are willing to sell large quantities of cloth in Canada for only $25 per unit. b. Assuming that Canadian textile producers have large fixed costs, what is the short-run effect of these imports on the quantity produced by an individual producer an ...
By the end of this chapter, students will be able to
... Understand the advantages of individuals exchanging with each other Understand the differences between absolute and comparative advantage Use an opportunity cost table to determine in what good/service/job individuals or firms should specialize to maximize their comparative advantage ...
... Understand the advantages of individuals exchanging with each other Understand the differences between absolute and comparative advantage Use an opportunity cost table to determine in what good/service/job individuals or firms should specialize to maximize their comparative advantage ...
ECONOMICS
... potatoes and the income effect results in reduced consumption. The substitution effect and the income effect of the price change both result in increased consumption of potatoes. The substitution effect and the income effect of the price change both result in reduced consumption of potatoes. The sub ...
... potatoes and the income effect results in reduced consumption. The substitution effect and the income effect of the price change both result in increased consumption of potatoes. The substitution effect and the income effect of the price change both result in reduced consumption of potatoes. The sub ...
Substitutes in production – goods for which producing more of one
... A changes in the price of a factor of production and a change in technology cause the supply curve to shift. Each shift is discussed below. Change in the price of a factor of production – increases in the price of factors of production cause the supply curve to shift to the left. The supply curve c ...
... A changes in the price of a factor of production and a change in technology cause the supply curve to shift. Each shift is discussed below. Change in the price of a factor of production – increases in the price of factors of production cause the supply curve to shift to the left. The supply curve c ...
English
... consumers want to by an extra amount to store and use at a later time. ii. Increased population means there are more consumers to purchase products. iii. Increased demand may also be caused by a sudden interest in the product. Consumers may have found a new use for the product or believe the product ...
... consumers want to by an extra amount to store and use at a later time. ii. Increased population means there are more consumers to purchase products. iii. Increased demand may also be caused by a sudden interest in the product. Consumers may have found a new use for the product or believe the product ...
Test 3 Scoring Rubric
... 1 pt - Supply & Demand established for the market with Equilibrium Price & Quantity labeled (Pe,Qe) 1pt – X & Y Axis labeled properly (price and quantity) Firm 1 pt – MC=MR at the Equilibrium price established by the market with P=MR and MC curve labeled 1 pt – MC=MR shows that Price > ATC (indicati ...
... 1 pt - Supply & Demand established for the market with Equilibrium Price & Quantity labeled (Pe,Qe) 1pt – X & Y Axis labeled properly (price and quantity) Firm 1 pt – MC=MR at the Equilibrium price established by the market with P=MR and MC curve labeled 1 pt – MC=MR shows that Price > ATC (indicati ...
MS-Word File [Chapter 4.]
... With no aid, the budget constraint is the line segment AB, from $300,000 for schools and nothing for law enforcement to $300,000 for law enforcement and nothing for schools. With program (1), the budget constraint, ACE, has two line segments, one parallel to the horizontal axis, until expenditures o ...
... With no aid, the budget constraint is the line segment AB, from $300,000 for schools and nothing for law enforcement to $300,000 for law enforcement and nothing for schools. With program (1), the budget constraint, ACE, has two line segments, one parallel to the horizontal axis, until expenditures o ...
File
... A) Summing the marginal cost curves of all individual firms B) Averaging the individual supply curves C) Summing the prices from individual supply curves D) Averaging individual cost curves below the ATC ...
... A) Summing the marginal cost curves of all individual firms B) Averaging the individual supply curves C) Summing the prices from individual supply curves D) Averaging individual cost curves below the ATC ...
Problem Set 1
... c. Is it possible that the burden of the tax be shared equally by all buyers and all sellers of every good and services? (Answer: yes.) 15. The government has decided that the free-market price of cheese is too low. a. Suppose the government imposes a binding price floor in the cheese market. Use a ...
... c. Is it possible that the burden of the tax be shared equally by all buyers and all sellers of every good and services? (Answer: yes.) 15. The government has decided that the free-market price of cheese is too low. a. Suppose the government imposes a binding price floor in the cheese market. Use a ...
Principles of Economics, Case/Fair/Oster, 11e
... ◦ Each buyer/seller has a negligible impact on market price ◦ Why? (Key assumptions) Goods offered for sale - exactly the same Buyers and sellers – numerous ...
... ◦ Each buyer/seller has a negligible impact on market price ◦ Why? (Key assumptions) Goods offered for sale - exactly the same Buyers and sellers – numerous ...
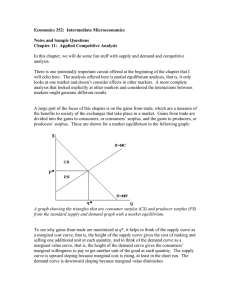
Economics 352
... are gains to be had by producing and selling additional units because consumers’ willingness to pay is greater than the marginal cost. For example, if I’m willing to pay $10 to get another unit of something and it costs you only $3 to make and sell it, there is the potential for an additional $10-$3 ...
... are gains to be had by producing and selling additional units because consumers’ willingness to pay is greater than the marginal cost. For example, if I’m willing to pay $10 to get another unit of something and it costs you only $3 to make and sell it, there is the potential for an additional $10-$3 ...
1973 1973 Oil Embargo
... Government Action: Information • Educate the public on energy use impacts – Vulnerability to oil imports • Economic policy implications • Foreign policy implications – Effects on climate and local air quality • Provide “signals” other than price – What might influence consumption decisions? ...
... Government Action: Information • Educate the public on energy use impacts – Vulnerability to oil imports • Economic policy implications • Foreign policy implications – Effects on climate and local air quality • Provide “signals” other than price – What might influence consumption decisions? ...
micro15
... • For instance, on Cowick street they just opened a new Pharmacy right next to another one. • Why do political parties (at least in the US) seem to have the same agenda? • This can be explained by firms trying to get the most customers. ...
... • For instance, on Cowick street they just opened a new Pharmacy right next to another one. • Why do political parties (at least in the US) seem to have the same agenda? • This can be explained by firms trying to get the most customers. ...
Supply and demand
In microeconomics, supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good, or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets, will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded (at the current price) will equal the quantity supplied (at the current price), resulting in an economic equilibrium for price and quantity transacted.The four basic laws of supply and demand are: If demand increases (demand curve shifts to the right) and supply remains unchanged, a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price. If demand decreases (demand curve shifts to the left) and supply remains unchanged, a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply increases (supply curve shifts to the right), a surplus occurs, leading to a lower equilibrium price. If demand remains unchanged and supply decreases (supply curve shifts to the left), a shortage occurs, leading to a higher equilibrium price.↑













![MS-Word File [Chapter 4.]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010193924_1-17ae3edd11034a762d95f58254e5586f-300x300.png)